IMMUNOLOGY (Ms. Lucky Juneja)
... distinguish subtle differences among antigens. Antibodies can distinguish between two protein molecules that differ in only a single amino acid. The immune system is capable of generating tremendous diversity in its recognition molecules,allowing it to recognize billions of unique structures on ...
... distinguish subtle differences among antigens. Antibodies can distinguish between two protein molecules that differ in only a single amino acid. The immune system is capable of generating tremendous diversity in its recognition molecules,allowing it to recognize billions of unique structures on ...
Adaptive or Acquired Immunity
... Note – Precipitation and agglutination reactions are less beneficial because they can cause the formation of complexes that block tiny blood and lymphatic vessels as well as kidney tubules. T-cells do not produce antibodies, but are able to recognize and bind with specific antigens. They have recep ...
... Note – Precipitation and agglutination reactions are less beneficial because they can cause the formation of complexes that block tiny blood and lymphatic vessels as well as kidney tubules. T-cells do not produce antibodies, but are able to recognize and bind with specific antigens. They have recep ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 11. _______ is added in the HAT medium to block dihydrofolate reductase. 12. Immunoproteasomes generate peptides that can bind with MHC class _____ molecules. 13. ________ graft rejection occurs months or years after transplantation. 14. ________ bind to antibodies but do not induce an immune respon ...
... 11. _______ is added in the HAT medium to block dihydrofolate reductase. 12. Immunoproteasomes generate peptides that can bind with MHC class _____ molecules. 13. ________ graft rejection occurs months or years after transplantation. 14. ________ bind to antibodies but do not induce an immune respon ...
Complexity and the Immune System
... • Theory of antibody formation (from genetic variation rather than a response to pathogens) - 1955 • The body learns to distinguish between self and nonself in the thymus - 1971 • Concept of the immune system as complex, self-regulating network - 1974 ...
... • Theory of antibody formation (from genetic variation rather than a response to pathogens) - 1955 • The body learns to distinguish between self and nonself in the thymus - 1971 • Concept of the immune system as complex, self-regulating network - 1974 ...
Chapter 40 review notes
... -Asthma can also be triggered by certain antigens -when the immune system makes a mistake and attacks the body’s own cells, it produces autoimmune disease such as juvenile-onset diabetes, myasthenia gravis, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatic fever -AIDS - Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome -spread b ...
... -Asthma can also be triggered by certain antigens -when the immune system makes a mistake and attacks the body’s own cells, it produces autoimmune disease such as juvenile-onset diabetes, myasthenia gravis, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatic fever -AIDS - Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome -spread b ...
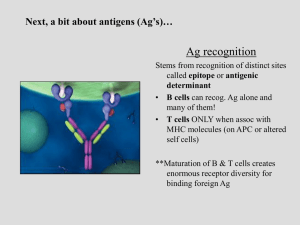
Next, a bit about antigens (Ag`s)…
... MHC molecules bind Antigenic peptides after Ag processing •Relation of Ag with MHC I or II appears to be determined by the route in which Ag enters the cell •Exogenous Ag is found OUTSIDE host cells and enters via phagocytosis in APC’s ONLY! •then APC digests Ag into peptide fragments, combines fra ...
... MHC molecules bind Antigenic peptides after Ag processing •Relation of Ag with MHC I or II appears to be determined by the route in which Ag enters the cell •Exogenous Ag is found OUTSIDE host cells and enters via phagocytosis in APC’s ONLY! •then APC digests Ag into peptide fragments, combines fra ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 6. Formation and development of WBC is called as Hematopoiesis. 7. Apoptosis leads in damage to surrounding cells. 8. All TH cells express CD4 and only recognize antigen associated with class II MHC molecule. 9. The puri potent stem cell is one of the most abundant cell types in the bone marrow. 10. ...
... 6. Formation and development of WBC is called as Hematopoiesis. 7. Apoptosis leads in damage to surrounding cells. 8. All TH cells express CD4 and only recognize antigen associated with class II MHC molecule. 9. The puri potent stem cell is one of the most abundant cell types in the bone marrow. 10. ...
ppt 3.2.4 immunity revision Revision powerpoint on
... immune system and stimulates an immune response. For example – proteins that are part of the cell membrane or cell wall of invading cells such as microorganisms. The presence of an antigen triggers the production of an antibody. ...
... immune system and stimulates an immune response. For example – proteins that are part of the cell membrane or cell wall of invading cells such as microorganisms. The presence of an antigen triggers the production of an antibody. ...
The Immune System
... 2. T cell response, an active, cell-mediated defense that involves the destruction of pathogens by cytotoxic T cells ...
... 2. T cell response, an active, cell-mediated defense that involves the destruction of pathogens by cytotoxic T cells ...
1. dia
... Normal tissue cells do not express co-stimulatory molecules and do not produce T cell differentiating cytokines NO SIGNAL 2. for CD4+ Th activation Migration of naive T lymphocytes to normal tissues is limited Antigen presenting cells are not activated in normal tissues ...
... Normal tissue cells do not express co-stimulatory molecules and do not produce T cell differentiating cytokines NO SIGNAL 2. for CD4+ Th activation Migration of naive T lymphocytes to normal tissues is limited Antigen presenting cells are not activated in normal tissues ...
Assignment I
... 2. What is adaptive immunity? Give three differences between humoral and cell mediated immune response. 3. What is passive immunity? Discuss the differences between active and passive immunity. 4. What are memory cells? Why they are important component of a host immune system. 5. What do you mean by ...
... 2. What is adaptive immunity? Give three differences between humoral and cell mediated immune response. 3. What is passive immunity? Discuss the differences between active and passive immunity. 4. What are memory cells? Why they are important component of a host immune system. 5. What do you mean by ...
Immune System - wappingersschools.org
... Antibiotics work by interfering with the cellular processes of microorganisms. They have no affect on viruses Penicillin was discovered in 1928 by Alexander Fleming. http://www.biography.com/people/ale xander-fleming-9296894 ...
... Antibiotics work by interfering with the cellular processes of microorganisms. They have no affect on viruses Penicillin was discovered in 1928 by Alexander Fleming. http://www.biography.com/people/ale xander-fleming-9296894 ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 16. What is the difference between affinity and avidity? 17. What is Antigenic drift? 18. What is HLA typing? 19. Write about the role of adjuvants. 20. What is immunochromatography ? ...
... 16. What is the difference between affinity and avidity? 17. What is Antigenic drift? 18. What is HLA typing? 19. Write about the role of adjuvants. 20. What is immunochromatography ? ...
How does my immune system react when I puncture my skin on
... to the immune system for evaluation Appropriate Helper T cell binds with the APC's MHCII/Antigen This activates a Helper T cell which then finds a B-cell expressing the same surface protein. When the activated Helper T cell binds to the B cell it releases Interleukin II (IL-II) which activates B cel ...
... to the immune system for evaluation Appropriate Helper T cell binds with the APC's MHCII/Antigen This activates a Helper T cell which then finds a B-cell expressing the same surface protein. When the activated Helper T cell binds to the B cell it releases Interleukin II (IL-II) which activates B cel ...
Immune System
... White blood cells • Some WBCs mark pathogens for destruction while others engulf microbes during an immune response • And yet others produce antibodies ...
... White blood cells • Some WBCs mark pathogens for destruction while others engulf microbes during an immune response • And yet others produce antibodies ...
Autoimmunity
... Autoimmune disease occurs when an immune response attacks our own tissues. Like all adaptive immune responses, it is focused on specific antigens by T-cell receptors and B cell receptors. In contrast to infection, the antigens that these cells recognise are processed from proteins within the target ...
... Autoimmune disease occurs when an immune response attacks our own tissues. Like all adaptive immune responses, it is focused on specific antigens by T-cell receptors and B cell receptors. In contrast to infection, the antigens that these cells recognise are processed from proteins within the target ...
Document
... Autoimmune disease occurs when an immune response attacks our own tissues. Like all adaptive immune responses, it is focused on specific antigens by T-cell receptors and B cell receptors. In contrast to infection, the antigens that these cells recognise are processed from proteins within the target ...
... Autoimmune disease occurs when an immune response attacks our own tissues. Like all adaptive immune responses, it is focused on specific antigens by T-cell receptors and B cell receptors. In contrast to infection, the antigens that these cells recognise are processed from proteins within the target ...
Immunology_IX__immunity_against_infections
... • Cytotoxic mechanisms are similar to Tc cells: perforin and induction of apoptosis. ...
... • Cytotoxic mechanisms are similar to Tc cells: perforin and induction of apoptosis. ...