* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. Summarize the philosophies of vitalism and
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
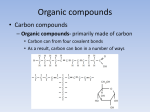
Chapter 4 Reading Quiz 1. The atoms of what element are considered the most “versatile” carbon building blocks? 2. “Tetra-” refers to what number? four 3. A “hydroxyl” group is represented by what formula? OH4. What’s in a “sulfhydryl” group? S & H 5. Name a biological structure in which phosphates are necessary. 1. Summarize the philosophies of vitalism and mechanism. Vitalism = belief in a life force outside the jurisdiction of chemical or physical laws - 19th century built on this because chemists couldn’t synthesize organic compounds Mechanism = belief that all natural phenomena are governed by physical and chemical laws - could synthesize organic molecules from inorganic molecules - Miller showed possibility that organic compounds could have been made in primitive earth 2. Explain how carbon’s electron configuration determines the kinds and number of bonds carbon will form. • Carbon shows a tetravalent electron configuration • 4 bonds are allowed due to the emergent properties from the 4 valence electrons • 6 protons; 6 neutrons; 6 electrons • Carbon forms covalent bonds and acts as the central atom from which the molecule branches 3. Describe how carbon skeletons may vary, and explain how this variation contributes to the diversity and complexity of organic molecules. • Carbon skeletons vary in: 1. Length 2. Shape (straight, branched, ring) 3. Number and location of double bonds 4. Other elements covalently bonded Many different molecules can form 4. Distinguish among 3 types of isomers: structural, geometric, & enantiomers. Structural Isomers • Isomers that differ in the covalent arrangement of their atoms number of possible isomers increases as carbons increase location of double bonds differ 4. Continued… Geometric Isomers • Share same covalent partnerships, but differ in their spatial arrangement • Double bonds don’t allow free movement • Can affect biological diversity 4. Continued… Enantiomers • Molecules are mirror images of each other • Usually one form is biologically active and one is not 5. Recognize the 6 major functional groups, and describe the chemical properties of organic molecules in which they occur. 1. Hydroxyl Group a functional group that consists of a hydrogen atom bonded to an oxygen atom, which in turn is bonded to a carbon it is polar & water soluble organic compounds with these are alcohols C – OH 5. Continued… 2. Carbonyl Group functional group with a carbon atom double bonded to oxygen polar & water soluble is the group found in SUGARS • if at the end of the skeleton – aldehyde • if in the middle of the skeleton – ketone 5. Continued… 3. Carboxyl group functional group that has a carbon atom which is both double bonded to an oxygen and single bonded to an oxygen of a hydroxyl (-OH) group water soluble VERY polar due to 2 oxygens bonded to 1 carbon has acidic properties; “carboxylic acids” -COOH 5. Continued… 4. Amino Group functional group consists of nitrogen atom bonded to 2 hydrogens and to the carbon skeleton polar & water soluble acts as a weak base -NH2 5. Continued… 5. Sulfhydryl Group functional group with an atom of sulfur bonded to an atom of hydrogen helps stabilize the structure of proteins when in organic compoundscalled ‘thiols’ 5. Continued… 6. Phosphate Group functional group which is the dissociated form of phosphoric acid acid properties polar & water soluble important in cellular energy storage & transfer H3PO4