Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Chapter 4: 1. Organic Molecules
... Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of carbon-based compounds, in particular hydrocarbons (CnHn) and their derivatives. • hydrocarbon derivatives have something else in place of one or more hydrogens: ...
... Organic Chemistry Organic chemistry is the study of carbon-based compounds, in particular hydrocarbons (CnHn) and their derivatives. • hydrocarbon derivatives have something else in place of one or more hydrogens: ...
Biochemistry Worksheet
... 56. What is meant by a lipid bilayer? What makes this such an effective barrier between the inside & the outside of the cell? 57. Wax is another complex lipid. Describe its structure. 58. Waxes are highly _________________. Explain how plants make use of this property? Animals? 59. What makes up ste ...
... 56. What is meant by a lipid bilayer? What makes this such an effective barrier between the inside & the outside of the cell? 57. Wax is another complex lipid. Describe its structure. 58. Waxes are highly _________________. Explain how plants make use of this property? Animals? 59. What makes up ste ...
Mixtures & Organic Compounds
... more substances (solute) are distributed evenly in another substance (solvent). Ex: Kool-aid *The concentration of solute is important to organisms A suspension is a mixture of water and nondissolved materials ...
... more substances (solute) are distributed evenly in another substance (solvent). Ex: Kool-aid *The concentration of solute is important to organisms A suspension is a mixture of water and nondissolved materials ...
Organic Chemistry
... Fats are important to our body, they provide padding, energy storage, and are essential for our nervous system; there are also several essential vitamins that are fat soluble (vit. A, D, E, and K) Fats are known as triglycerides which are made up of 3 fatty acids and a glycerol molecule. They’re cal ...
... Fats are important to our body, they provide padding, energy storage, and are essential for our nervous system; there are also several essential vitamins that are fat soluble (vit. A, D, E, and K) Fats are known as triglycerides which are made up of 3 fatty acids and a glycerol molecule. They’re cal ...
Organic Chemistry Unit
... Found in all living matter Found in body tissue Found in food Found in fuels (coal, wood, petroleum) Found in Nature ( ranked 17th in crust) ...
... Found in all living matter Found in body tissue Found in food Found in fuels (coal, wood, petroleum) Found in Nature ( ranked 17th in crust) ...
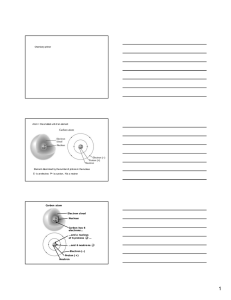
Chemistry primer Atom = the smallest unit of an element Element
... Streak: Color in power form. This is more reliable than color due to uniformit y of grains. Color: Determined by the composition (chemical formula) but it can also be affected by impurities. This is why color is a poor mineral identifier. Fracture: How a mineral breaks across cleavage planes. Relate ...
... Streak: Color in power form. This is more reliable than color due to uniformit y of grains. Color: Determined by the composition (chemical formula) but it can also be affected by impurities. This is why color is a poor mineral identifier. Fracture: How a mineral breaks across cleavage planes. Relate ...
Test #1 Study Guide
... as is. The nonmetal anion goes second and is given as the root + ide. o If the metal anion is a transition metal, be sure to place the charge of the metal in roman numeral form inside brackets between the metal and the nonmetal. Molecular compounds are made up of two nonmetals and are easily disting ...
... as is. The nonmetal anion goes second and is given as the root + ide. o If the metal anion is a transition metal, be sure to place the charge of the metal in roman numeral form inside brackets between the metal and the nonmetal. Molecular compounds are made up of two nonmetals and are easily disting ...
Warm-Up
... specializes in study of carbon compounds Organic compounds: contain Carbon (& H) Major elements of life: CHNOPS Carbon can form large, complex, and diverse molecules ...
... specializes in study of carbon compounds Organic compounds: contain Carbon (& H) Major elements of life: CHNOPS Carbon can form large, complex, and diverse molecules ...
organic chemistry - Turner Fenton Secondary School
... August Kekule proposed a ring structure with alternating single and double bonds. (1864) It is a planar molecule (flat) Studies show that the bond length are all the same: 139pm. (the bond length of C-C bond is 148pm while a C=C is 134pm) ...
... August Kekule proposed a ring structure with alternating single and double bonds. (1864) It is a planar molecule (flat) Studies show that the bond length are all the same: 139pm. (the bond length of C-C bond is 148pm while a C=C is 134pm) ...
C - Milwaukie High
... 2. Number the chain carbons, starting with the end nearest a substituent. -- A non-HC substituent takes precedence over an HC branch. 3. Name and give the #ed location of each substituent. -- If necessary, choose #s so that their sum is as low as possible. ...
... 2. Number the chain carbons, starting with the end nearest a substituent. -- A non-HC substituent takes precedence over an HC branch. 3. Name and give the #ed location of each substituent. -- If necessary, choose #s so that their sum is as low as possible. ...
Chapter 4 mastery check
... they have different chemical properties they have the same molecular formula their atoms and bonds are arranged in different sequences they are a result of restricted movement around a carbon double bond their possible numbers increase as carbon skeletons increase in size. ...
... they have different chemical properties they have the same molecular formula their atoms and bonds are arranged in different sequences they are a result of restricted movement around a carbon double bond their possible numbers increase as carbon skeletons increase in size. ...
Organic Chemistry - Salisbury Composite High | Home
... Naming Cyclical Hydrocarbons same as naming alkanes, alkenes and alkynes except the ...
... Naming Cyclical Hydrocarbons same as naming alkanes, alkenes and alkynes except the ...
Lecture 6
... Examples: X2 (X = Cl, Br, I), R-X, Ar-X, H-X, O2 The most common substrates used are R-X (alkyl halides), Ar-X (aryl halides), and H-X. ...
... Examples: X2 (X = Cl, Br, I), R-X, Ar-X, H-X, O2 The most common substrates used are R-X (alkyl halides), Ar-X (aryl halides), and H-X. ...
Nomenclature and symbols for folic acid and related compounds
... S , or ambo- should be used to designate the configuration whenever possible. (The prefix ambo- indicates that a mixture is present, one of whose components is R and the other S at the locus designated; it is especially useful when they are not present in equal proportions, because of the presence o ...
... S , or ambo- should be used to designate the configuration whenever possible. (The prefix ambo- indicates that a mixture is present, one of whose components is R and the other S at the locus designated; it is especially useful when they are not present in equal proportions, because of the presence o ...
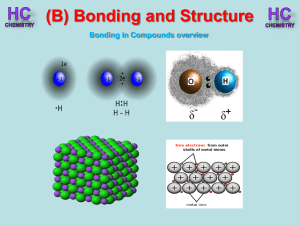
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... m.p.’s increase because the strength of the London dispersion forces increase with the increasing size of the molecule. So more Energy is needed to separate molecules. ...
... m.p.’s increase because the strength of the London dispersion forces increase with the increasing size of the molecule. So more Energy is needed to separate molecules. ...
4. bonding - New Hartford Central Schools
... Either absorb or release energy when formed Create new species with chemical and physical properties unlike constituent atoms Form because atoms want to have complete outer shells ...
... Either absorb or release energy when formed Create new species with chemical and physical properties unlike constituent atoms Form because atoms want to have complete outer shells ...
Chapter_04
... Vitalism, the idea that organic compounds arise only in organisms, was shown to be false when chemists synthesized many organic compounds in the laboratory ...
... Vitalism, the idea that organic compounds arise only in organisms, was shown to be false when chemists synthesized many organic compounds in the laboratory ...
Homoaromaticity

Homoaromaticity in organic chemistry refers to a special case of aromaticity in which conjugation is interrupted by a single sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Although this sp3 center disrupts the continuous overlap of p-orbitals, traditionally thought to be a requirement for aromaticity, considerable thermodynamic stability and many of the spectroscopic, magnetic, and chemical properties associated with aromatic compounds are still observed for such compounds. This formal discontinuity is apparently bridged by p-orbital overlap, maintaining a contiguous cycle of π electrons that is responsible for this preserved chemical stability.The concept of homoaromaticity was pioneered by Saul Winstein in 1959, prompted by his studies of the “tris-homocyclopropenyl” cation. Since the publication of Winstein's paper, much research has been devoted to understanding and classifying these molecules, which represent an additional “class” of aromatic molecules included under the continuously broadening definition of aromaticity. To date, homoaromatic compounds are known to exist as cationic and anionic species, and some studies support the existence of neutral homoaromatic molecules, though these are less common. The 'homotropylium' cation (C8H9+) is perhaps the best studied example of a homoaromatic compound.