Comparative efficacy of diffusible and volatile compounds of tea
... fungi. This diffusible effect was attributed to the production of diffusible and volatile compounds which were found to be potent antifungal in nature. The antifungal substances in bacterial strains were found to be extracellular, proteinacious in nature. The colony forming units (cfu) of pathogenic ...
... fungi. This diffusible effect was attributed to the production of diffusible and volatile compounds which were found to be potent antifungal in nature. The antifungal substances in bacterial strains were found to be extracellular, proteinacious in nature. The colony forming units (cfu) of pathogenic ...
to get Period 2 8
... Hydrocarbon: They only contain carbon hydrogen Carbon can form stable bond with oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. Substituted Hydrocarbons include halogen-containing compounds, alcohols and organic acids. ...
... Hydrocarbon: They only contain carbon hydrogen Carbon can form stable bond with oxygen, nitrogen, and sulfur. Substituted Hydrocarbons include halogen-containing compounds, alcohols and organic acids. ...
Covalent Bonds
... The central atom is often the 1st atom in the formula. c. Carbon is ALWAYS central. d. Hydrogen/halogens are always terminal (on end). ...
... The central atom is often the 1st atom in the formula. c. Carbon is ALWAYS central. d. Hydrogen/halogens are always terminal (on end). ...
Carbon Compounds
... Alkynes • Hydrocarbons which have at least one triple bond between two carbons. We will always use one triple bond only. • Unsaturated • The naming prefixes are the same as for alkanes with an yne ending • The general formula is CnH2n-2 • pharmaceuticals ...
... Alkynes • Hydrocarbons which have at least one triple bond between two carbons. We will always use one triple bond only. • Unsaturated • The naming prefixes are the same as for alkanes with an yne ending • The general formula is CnH2n-2 • pharmaceuticals ...
AP BIOLOGY CHAPTER 4 REVIEW SHEET
... Structural Isomer - different covalent arrangement, bond location Geometric Isomer - different spatial arrangement around a double bond but same covalent, have carbon double bond → doesn’t allow moving o cis - isomer : X (atom or group of atoms) on same side o trans - isomer : X (atom or group of at ...
... Structural Isomer - different covalent arrangement, bond location Geometric Isomer - different spatial arrangement around a double bond but same covalent, have carbon double bond → doesn’t allow moving o cis - isomer : X (atom or group of atoms) on same side o trans - isomer : X (atom or group of at ...
(a) Structural isomers
... Concept 4.1: Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds • Organic chemistry is the study of compounds that contain carbon • Organic compounds range from simple molecules to colossal ones • Most organic compounds contain hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon atoms ...
... Concept 4.1: Organic chemistry is the study of carbon compounds • Organic chemistry is the study of compounds that contain carbon • Organic compounds range from simple molecules to colossal ones • Most organic compounds contain hydrogen atoms in addition to carbon atoms ...
Atomic Structure, Molecular Structure & Bonding
... – H is never central; C is often central 3. Draw in electrons to fulfill octet and duet rules – C “likes” 8 electrons; H “likes” 2 electrons 4. Count ve-’s and compare to #2 5. If too many e-’s, make a double bond 6. Calculate formal charge (FC) to double check structure – No or low FCs (e.g. +1) mo ...
... – H is never central; C is often central 3. Draw in electrons to fulfill octet and duet rules – C “likes” 8 electrons; H “likes” 2 electrons 4. Count ve-’s and compare to #2 5. If too many e-’s, make a double bond 6. Calculate formal charge (FC) to double check structure – No or low FCs (e.g. +1) mo ...
Honors Chemistry - Stout Middle School
... form an ionic compound (which is neutral in charge). 6. Know why transition elements can have more than one oxidation number. 7. Know the four elements, outside groups 1 and 2, that have only one oxidation number and know these elements oxidation numbers. 8. Know what an ionic compound is and what f ...
... form an ionic compound (which is neutral in charge). 6. Know why transition elements can have more than one oxidation number. 7. Know the four elements, outside groups 1 and 2, that have only one oxidation number and know these elements oxidation numbers. 8. Know what an ionic compound is and what f ...
Chemical Stability
... 1) Metals form ionic bonds with nonmetals. 2) Metal form ionic bonds with polyatomic ions. 3) Polyatomic ions form ionic bonds with each other. ...
... 1) Metals form ionic bonds with nonmetals. 2) Metal form ionic bonds with polyatomic ions. 3) Polyatomic ions form ionic bonds with each other. ...
video slide
... weak chemical bonds also important reinforce shapes help molecules adhere to each other ...
... weak chemical bonds also important reinforce shapes help molecules adhere to each other ...
Ionic Bonding - cloudfront.net
... Occurs when more than ___ valid Lewis Structure can be written for a molecule or ion ...
... Occurs when more than ___ valid Lewis Structure can be written for a molecule or ion ...
4. bonding - New Hartford Central Schools
... Either absorb or release energy when formed Create new species with chemical and physical properties unlike constituent atoms Form because atoms want to have complete outer shells ...
... Either absorb or release energy when formed Create new species with chemical and physical properties unlike constituent atoms Form because atoms want to have complete outer shells ...
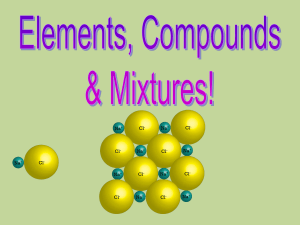
What is a mixture?
... Pure Substances • Pure substances are substances in which there is only one type of particle. • These particles are called atoms. • The only two things that are pure substances are: 1. Elements 2. Compounds ...
... Pure Substances • Pure substances are substances in which there is only one type of particle. • These particles are called atoms. • The only two things that are pure substances are: 1. Elements 2. Compounds ...
CARBONYL COMPOUNDS
... and HCHO (MR = 30) and put these compounds in order with respect to increasing boiling point. C2H6 CH3OH HCHO Methanal is a gas, other important carbonyl compounds are …………………... Early members are soluble in water due to ……………….. ………………. between hydrogen from water and oxygen from the carboxylic gro ...
... and HCHO (MR = 30) and put these compounds in order with respect to increasing boiling point. C2H6 CH3OH HCHO Methanal is a gas, other important carbonyl compounds are …………………... Early members are soluble in water due to ……………….. ………………. between hydrogen from water and oxygen from the carboxylic gro ...
Lecture 1
... EPR spectra show that the odd electron is delocalized in an antibonding orbital of C 10H 8 . Formation of radical anion is more favorable when the π of LUMO of the arene is low in energy. Simple MOT predicts that the energy of LUMO decreases steadily on going from benzene to more extensively conjuga ...
... EPR spectra show that the odd electron is delocalized in an antibonding orbital of C 10H 8 . Formation of radical anion is more favorable when the π of LUMO of the arene is low in energy. Simple MOT predicts that the energy of LUMO decreases steadily on going from benzene to more extensively conjuga ...
Chem 20 Final Exam Outline
... Recall the structure of the atom. Understand the importance of the interaction of electrons when two atoms or ions approach each other. Contrast the bonding produced by shared pairs of valence electrons and by transfer of electrons to form ions. Apply the octet rule to determine the number of covale ...
... Recall the structure of the atom. Understand the importance of the interaction of electrons when two atoms or ions approach each other. Contrast the bonding produced by shared pairs of valence electrons and by transfer of electrons to form ions. Apply the octet rule to determine the number of covale ...
Fundamentals of Chemistry
... • An atom is uniquely defined by #p+ = Z = atomic number (see Periodic Table) • In a neutral atom, #p+ = #e-; note that #n is not equal to #p+ nor #e-. • In an atomic ion, #p+ ≠ #e- resulting in a net nonzero charge on the species – Neutral atoms can lose electrons producing a positive ion or cation ...
... • An atom is uniquely defined by #p+ = Z = atomic number (see Periodic Table) • In a neutral atom, #p+ = #e-; note that #n is not equal to #p+ nor #e-. • In an atomic ion, #p+ ≠ #e- resulting in a net nonzero charge on the species – Neutral atoms can lose electrons producing a positive ion or cation ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.