* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 21 Worksheet
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
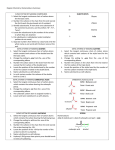
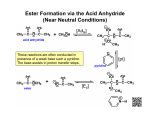
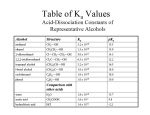
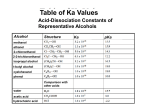
Chem 1C - CLAS - Chapter 21 1. Classify the following compounds as saturated or unsaturated. O OH Cl 2. What is the general formula for a hydrocarbon with one ring and a triple bond? 9. How many compounds can be produced if you mix chlorine with ethane in the presence of high energy photons? 10. Predict the product for the following addition reactions: a. 1-pentene + Br2 → b. 2-pentene + HBr → c. 1-butene + HCl → 11. Which of the following transitions does not represent a hydrogenation reaction? a. 1-butene → butane b. 1-pentyne → pentane c. pentane → 2-pentene a. CnH2n+2 b. CnH2n c. CnH2n–2 d. CnH2n–4 e. CnH2n–6 3. Name the following alkanes: a. b. c. Cl Br 12. Identify the functional groups that are present in the following compounds: Cl 4. Name the following alkenes: a. b. Br 13. For each of the following (1) provide a name (2) draw the products of oxidation and (3) name the products: a. b. c. 5. Name the following alkynes: a. b. OH OH OH 14. Name the following: 6. Which of the following is not a structural isomer of 2-heptene? a. b. c. d. e. 3-heptene 2,4-dimethyl-1-pentene 3-methylcyclohexene 1-methylcyclohexane 2-heptyne 7. Which of the following can have geometric isomers? a. 2-pentene b. 2-pentyne c. cyclopentene d. 1-pentene e. 2,3-dimethyl-2-pentene f. 1,3-dimethylcyclopentane 8. How many dibromobenzenes can you have? Draw and name them. a. O b. Br O OH c. O H 15. Classify the following amines as primary, secondary or tertiary a. tertbutylamine b. ethylhexylamine 16. Predict and name the products for the following: a. propanoic acid + 2-methyl-2-propanol → b. methanoic acid + 2-butanol → c. hexanoic acid + 2,3-dimethyl-1-pentanol → 17. What compounds would you use to synthesize the following esters? a. methyl ethanoate b. cyclohexyl propanoate 23. Draw the monomer used to make the following polymers. a. b. c. 18. Circle the chiral carbons in the following: O H H H d. OH OH OH e. OH 19. Peptide bonds in proteins are the result of ___________ reactions between __________. What’s the difference between the primary, secondary and tertiary structure of a protein? How many possible tripeptides will result if you were to mix valine, leucine and cysteine together? O O NH2 Valine OH OH OH SH O NH2 Leucine NH2 Cysteine 20. What type of monomers are used to make addition polymers? a. b. c. d. Alkanes Alkenes Alcohols and carboxylic acids Amines and carboxylic acids 21. What type of monomers are used to make condensation polymers? a. Alkanes b. Alkenes c. Alcohols and carboxylic acids d. Amines and carboxylic acids 22. Draw a short segment of the polymer that is the result of the following monomers: a. tetrafluoroethene b. 4-methyl-2-pentene c. 1,1-dichloro-1-butene 24. Which of the following are examples of condensation polymers? a. Proteins b. DNA c. Polysaccharides d. Polystyrene -------------------------------------------------------- # of H’s = 2(# of C’s) + 2 – 2(# π bonds) – 2 (# of rings) – halogens Systematic Nomenclature of Organic Compounds 1. Find the longest continuous carbon chain (parent chain). a. If there is a functional group (double or triple bond, alcohol etc) it must be on or part of the parent chain. b. If there is a ring in the compound either the ring itself or the non-ringed chain will be the parent chain but never both combined. c. If there are two or more chains of equal length, pick the one with the greatest number of substituents. 2. Number the carbons in the parent chain. a. If there is a functional group, assign it the lowest possible position. If the functional group gets the same position from either end then consider the lowest number for the substituents. If there is a functional group on a ring, assign it position 1. Double bonds in a ring are at positions 1 and 2. b. If there is multiple functional groups the priority is carbonyls > alcohols > carbon-carbon multiple bonds > amines. If you have a carbon-carbon double bond and a carbon-carbon triple bond, go in the directions that gives the lowest possible positions. If both directions give the same numbers, the double bond will take priority. c. If there are no functional groups, give the substituents the lowest possible numbers. If you get the same numbers from either end assign the alphabetically first substituent the lowest number. 3. Naming your compound. a. If the compound has a specific configuration or geometry (cis/trans, E/Z or R/S) indicate this first. b. The first name is the substituents in alphabetical order. Prefixes that denote a number (di, tri, sec, tert etc.) are not alphabetized. List the position(s) on the parent chain and denote how many with a Greek prefix. If a substituent is on a nitrogen the letter N is used to denote the position in lieu of a number. Hyphens are placed between letters and number whereas commas between two numbers. c. The last name of the compound is the parent chain. The stem of the name indicates the length of the parent chain and the suffix reflects the type of compound. If your parent chain is a ring add the prefix cyclo. If your parent chain had a functional group indicate the position if it’s not obvious. #C’s 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Root meth eth prop but pent hex hept oct non dec Structure Classification Systematic suffix C–C alkane ane C=C alkene ene C≡C alkyne yne C–X alkyl halide N/A C – OH C–O–C C–N alcohol anol enol ynol anediol enediol ynediol ether N/A amine anamine enamine ynamine Example pentane 3-hexene 1-butyne F 2-fluoropentane OH cyclopentanol O NH2 2-pentanamine anal enal ynal aldehyde or RCHO butanal O anone enone ynone ketone or R(CO)R’ cyclohexanone O OH anoic acid enoic acid ynoic acid carboxylic acid or RCOOH or RCOOR’ O ester anoate amide aka peptide anamide 2-propylpentanoic acid O O ethyl pentanoate O NH2 2-methylpropanamide Common substituents or branches methyl isopropyl ethyl isobutyl hexyl propyl pentyl sec-butyl butyl tert-butyl Sub-classifications of Alcohols ⇒ count the number of carbons directly bonded to the carbon with the alcohol tertiary OH HO secondary OH primary Sub-classifications of Amines ⇒ count the number of carbons directly bonded to the nitrogen H2N primary N tertiary N secondary H Chiral or Asymmetrical Carbons ⇒ sp3 carbons bonded to 4 different groups