BONDS AND LEWIS STRUCTURES
... Polarity of Bonds Differences in electronegativity can be used to determine how polar a bond is between two atoms. If the difference in the electronegativities of the atoms is 0.5 or less, the bond is considered to be nonpolar covalent and the electron sharing is more or less equal. If the differenc ...
... Polarity of Bonds Differences in electronegativity can be used to determine how polar a bond is between two atoms. If the difference in the electronegativities of the atoms is 0.5 or less, the bond is considered to be nonpolar covalent and the electron sharing is more or less equal. If the differenc ...
Saturated Hydrocarbon
... Name of molecule: ___________________________________ Substituent: The halogens and groups of atoms including carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or phosphorus may take the place of a hydrogen atom attached to the parent chain. Alkyl group: A hydrocarbon substituent like methyl ─ CH3, ethyl, ...
... Name of molecule: ___________________________________ Substituent: The halogens and groups of atoms including carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, or phosphorus may take the place of a hydrogen atom attached to the parent chain. Alkyl group: A hydrocarbon substituent like methyl ─ CH3, ethyl, ...
File
... monatomic- meaning they naturally occur as stable, single atoms. Right: Many gases, such as Hydrogen, are diatomic, which means they naturally occur as a molecule with two atoms. Not shown: Some gasses, such as Ozone- a form of oxygen, occur in a three atom arrangement called triatomic. ...
... monatomic- meaning they naturally occur as stable, single atoms. Right: Many gases, such as Hydrogen, are diatomic, which means they naturally occur as a molecule with two atoms. Not shown: Some gasses, such as Ozone- a form of oxygen, occur in a three atom arrangement called triatomic. ...
File - Riske Science
... this series differs from the previous compound by a –CH2 – • The general formula for these compounds could be written as CnH2n+1OH ...
... this series differs from the previous compound by a –CH2 – • The general formula for these compounds could be written as CnH2n+1OH ...
Document
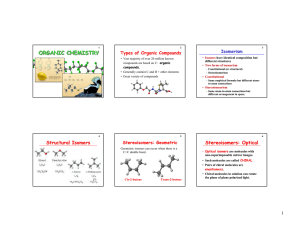
... 1. Organic compounds- compounds that contain carbon. 2. Hydrocarbon- is a compound that contains only the elements carbon and hydrogen. 3. Structural formula- shows the kind, number, and arrangement of atoms in a molecule. 4. Isomers- compounds that have the same chemical formula but different struc ...
... 1. Organic compounds- compounds that contain carbon. 2. Hydrocarbon- is a compound that contains only the elements carbon and hydrogen. 3. Structural formula- shows the kind, number, and arrangement of atoms in a molecule. 4. Isomers- compounds that have the same chemical formula but different struc ...
Study Guide for Exam 2_Sp12
... Periodic trends regarding atomic and ionic radii. What is meant by valence electrons? What is ionization energy? What is the octet rule? What are ions? How do they relate to the octet rule? How is charge balance related to writing formulas of ionic compounds? Write dot formulas for atoms, and show h ...
... Periodic trends regarding atomic and ionic radii. What is meant by valence electrons? What is ionization energy? What is the octet rule? What are ions? How do they relate to the octet rule? How is charge balance related to writing formulas of ionic compounds? Write dot formulas for atoms, and show h ...
PDF(343KB)
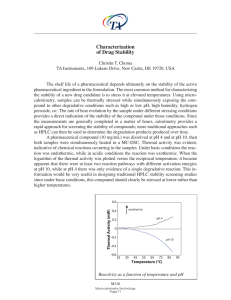
... indicative of chemical reactions occurring in the samples. Under basic conditions the reaction was endothermic, while in acidic conditions the reaction was exothermic. When the logarithm of the thermal activity was plotted versus the reciprocal temperature, it became apparent that there were at leas ...
... indicative of chemical reactions occurring in the samples. Under basic conditions the reaction was endothermic, while in acidic conditions the reaction was exothermic. When the logarithm of the thermal activity was plotted versus the reciprocal temperature, it became apparent that there were at leas ...
Mass Spec - Fragmentation
... 1. The relative height of the M+ peak is greatest for straightchain molecules and decreases as the branching increases. 2. The relative height of the M+ peak decreases with chain length for a homologous series. 3. Cleavage is favoured at alkyl-substituted carbons, with the probability of cleavage in ...
... 1. The relative height of the M+ peak is greatest for straightchain molecules and decreases as the branching increases. 2. The relative height of the M+ peak decreases with chain length for a homologous series. 3. Cleavage is favoured at alkyl-substituted carbons, with the probability of cleavage in ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... Methane Hydrate, CH4(H2O)x Gas hydrates have been known for many years, and combustion of a sample of methane hydrate is seen on the front cover. Recently, however, vast deposits of methane hydrate were discovered deep within sediments on the floor of the world’s oceans. How these deposits were form ...
... Methane Hydrate, CH4(H2O)x Gas hydrates have been known for many years, and combustion of a sample of methane hydrate is seen on the front cover. Recently, however, vast deposits of methane hydrate were discovered deep within sediments on the floor of the world’s oceans. How these deposits were form ...
Topic 4: Classifying Elements What did the early chemists use to
... EXAMPLE: H2O(l), NaCl(s) What is a SUPERSCRIPT? What does it indicate? Provide an example. The small number at the top of the element. It indicates the charge of the ion. EXAMPLE: ...
... EXAMPLE: H2O(l), NaCl(s) What is a SUPERSCRIPT? What does it indicate? Provide an example. The small number at the top of the element. It indicates the charge of the ion. EXAMPLE: ...
Alkanes - Warren County Schools
... 1) Aromatic- compounds with carbon and hydrogen that contain benzene rings 2) Aliphatic- compounds with carbon and hydrogen that are not aromatic (alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and cycloalkanes) ...
... 1) Aromatic- compounds with carbon and hydrogen that contain benzene rings 2) Aliphatic- compounds with carbon and hydrogen that are not aromatic (alkanes, alkenes, alkynes, and cycloalkanes) ...
Matter Quiz 2 With Answers
... 6. In any physical or chemical change, matter is neither created nor destroyed. Matter can only be changed from one form to another. This scientific law is called _______________________. a. The second law of thermodynamics b. The third law of thermodynamics. c. The law of conservation of matter. d. ...
... 6. In any physical or chemical change, matter is neither created nor destroyed. Matter can only be changed from one form to another. This scientific law is called _______________________. a. The second law of thermodynamics b. The third law of thermodynamics. c. The law of conservation of matter. d. ...
22.4 Hydrocarbon Rings
... “WE R FAMILY” Functional groups determine the family a substance is in. ...
... “WE R FAMILY” Functional groups determine the family a substance is in. ...
COURSE: Organic chemistry ACADEMIC YEAR:2016/2017 TYPE
... The course wants to give basic information on the principal properties of the organic compounds, allowing the student to understand the physical properties and the chemical behavior of every organic compounds. PRE-REQUIREMENTS General and inorganic chemistry SYLLABUS Electronic configuration. Bonds. ...
... The course wants to give basic information on the principal properties of the organic compounds, allowing the student to understand the physical properties and the chemical behavior of every organic compounds. PRE-REQUIREMENTS General and inorganic chemistry SYLLABUS Electronic configuration. Bonds. ...
PART I: Multiple Choice
... Carbon has 4 electrons in its outer valence shell, it wants to share these electrons with other carbons and other atoms (especially other carbons, because 4+4=8, with 8 carbon has a full outer shell and is stable). In other words, one carbon can bond with 4 other carbons for a total of 8 electrons ...
... Carbon has 4 electrons in its outer valence shell, it wants to share these electrons with other carbons and other atoms (especially other carbons, because 4+4=8, with 8 carbon has a full outer shell and is stable). In other words, one carbon can bond with 4 other carbons for a total of 8 electrons ...
Unit 2: Learning outcomes
... Stereoisomers have identical molecular formulae and the atoms are bonded together in the same order but the arrangement of the atoms in space is different, making them non – superimposable. Geometric isomerism is one type of stereoisomerism and can arise due to the lack of free rotation around a bon ...
... Stereoisomers have identical molecular formulae and the atoms are bonded together in the same order but the arrangement of the atoms in space is different, making them non – superimposable. Geometric isomerism is one type of stereoisomerism and can arise due to the lack of free rotation around a bon ...
Skill Sheet 19-C Naming Chemical Compounds
... forming the compound, the numbers of atoms of each element in one molecule, and even some indication, perhaps, of the arrangement of the atoms when they form the molecule. In addition to having a unique chemical formula, each compound has a unique name. These names provide scientists with valuable i ...
... forming the compound, the numbers of atoms of each element in one molecule, and even some indication, perhaps, of the arrangement of the atoms when they form the molecule. In addition to having a unique chemical formula, each compound has a unique name. These names provide scientists with valuable i ...
7A SCIENCE FINAL REVIEW - MERRICK 7th SCIENCE REVIEW
... ___ Recognize elements from compounds if given the chemical symbol or a model. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical property of matter, give examples of each. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical change, list examples of each. ___ List evidence to show a ...
... ___ Recognize elements from compounds if given the chemical symbol or a model. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical property of matter, give examples of each. ___ Describe the difference between a chemical and physical change, list examples of each. ___ List evidence to show a ...
Organic Chemistry
... • 3. The first carbon atom involved in the bond is followed by a hyphen and placed in front of the ...
... • 3. The first carbon atom involved in the bond is followed by a hyphen and placed in front of the ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.