Hydrocarbon Worksheet - Building Aliphatic
... single electron on each of its four sides, meaning that it can bond with four other atoms. Carbon also has the unique ability to form double and triple bonds within long carbon chains. As a result of these many unique characteristics, the number of possible organic molecules is virtually infinite. I ...
... single electron on each of its four sides, meaning that it can bond with four other atoms. Carbon also has the unique ability to form double and triple bonds within long carbon chains. As a result of these many unique characteristics, the number of possible organic molecules is virtually infinite. I ...
Chemistry revision Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice
... 1. In the compound sodium fluoride, NaF, the sodium atom loses one electron and the fluorine atom gains one electron to form ions that have electron configurations similar to a. helium. ...
... 1. In the compound sodium fluoride, NaF, the sodium atom loses one electron and the fluorine atom gains one electron to form ions that have electron configurations similar to a. helium. ...
Study Guide for Exam 2 Chapter 12
... From their structural or line-angle formulas, write names of alkenes and alkynes. This includes cycloalkenes and compounds with more than one double bond. Where geometry is shown, identify cis and trans isomers From their names, draw condensed structural or line-angle formulas of alkenes and alkynes ...
... From their structural or line-angle formulas, write names of alkenes and alkynes. This includes cycloalkenes and compounds with more than one double bond. Where geometry is shown, identify cis and trans isomers From their names, draw condensed structural or line-angle formulas of alkenes and alkynes ...
1. Summarize the philosophies of vitalism and
... governed by physical and chemical laws - could synthesize organic molecules from inorganic molecules - Miller showed possibility that organic compounds could have been made in primitive earth ...
... governed by physical and chemical laws - could synthesize organic molecules from inorganic molecules - Miller showed possibility that organic compounds could have been made in primitive earth ...
Winter 2004 Final Exam
... 6. A) Aspartame, an artificial sweetener which is marketed as NutraSweet®, has the structure given below. Answer the following questions about Aspartame. ...
... 6. A) Aspartame, an artificial sweetener which is marketed as NutraSweet®, has the structure given below. Answer the following questions about Aspartame. ...
Name: Date: Period: Who is the Father of Atomic Theory? What
... charge: 2. from the innermost energy level and the outermost energy of the electron cloud. ...
... charge: 2. from the innermost energy level and the outermost energy of the electron cloud. ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... These are topics from a traditional 1st quarter. If you used the thematic approach with me this year, you will notice that the topics are not in order of their presentation throughout the year. The final exam is cumulative so this review will help you with reviewing the concepts and calculations. No ...
... These are topics from a traditional 1st quarter. If you used the thematic approach with me this year, you will notice that the topics are not in order of their presentation throughout the year. The final exam is cumulative so this review will help you with reviewing the concepts and calculations. No ...
1. Rank the following compounds in order of decreasing acidity (1
... 2. Show the enol tautomer of 1,3,5-cyclohexatrione. Would you expect this compound to exist predominantly in the keto or enol form? O ...
... 2. Show the enol tautomer of 1,3,5-cyclohexatrione. Would you expect this compound to exist predominantly in the keto or enol form? O ...
Abstract Substituted phenyl carbametes and. Isomeric azepines
... ethylazidoformate and toluene was analyzed on capillary SE-54. column GC-MS. The analysis reveal that all the three methyl substituted (2, 3 and 4) isomers are formed in equal proportions. This indicates that insertion of carbethoxynitrene in aromatics is not selective. The work regarding selectivit ...
... ethylazidoformate and toluene was analyzed on capillary SE-54. column GC-MS. The analysis reveal that all the three methyl substituted (2, 3 and 4) isomers are formed in equal proportions. This indicates that insertion of carbethoxynitrene in aromatics is not selective. The work regarding selectivit ...
2.4 Revision 1: There were two atoms. One got hit by an extremely
... c. Conducts electricity when solid and melted? d. Conducts electricity when dissolved or melted but not as a solid? e. Forces that hold non-polar molecular solids together. f. Can conduct heat and electrical charge. g. Which of the following solids have hydrogen bonds between molecules; hydrogen chl ...
... c. Conducts electricity when solid and melted? d. Conducts electricity when dissolved or melted but not as a solid? e. Forces that hold non-polar molecular solids together. f. Can conduct heat and electrical charge. g. Which of the following solids have hydrogen bonds between molecules; hydrogen chl ...
Lecture 2: Powerpoint
... Have complex, organized structure made mostly of organic molecules. Respond to stimuli from their environment Actively maintain their complex structure/ internal environment (homeostatis) Acquire and use materials and energy/ convert to different forms Grow Reproduce themselves (involves DNA) Have t ...
... Have complex, organized structure made mostly of organic molecules. Respond to stimuli from their environment Actively maintain their complex structure/ internal environment (homeostatis) Acquire and use materials and energy/ convert to different forms Grow Reproduce themselves (involves DNA) Have t ...
AP Unit 1 Test Review
... (E) No two electrons in one atom can have the same four quantum numbers. 2. Use these answers for questions 2 - 5. (A) 1s2 2s22p5 3s23p5 (B) 1s2 2s22p6 3s23p6 (C) 1s2 2s22p62d10 3s23p6 (D) 1s2 2s22p6 3s23p63d5 (E) 1s2 2s22p6 3s23p63d3 4s2 ...
... (E) No two electrons in one atom can have the same four quantum numbers. 2. Use these answers for questions 2 - 5. (A) 1s2 2s22p5 3s23p5 (B) 1s2 2s22p6 3s23p6 (C) 1s2 2s22p62d10 3s23p6 (D) 1s2 2s22p6 3s23p63d5 (E) 1s2 2s22p6 3s23p63d3 4s2 ...
here
... Carbon has four (4) electrons in the outer shell that need to bond for stability. Carbon can also share electrons with other carbon atoms to form the following types of carbon bonds: C – C (single bond) C = C (double bond) C Ξ C (triple bond) ...
... Carbon has four (4) electrons in the outer shell that need to bond for stability. Carbon can also share electrons with other carbon atoms to form the following types of carbon bonds: C – C (single bond) C = C (double bond) C Ξ C (triple bond) ...
CHM 222: Organic Chemistry III
... chloroalkanes forms, including chiefly 2-ethyl-1-chlorobutane, 3-chlorohexane, 2-chlorohexane, and 3-chloro3-methylpentane. When 2-ethyl-1-butanol is treated with thionyl chloride in pyridine, only 1-chloro-2ethylbutane is formed. Write a detailed mechanism which accounts for these observations. ...
... chloroalkanes forms, including chiefly 2-ethyl-1-chlorobutane, 3-chlorohexane, 2-chlorohexane, and 3-chloro3-methylpentane. When 2-ethyl-1-butanol is treated with thionyl chloride in pyridine, only 1-chloro-2ethylbutane is formed. Write a detailed mechanism which accounts for these observations. ...
Unit 6 Worksheet Package
... between these two types of ions forms an _____________ bond. Nearly all ionic compounds are _____________ solids at room temperature. In these solids the total _____________ charge is balanced by the total _____________ charge. Ionic compounds in general have very _____________ melting points. This ...
... between these two types of ions forms an _____________ bond. Nearly all ionic compounds are _____________ solids at room temperature. In these solids the total _____________ charge is balanced by the total _____________ charge. Ionic compounds in general have very _____________ melting points. This ...
Ch 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Atoms and Ions
... Example problem: Three isotopes of silicon occur in nature: 28Si (92.23%), which has an atomic mass of 27.97693 amu; 29Si (4.68%), which has an atomic mass of 28.97649 amu; and 30Si (3.09%), which ha ...
... Example problem: Three isotopes of silicon occur in nature: 28Si (92.23%), which has an atomic mass of 27.97693 amu; 29Si (4.68%), which has an atomic mass of 28.97649 amu; and 30Si (3.09%), which ha ...
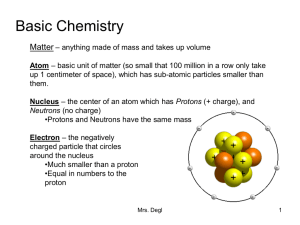
Basic Chemistry
... neutrons. Some Carbon atoms have 6 neutrons and some have 7/ 8. •Some isotopes can be radioactive (unstable nuclei that breaks down at a constant rate over time). Compound – when two or more elements are chemically combined •Bonds attach one element to another to from a compound •The compound has to ...
... neutrons. Some Carbon atoms have 6 neutrons and some have 7/ 8. •Some isotopes can be radioactive (unstable nuclei that breaks down at a constant rate over time). Compound – when two or more elements are chemically combined •Bonds attach one element to another to from a compound •The compound has to ...
SO2 SO3 - mrkearsley.com - The Web Site of Mr. Kearsley
... 2)More electronegative element takes its anion charge. The less electronegative takes its cation charge. ...
... 2)More electronegative element takes its anion charge. The less electronegative takes its cation charge. ...
exam #1 study guide
... 10. true / false Ions usually form when electrons are transferred from one atom to another. 11. Shared pairs of electrons fill the innermost / outermost energy levels of bonded atoms. 12. Covalent bonds are generally very strong / weak. 13. Two atoms may form several covalent bonds to share several ...
... 10. true / false Ions usually form when electrons are transferred from one atom to another. 11. Shared pairs of electrons fill the innermost / outermost energy levels of bonded atoms. 12. Covalent bonds are generally very strong / weak. 13. Two atoms may form several covalent bonds to share several ...
Matter and Atoms
... bonds that unit atoms to form compounds • Relate the nature of chemical bonds that hold compounds together to the physical structures of compounds •Distinguish between different types of mixtures and solutions ...
... bonds that unit atoms to form compounds • Relate the nature of chemical bonds that hold compounds together to the physical structures of compounds •Distinguish between different types of mixtures and solutions ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.