Life
... • These are chain formed molecules with no branches • Surprisingly simple in design: A nucleo8de is a monosaccharide consis8ng of 5 C, at least one phosphate group and 4 nitrogeneous bases • RNA is a long chain with the nucleo8des connected one aber the other and one different nitrogeneous ...
... • These are chain formed molecules with no branches • Surprisingly simple in design: A nucleo8de is a monosaccharide consis8ng of 5 C, at least one phosphate group and 4 nitrogeneous bases • RNA is a long chain with the nucleo8des connected one aber the other and one different nitrogeneous ...
CSC 121 Computers and Scientific Thinking David
... molecular biology, biochemistry, and molecular genetics study life at the atomic and molecular level ...
... molecular biology, biochemistry, and molecular genetics study life at the atomic and molecular level ...
Midterm IV Key
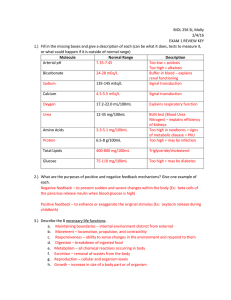
... Instructions: The exam consists of 20 multiple choice (3 points each) and 6 short answer questions (40 points). Indicate your answers to the multiple choice questions by writing the letter choice in the space provided in the answer sheet, below. Write your short answers in the space provided. Answer ...
... Instructions: The exam consists of 20 multiple choice (3 points each) and 6 short answer questions (40 points). Indicate your answers to the multiple choice questions by writing the letter choice in the space provided in the answer sheet, below. Write your short answers in the space provided. Answer ...
Evelyn Section A
... THE STRUCTURE AND SIGNIFICANT OF DNA TO LIFE The DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is "a complex, high-molecular-weight biochemical macromolecule composed of nucleotide chains that convey genetic information’' (1, 4). It is regularly in the form of a double helix, having the hereditary instructions indica ...
... THE STRUCTURE AND SIGNIFICANT OF DNA TO LIFE The DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid) is "a complex, high-molecular-weight biochemical macromolecule composed of nucleotide chains that convey genetic information’' (1, 4). It is regularly in the form of a double helix, having the hereditary instructions indica ...
RNA and Protein Synthesis - Port Washington School District
... – 1st triplet codon of mRNa attaches to ribosome – tRNA carrying amino acid pairs with mRNA codon – Usually mRNA at start is AUG (“start codon”) – mRNA slides along ribosome to next codon – New tRNA with amino acid pairs to mRNA codon – Amino acids get joined by enzyme by a peptide bond – Process co ...
... – 1st triplet codon of mRNa attaches to ribosome – tRNA carrying amino acid pairs with mRNA codon – Usually mRNA at start is AUG (“start codon”) – mRNA slides along ribosome to next codon – New tRNA with amino acid pairs to mRNA codon – Amino acids get joined by enzyme by a peptide bond – Process co ...
I - Decatur ISD
... Nucleotide Monomers Form long chains called DNA Nucleotides are joined by sugars & phosphates on the side DNA Two strands of DNA join together to form a _________________ RNA – Ribonucleic Acid Ribose sugar has an extra –OH or hydroxyl group It has the base ____________ (U) instead of thymine ...
... Nucleotide Monomers Form long chains called DNA Nucleotides are joined by sugars & phosphates on the side DNA Two strands of DNA join together to form a _________________ RNA – Ribonucleic Acid Ribose sugar has an extra –OH or hydroxyl group It has the base ____________ (U) instead of thymine ...
More Exam Practice - Iowa State University
... tRNA base-pairs with start codon AUG, and then the large ribosomal subunit binds b. Elongation- the mRNA is pulled through the ribosome so a new codon is exposed in the A site and a charged tRNA docks in the A site. The mRNA will be pulled through again, which will make the first bound tRNA in the P ...
... tRNA base-pairs with start codon AUG, and then the large ribosomal subunit binds b. Elongation- the mRNA is pulled through the ribosome so a new codon is exposed in the A site and a charged tRNA docks in the A site. The mRNA will be pulled through again, which will make the first bound tRNA in the P ...
syllabus - option b(human biochemistry)
... Students should recognize, but do not need to recall, the structures of the five bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T) and uracil (U). Nucleic acids are joined by covalent bonds between the phosphate of one nucleotide and the sugar of the next, resulting in a backbone with a rep ...
... Students should recognize, but do not need to recall, the structures of the five bases: adenine (A), cytosine (C), guanine (G), thymine (T) and uracil (U). Nucleic acids are joined by covalent bonds between the phosphate of one nucleotide and the sugar of the next, resulting in a backbone with a rep ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... experiment. Four pairs of PCR primers were used to amplify DNA isolated from one man's somatic cells, and from 21 single sperm that he donated for this study. Each primer pair amplifies a different region of the human genome, referred to as genes A, B, C and D. Each of these amplified regions was th ...
... experiment. Four pairs of PCR primers were used to amplify DNA isolated from one man's somatic cells, and from 21 single sperm that he donated for this study. Each primer pair amplifies a different region of the human genome, referred to as genes A, B, C and D. Each of these amplified regions was th ...
Chapter 17 Power Point
... genome than what was expected • The human genome contains about 21,000 protein-encoding genes, but the total number of proteins in human cells is estimated to be between 250,000 to one million. ...
... genome than what was expected • The human genome contains about 21,000 protein-encoding genes, but the total number of proteins in human cells is estimated to be between 250,000 to one million. ...
EXAM B
... B.that is identical to part of a single strand of DNA. C.that is double-stranded. D.inside the nucleus. ...
... B.that is identical to part of a single strand of DNA. C.that is double-stranded. D.inside the nucleus. ...
DNA Helicase - TASIS IB Biology
... Role of DNA Helicase DNA is an ATP-driven motor protein. Its role is to unwind the duplex DNA in order to provide a single-stranded DNA for replication, transcription, and recombination for instance. ...
... Role of DNA Helicase DNA is an ATP-driven motor protein. Its role is to unwind the duplex DNA in order to provide a single-stranded DNA for replication, transcription, and recombination for instance. ...
Constructing a Model of Protein Synthesis
... Genes are the biological units that determine inherited characteristics, such as hair color and blood type. Genes are short segments of DNA that have the instructions for making the proteins that our cells need to make. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in pro ...
... Genes are the biological units that determine inherited characteristics, such as hair color and blood type. Genes are short segments of DNA that have the instructions for making the proteins that our cells need to make. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA determines the sequence of amino acids in pro ...
A general video on DNA sequencing is
... expression, which gene(s) from the diagram might you choose to target and why? c) If you could design a drug to increase the expression of any particular gene product, which gene(s) from the diagram might you choose as a target and why? NOTE: Cancers can be caused by overexpression of certain genes, ...
... expression, which gene(s) from the diagram might you choose to target and why? c) If you could design a drug to increase the expression of any particular gene product, which gene(s) from the diagram might you choose as a target and why? NOTE: Cancers can be caused by overexpression of certain genes, ...
this lecture as PDF here
... complementary nucleotide RNA strand. One significant difference between RNA and DNA sequence is the presence of U, or uracil in RNA instead of the T, or thymine of DNA. In the case of protein-encoding DNA, transcription is the first step that ultimately leads to the translation of the genetic code, ...
... complementary nucleotide RNA strand. One significant difference between RNA and DNA sequence is the presence of U, or uracil in RNA instead of the T, or thymine of DNA. In the case of protein-encoding DNA, transcription is the first step that ultimately leads to the translation of the genetic code, ...
RNA and Differentiation
... Genes are read and copied before use! The instructions that are needed by the cell are copied from the DNA into a similar molecule called RNA ...
... Genes are read and copied before use! The instructions that are needed by the cell are copied from the DNA into a similar molecule called RNA ...
CHEM 331 Problem Set #7
... sequences and bending the DNA in that region, which promotes strand separation, making it easier for RNA polymerase to gain access to the region downstream of the TATA box. In addition to hydrogen bonds with the phosphate backbone, the TATA binding protein has four Phenylalanine residues (Phe single ...
... sequences and bending the DNA in that region, which promotes strand separation, making it easier for RNA polymerase to gain access to the region downstream of the TATA box. In addition to hydrogen bonds with the phosphate backbone, the TATA binding protein has four Phenylalanine residues (Phe single ...
Gene Technology - Byron Senior High School
... • Moving genes from one organism to another – Making human proteins in bacteria (insulin, clotting factor for hemophilia) – Improving medicines – antibiotics, vaccines – Genes placed in crop plants to make them more resistant to pests, produce more – Genes put in farm animals to make them bigger, le ...
... • Moving genes from one organism to another – Making human proteins in bacteria (insulin, clotting factor for hemophilia) – Improving medicines – antibiotics, vaccines – Genes placed in crop plants to make them more resistant to pests, produce more – Genes put in farm animals to make them bigger, le ...
Genetic engineering
... information needed for the synthesis of all cellular proteins. In other words, the main function of the genetic blueprint is to code for the production of cellular proteins in the correct cell, at the proper time, and in suitable amounts. This is an extremely complicated task because living cells ma ...
... information needed for the synthesis of all cellular proteins. In other words, the main function of the genetic blueprint is to code for the production of cellular proteins in the correct cell, at the proper time, and in suitable amounts. This is an extremely complicated task because living cells ma ...
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
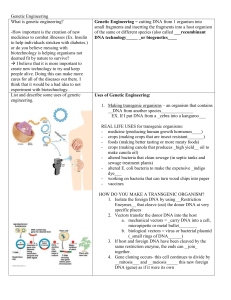
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using __Restriction Enzymes__ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = _carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet________ b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid ...
... 1. Isolate the foreign DNA by using __Restriction Enzymes__ that cleave (cut) the donor DNA at very specific places 2. Vectors transfer the donor DNA into the host a. mechanical vectors = _carry DNA into a cell, micropipette or metal bullet________ b. biological vectors = virus or bacterial plasmid ...
Nucleic acid analogue
Nucleic acid analogues are compounds which are analogous (structurally similar) to naturally occurring RNA and DNA, used in medicine and in molecular biology research.Nucleic acids are chains of nucleotides, which are composed of three parts: a phosphate backbone, a pucker-shaped pentose sugar, either ribose or deoxyribose, and one of four nucleobases.An analogue may have any of these altered. Typically the analogue nucleobases confer, among other things, different base pairing and base stacking properties. Examples include universal bases, which can pair with all four canonical bases, and phosphate-sugar backbone analogues such as PNA, which affect the properties of the chain (PNA can even form a triple helix).Nucleic acid analogues are also called Xeno Nucleic Acid and represent one of the main pillars of xenobiology, the design of new-to-nature forms of life based on alternative biochemistries.Artificial nucleic acids include peptide nucleic acid (PNA), Morpholino and locked nucleic acid (LNA), as well as glycol nucleic acid (GNA) and threose nucleic acid (TNA). Each of these is distinguished from naturally occurring DNA or RNA by changes to the backbone of the molecule.In May 2014, researchers announced that they had successfully introduced two new artificial nucleotides into bacterial DNA, and by including individual artificial nucleotides in the culture media, were able to passage the bacteria 24 times; they did not create mRNA or proteins able to use the artificial nucleotides. The artificial nucleotides featured 2 fused aromatic rings.