Unit 4 Compounds, Naming, Formula Writing
... Whenever 2 elements form more than one compound, the different masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. ...
... Whenever 2 elements form more than one compound, the different masses of one element that combine with the same mass of the other element are in the ratio of small whole numbers. ...
Unit 6 part 1 notes on Naming Compounds
... Write symbol of cation followed by symbol of anion along with their oxidation numbers. Use the oxidation number of the charge of each ion as the subscript for the other ion. If a subscript is 1 omit it. If the subscripts are the same, reduce them. Subscripts must be simplified in an ionic formula ...
... Write symbol of cation followed by symbol of anion along with their oxidation numbers. Use the oxidation number of the charge of each ion as the subscript for the other ion. If a subscript is 1 omit it. If the subscripts are the same, reduce them. Subscripts must be simplified in an ionic formula ...
Pre AP Chemistry Chapter 6: Bonding Homework #2
... Write the appropriate formula for the ion formed by the elements from question 8. Use a + or a minus sign to indicate what charge the ion assume when electrons are gained or lost a. strontium____________ b. nitrogen____________ c. zinc__________ d. bromine_____________ ...
... Write the appropriate formula for the ion formed by the elements from question 8. Use a + or a minus sign to indicate what charge the ion assume when electrons are gained or lost a. strontium____________ b. nitrogen____________ c. zinc__________ d. bromine_____________ ...
Organic Chemistry - EO-204-Distillation
... So……even though they have the same formula ….they have different properties Whether the compounds are Saturated or Unsaturated they are called “Aliphatic Compounds” because they are either straight or branched Hydrocarbons. Isomers of Butane Animation of Isomerism ...
... So……even though they have the same formula ….they have different properties Whether the compounds are Saturated or Unsaturated they are called “Aliphatic Compounds” because they are either straight or branched Hydrocarbons. Isomers of Butane Animation of Isomerism ...
Guideline
... 5. Double bonds favor allylic cleavage and give the resonance-stabilized allylic carbocation. This rule does not hold for simple alkenes because of the ready migration of the double bond, but it does hold for cycloalkanes. 6. Saturated rings tend to lose alkyl side chains at the alpha bond. This is ...
... 5. Double bonds favor allylic cleavage and give the resonance-stabilized allylic carbocation. This rule does not hold for simple alkenes because of the ready migration of the double bond, but it does hold for cycloalkanes. 6. Saturated rings tend to lose alkyl side chains at the alpha bond. This is ...
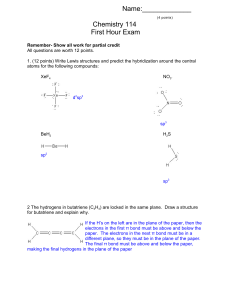
Chapter 9 Review quizdom
... transition elements. b. composed of positive and negative ions. c. composed of two or more nonmetallic elements. d. exceptions to the law of definite proportions. ...
... transition elements. b. composed of positive and negative ions. c. composed of two or more nonmetallic elements. d. exceptions to the law of definite proportions. ...
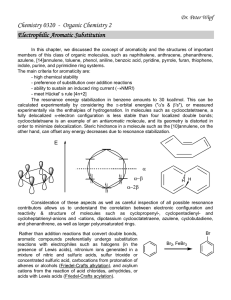
In this chapter, alkanes, alkenes, alkynes
... indole, purine, and pyrimidine ring systems. The main criteria for aromaticity are: - high chemical stability - preference of substitution over addition reactions - ability to sustain an induced ring current (NMR!) - meet Hückel' s rule [4n+2] The resonance energy stabilization in benzene amounts t ...
... indole, purine, and pyrimidine ring systems. The main criteria for aromaticity are: - high chemical stability - preference of substitution over addition reactions - ability to sustain an induced ring current (NMR!) - meet Hückel' s rule [4n+2] The resonance energy stabilization in benzene amounts t ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.