Q9 Describe how the body defends against infection
... o T cells à activated by the presentation of a microorganisms via the Major Histocompatibility complex MHC of an Antigen Presenting Cell. Several subtypes: § CD4 T cell • CD4 Th1 à activated by the ...
... o T cells à activated by the presentation of a microorganisms via the Major Histocompatibility complex MHC of an Antigen Presenting Cell. Several subtypes: § CD4 T cell • CD4 Th1 à activated by the ...
PE anti-mouse RAE-1δ Antibody
... consisting of alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon. They are strong homology within the family, related by 92%-95% sequence identity. They are distantly related to MHC class I proteins. RAE-1 proteins are abundantly expressed in fetal tissues, but not in normal adult tissue. They are constitutivel ...
... consisting of alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and epsilon. They are strong homology within the family, related by 92%-95% sequence identity. They are distantly related to MHC class I proteins. RAE-1 proteins are abundantly expressed in fetal tissues, but not in normal adult tissue. They are constitutivel ...
Section Assignment 1.3 Part C: Defence Systems
... Antibodies Immune response Immunity Inflammation ...
... Antibodies Immune response Immunity Inflammation ...
Immunity - De Anza College
... • Macrophages (monocytes) engulf pathogen, digest it • Parts of proteins “displayed” • Presented to helper T cells with matching receptor – T cells will form cytotoxic T cells or helper T cells. ...
... • Macrophages (monocytes) engulf pathogen, digest it • Parts of proteins “displayed” • Presented to helper T cells with matching receptor – T cells will form cytotoxic T cells or helper T cells. ...
immune response
... The consequences are usually beneficial or some times may be injurious to the host. The adaptive response can be antibody-mediated (humoral), cell-mediated (cellular), or both. ...
... The consequences are usually beneficial or some times may be injurious to the host. The adaptive response can be antibody-mediated (humoral), cell-mediated (cellular), or both. ...
Poster
... diet to alleviate symptoms, since there is currently no medical treatment. The HLADQ2 allele is the second highest risk factor for CD. HLA-DQ2 is a MHCII molecule, which presents antigens to a specific subset of T cells (T helper). An MHCII molecule is a protein exposed on the membrane of antigen pr ...
... diet to alleviate symptoms, since there is currently no medical treatment. The HLADQ2 allele is the second highest risk factor for CD. HLA-DQ2 is a MHCII molecule, which presents antigens to a specific subset of T cells (T helper). An MHCII molecule is a protein exposed on the membrane of antigen pr ...
IMMUNE SYSTEM:
... 2. If pathogens get past the barrier of your skin, the inflammatory response helps attack the pathogens. It is called the body’s general defense. 3. A white blood cell that surrounds the pathogen and destroys it is called a phagocyte. 4. If the inflammatory response is not enough to overcome the pat ...
... 2. If pathogens get past the barrier of your skin, the inflammatory response helps attack the pathogens. It is called the body’s general defense. 3. A white blood cell that surrounds the pathogen and destroys it is called a phagocyte. 4. If the inflammatory response is not enough to overcome the pat ...
2.11.15 - WordPress.com
... 2. A certain portion of the resulting effector T cells then activate specific B cells through ...
... 2. A certain portion of the resulting effector T cells then activate specific B cells through ...
File - The Building Blocks For Learning
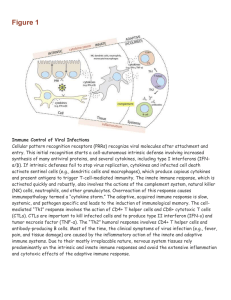
... Cellular pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize viral molecules after attachment and entry. This initial recognition starts a cell-autonomous intrinsic defense involving increased synthesis of many antiviral proteins, and several cytokines, including type I interferons (IFNα/β). If intrinsic ...
... Cellular pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) recognize viral molecules after attachment and entry. This initial recognition starts a cell-autonomous intrinsic defense involving increased synthesis of many antiviral proteins, and several cytokines, including type I interferons (IFNα/β). If intrinsic ...
Poster
... The CTL response to the HLA-A2/MP(58–66) complex can be an instructive model of immune memory to an antigen of a frequently encountered virus that usually is cleared from the body. Interestingly, this response mainly recruits T cells bearing particular TCR-α and β chains. TCR Vβ17 accounts for betwe ...
... The CTL response to the HLA-A2/MP(58–66) complex can be an instructive model of immune memory to an antigen of a frequently encountered virus that usually is cleared from the body. Interestingly, this response mainly recruits T cells bearing particular TCR-α and β chains. TCR Vβ17 accounts for betwe ...
Autoimmunity
... bound to a gene regulatory protein (possessing three alphahelix domains – 1, 2, & 3). Explain how a B-cell with a surface receptor specific for an epitope in domain 1 could potentially present to and activate a T-cell with a TCR for an epitope in domain 2. ...
... bound to a gene regulatory protein (possessing three alphahelix domains – 1, 2, & 3). Explain how a B-cell with a surface receptor specific for an epitope in domain 1 could potentially present to and activate a T-cell with a TCR for an epitope in domain 2. ...
Outline for Combined Document
... both natural and experimental infection or, in some cases, it may be clearer to separate the two. In addition to text with the following section, please provide diagrams that illustrate them. ...
... both natural and experimental infection or, in some cases, it may be clearer to separate the two. In addition to text with the following section, please provide diagrams that illustrate them. ...
Kuby Immunology 6/e
... Bind to BOTH the TCR and MHC Can cause over-activation Overproduction of TH-cell cytokines, leading to systemic toxicity ...
... Bind to BOTH the TCR and MHC Can cause over-activation Overproduction of TH-cell cytokines, leading to systemic toxicity ...
Immunology
... bind to body's own biological molecules (proteins); antigen when bound to body's own molecules may cause an immune response, this is called an allergy. Small antigens are called haptens (incomplete antigen) and alone are not immunogenic. Reactivity (immune response) is dependent upon antigen structu ...
... bind to body's own biological molecules (proteins); antigen when bound to body's own molecules may cause an immune response, this is called an allergy. Small antigens are called haptens (incomplete antigen) and alone are not immunogenic. Reactivity (immune response) is dependent upon antigen structu ...
Chapter 40 Review
... host, they should cause the same disease that infected the original host 4. The injected pathogen should be isolated from the second host. It should be identical to the original pathogen. ...
... host, they should cause the same disease that infected the original host 4. The injected pathogen should be isolated from the second host. It should be identical to the original pathogen. ...
presentation
... – Produced by B-Lymphocytes (from bone marrow) – Antibodies belong to a group of proteins called Immunoglobulins (Ig) – General structure is “Y” shaped, made of two light and two heavy polypeptide chains – Heavy chains specify type of antibody (IgM, IgG, IgA, etc.) – Light chains responsible for ant ...
... – Produced by B-Lymphocytes (from bone marrow) – Antibodies belong to a group of proteins called Immunoglobulins (Ig) – General structure is “Y” shaped, made of two light and two heavy polypeptide chains – Heavy chains specify type of antibody (IgM, IgG, IgA, etc.) – Light chains responsible for ant ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Defense against Disease
... Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) receptors • As T cells mature, they randomly produce and display a variety of receptors • Any T cell with receptors that bind to self MHCHLA complexes will commit apoptosis • Only T cells that do NOT bind to self cells should emerge from the thymus and enter circulat ...
... Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) receptors • As T cells mature, they randomly produce and display a variety of receptors • Any T cell with receptors that bind to self MHCHLA complexes will commit apoptosis • Only T cells that do NOT bind to self cells should emerge from the thymus and enter circulat ...
Chapter 8
... Costimulation and growth factors like IL-2 stimulate expression of the antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL in the activated lymphocytes, and these proteins keep cells viable ...
... Costimulation and growth factors like IL-2 stimulate expression of the antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-XL in the activated lymphocytes, and these proteins keep cells viable ...
DEFINITIONS - Tehran University of Medical Sciences
... B cells can recognize linear or conformational epitopes on cell surfaces carbohydrates or of lipids. The B cell antigen receptor is a form of mem ...
... B cells can recognize linear or conformational epitopes on cell surfaces carbohydrates or of lipids. The B cell antigen receptor is a form of mem ...
Immunity Student Outline
... qualitatively the effects of disruptions to dynamic homeostasis in biological systems. 2.29 The student can create representations and models to describe immune responses. 2.30 The students can create representations or models to describe nonspecific immune defenses in plants and animals. 3.34 The s ...
... qualitatively the effects of disruptions to dynamic homeostasis in biological systems. 2.29 The student can create representations and models to describe immune responses. 2.30 The students can create representations or models to describe nonspecific immune defenses in plants and animals. 3.34 The s ...