
chapter4_powerpoint - Northern Highlands Regional HS
... • Stanley Miller’s classic experiment demonstrated the abiotic synthesis of organic compounds • Experiments support the idea that abiotic synthesis of organic compounds, perhaps near volcanoes, could have been a stage in the origin of life ...
... • Stanley Miller’s classic experiment demonstrated the abiotic synthesis of organic compounds • Experiments support the idea that abiotic synthesis of organic compounds, perhaps near volcanoes, could have been a stage in the origin of life ...
Chemical Nomenclature (ionic compounds)
... Chemical Nomenclature (ionic compounds) CONVENTIONS Scientists have agreed on a set of rules that govern the naming and formulation of compounds. It is universal! The following pages are a programmed approach to the problem of obtaining either the formula or name of a chemical compound. a) The comp ...
... Chemical Nomenclature (ionic compounds) CONVENTIONS Scientists have agreed on a set of rules that govern the naming and formulation of compounds. It is universal! The following pages are a programmed approach to the problem of obtaining either the formula or name of a chemical compound. a) The comp ...
Alkanes and alkenes
... Alkanes are saturated compounds and contain single C-C bonds. They undergo substitution reactions. They have the general formula CnH2n+2 Alkenes are unsaturated compounds and contain double C=C bonds. They undergo addition reactions. They have the general formula CnH2n. Cracking is the process of br ...
... Alkanes are saturated compounds and contain single C-C bonds. They undergo substitution reactions. They have the general formula CnH2n+2 Alkenes are unsaturated compounds and contain double C=C bonds. They undergo addition reactions. They have the general formula CnH2n. Cracking is the process of br ...
Topic 3 Structure of Metals and Ionic Compounds Bonding and
... • High melting point: typically several hundred or thousand Kelvin However: Salts that are liquid at room temperature have been prepared using organic cations • Very low electrical conductivity, but conduct electricity quite well when molten • Most dissolve in high polarity solvents to form conducti ...
... • High melting point: typically several hundred or thousand Kelvin However: Salts that are liquid at room temperature have been prepared using organic cations • Very low electrical conductivity, but conduct electricity quite well when molten • Most dissolve in high polarity solvents to form conducti ...
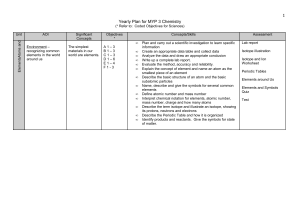
Yearly Plan for MYP 1 Science
... Name and give the formulas for some common compound ions Write the formula for simple compounds that include compound ions from their names Name simple compounds that include compound ions from their formulas Define and describe ionic and covalent bonds Name examples and describe general characteris ...
... Name and give the formulas for some common compound ions Write the formula for simple compounds that include compound ions from their names Name simple compounds that include compound ions from their formulas Define and describe ionic and covalent bonds Name examples and describe general characteris ...
Midterm Review Packet - Mrs. McKenzie`s Chemistry and ICP Classes
... 29. The breaking apart of water molecules into two ions of opposite charge is called ___________________________________. 30. An atom has six electrons, what is it atomic number? ____________ Name?___________ It is a stable or unstable atom? _________________. ...
... 29. The breaking apart of water molecules into two ions of opposite charge is called ___________________________________. 30. An atom has six electrons, what is it atomic number? ____________ Name?___________ It is a stable or unstable atom? _________________. ...
HW4
... If it is not provided, determine the molecular formula using clues from the IR spectrum (e.g., presence of O and N) and mass spectrum (e.g., presence of Cl, Br; molecular weight) Consider the mass spectra. Be on the lookout for peaks with even values of m/z in the mass spectra of compounds with even ...
... If it is not provided, determine the molecular formula using clues from the IR spectrum (e.g., presence of O and N) and mass spectrum (e.g., presence of Cl, Br; molecular weight) Consider the mass spectra. Be on the lookout for peaks with even values of m/z in the mass spectra of compounds with even ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 Part-A
... Identify the compound C9H12 that shows two singlets in 1:3 ratio in its 1HNMR spectrum. 2. Prove that the operations S31 and S35belong to the same class. 3. Distinguish between fundamental and hot bands. 4. Identify the point groups of NH3 and CCl4 molecules. 5. Mossbauer spectra are recorded as a f ...
... Identify the compound C9H12 that shows two singlets in 1:3 ratio in its 1HNMR spectrum. 2. Prove that the operations S31 and S35belong to the same class. 3. Distinguish between fundamental and hot bands. 4. Identify the point groups of NH3 and CCl4 molecules. 5. Mossbauer spectra are recorded as a f ...
Glossary of Key Terms in Chapter Two
... gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen; e.g., the conversion of an alcohol to an aldehyde or ketone via the use of an oxidizing agent. phenol (12.7) an organic compound that contains a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a benzene ring. primary (1˚) alcohol (12.4) an alcohol with the general formula RCH2OH ...
... gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen; e.g., the conversion of an alcohol to an aldehyde or ketone via the use of an oxidizing agent. phenol (12.7) an organic compound that contains a hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to a benzene ring. primary (1˚) alcohol (12.4) an alcohol with the general formula RCH2OH ...
Chapter 4
... • Total of __electrons (__ in the first shell and __in the second shell). • Carbon usually completes its ___________ shell by _________ electrons with other atoms in four covalent bonds. • This ______________ by carbon makes large, complex molecules possible. ...
... • Total of __electrons (__ in the first shell and __in the second shell). • Carbon usually completes its ___________ shell by _________ electrons with other atoms in four covalent bonds. • This ______________ by carbon makes large, complex molecules possible. ...
File
... Understand that the fragmentation of a molecular ion gives rise to a characteristic relative abundance spectrum that may give information about the structure of the molecule Know that the more stable X+ species give higher peaks, limited to carbocation and acylium (RCO+) ions Be able to use IR spect ...
... Understand that the fragmentation of a molecular ion gives rise to a characteristic relative abundance spectrum that may give information about the structure of the molecule Know that the more stable X+ species give higher peaks, limited to carbocation and acylium (RCO+) ions Be able to use IR spect ...
chemistry vocab unit 2 answers
... one small molecule that may become chemically bonded to other monomers to form a polymer ...
... one small molecule that may become chemically bonded to other monomers to form a polymer ...
First class notes
... rounded up to the nearest whole number). So you would subtract 35 from 80 leaving 45 for the number of neutrons found in the atom. Molecules are two or more atoms bonded. For example NaCl which is sodium chloride. To find the molecular mass of sodium chloride you would add the atomic masses of the t ...
... rounded up to the nearest whole number). So you would subtract 35 from 80 leaving 45 for the number of neutrons found in the atom. Molecules are two or more atoms bonded. For example NaCl which is sodium chloride. To find the molecular mass of sodium chloride you would add the atomic masses of the t ...
50 Chapter 4: Nonionic Compounds and Their Nomenclature A
... Many elements are found in their natural state in the form of molecules. Examples are hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and so on. The chemical formulas for these molecules are H2, O2, N2, S8, ...
... Many elements are found in their natural state in the form of molecules. Examples are hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, and so on. The chemical formulas for these molecules are H2, O2, N2, S8, ...
Group Activity 3 [10 PTS]
... Group Activity 3 [10 PTS] 1. Write the condensed structural formula of each of the following alcohols a. 1-propanol ...
... Group Activity 3 [10 PTS] 1. Write the condensed structural formula of each of the following alcohols a. 1-propanol ...
organic chemistry i
... Bond strength can be predicted using the orbital overlap model. Which makes the stronger bond, a face-to-face overlap or a sideways overlap? Explain your choice of answer ...
... Bond strength can be predicted using the orbital overlap model. Which makes the stronger bond, a face-to-face overlap or a sideways overlap? Explain your choice of answer ...
atom ion molecule element ionic bond electron compound covalent
... 6. A solution is a mixture of substances that is evenly / unevenly distributed throughout the entire mixture. 7. Blood plasma is an example of a solvent / solute. 8. “Oil and water don’t mix” because a polar / nonpolar molecule can’t easily dissolve in a polar solvent. MAIN IDEA: SOME ...
... 6. A solution is a mixture of substances that is evenly / unevenly distributed throughout the entire mixture. 7. Blood plasma is an example of a solvent / solute. 8. “Oil and water don’t mix” because a polar / nonpolar molecule can’t easily dissolve in a polar solvent. MAIN IDEA: SOME ...
8.1 Classifying inorganic compounds
... Classifying Inorganic Compounds (Section 8.1 pg 201-208) ...
... Classifying Inorganic Compounds (Section 8.1 pg 201-208) ...
Organic Chemistry HW PSI Chemistry
... D) water and its interaction with other kinds of molecules. E) inorganic compounds. 2) Which property of the carbon atom gives it compatibility with a greater number of different elements than any other type of atom? A) Carbon has 6 to 8 neutrons. B) Carbon has a valence of 4. C) Carbon forms ionic ...
... D) water and its interaction with other kinds of molecules. E) inorganic compounds. 2) Which property of the carbon atom gives it compatibility with a greater number of different elements than any other type of atom? A) Carbon has 6 to 8 neutrons. B) Carbon has a valence of 4. C) Carbon forms ionic ...
Organic Chemistry HW PSI Chemistry Name
... D) water and its interaction with other kinds of molecules. E) inorganic compounds. 2) Which property of the carbon atom gives it compatibility with a greater number of different elements than any other type of atom? A) Carbon has 6 to 8 neutrons. B) Carbon has a valence of 4. C) Carbon forms ionic ...
... D) water and its interaction with other kinds of molecules. E) inorganic compounds. 2) Which property of the carbon atom gives it compatibility with a greater number of different elements than any other type of atom? A) Carbon has 6 to 8 neutrons. B) Carbon has a valence of 4. C) Carbon forms ionic ...
Notes for powerpoint and worksheets PDF
... 2. Numbers called ______________________ that indicate ____________________________________________: AlCl3 = 1 Al and 3 Cl This should makes sense because Al has a +3 charge and Cl has a ‐1 charge 3. The subscript is ONLY associated with the element symbol to the immediate left. TRY THESE: ...
... 2. Numbers called ______________________ that indicate ____________________________________________: AlCl3 = 1 Al and 3 Cl This should makes sense because Al has a +3 charge and Cl has a ‐1 charge 3. The subscript is ONLY associated with the element symbol to the immediate left. TRY THESE: ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.
















![Group Activity 3 [10 PTS]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010780770_1-3445600a9b56e890a0f283c789afe8fb-300x300.png)





