Chapter 18 Answers to Even Numbered Study Questions
... 10. MHC I and II are very similar proteins with very different function. Both bind short peptides and present them on the cell surface, and both interact with T-cell receptors. MHC I is found in the membrane of virtually all cells in the body, and it presents peptides derived from the turnover of pr ...
... 10. MHC I and II are very similar proteins with very different function. Both bind short peptides and present them on the cell surface, and both interact with T-cell receptors. MHC I is found in the membrane of virtually all cells in the body, and it presents peptides derived from the turnover of pr ...
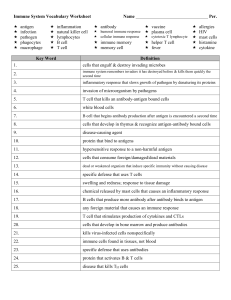
Immune System Review Worksheet
... B cells that produce more antibody after antibody binds to antigen ...
... B cells that produce more antibody after antibody binds to antigen ...
Antigens and Antibodies, Cell Receptors
... urushiol → quinone (reacts with skin proteins) hydralazine (blood pressure-lowering drug) → drug-induced lupus erythematosus halothane (anesthetic gas) → hepatitis penicillin-class drugs → autoimmune hemolytic anemia ...
... urushiol → quinone (reacts with skin proteins) hydralazine (blood pressure-lowering drug) → drug-induced lupus erythematosus halothane (anesthetic gas) → hepatitis penicillin-class drugs → autoimmune hemolytic anemia ...
Engineered Human Cells: SAY NO TO SEPSIS
... Design a feedback pathway that, while retaining an effective pathway against infection, limits excessive cell stimulation and corresponding immune response ...
... Design a feedback pathway that, while retaining an effective pathway against infection, limits excessive cell stimulation and corresponding immune response ...
A comprehensive platform for T cell Stimulation based on
... APC’s present antigen and create a stimulatory or inhibitory microenvironment for T cell stimulation Virus or Bacteria Tumor Cells Antigen Processing DC ...
... APC’s present antigen and create a stimulatory or inhibitory microenvironment for T cell stimulation Virus or Bacteria Tumor Cells Antigen Processing DC ...
autoimmunity
... SLE can damage almost any part or organ of the body. Many people are initially thought to have arthritis because SLE has caused inflammation of the joints. Kidneys are frequently affected. If SLE affects the brain, for example, a person might be initially diagnosed as psychotic, epileptic or sufferi ...
... SLE can damage almost any part or organ of the body. Many people are initially thought to have arthritis because SLE has caused inflammation of the joints. Kidneys are frequently affected. If SLE affects the brain, for example, a person might be initially diagnosed as psychotic, epileptic or sufferi ...
Another person Direct contact: shaking hands 1. 2. Contaminated
... 12. During the _____________________________, blood vessels widen in the area affected by pathogens. 13. In the ___________________________, the body reacts to each kind of pathogen with a defense targeted specifically for that pathogen. 14. A chemical that helps destroy a specific kind of pathogen ...
... 12. During the _____________________________, blood vessels widen in the area affected by pathogens. 13. In the ___________________________, the body reacts to each kind of pathogen with a defense targeted specifically for that pathogen. 14. A chemical that helps destroy a specific kind of pathogen ...
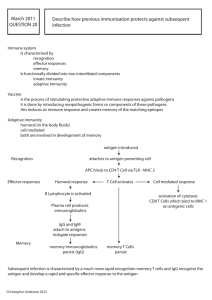
March 2011 QUESTION 20 Describe how previous
... innate immunity adaptive immunity Vaccine is the process of stimulating protective adaptive immune responses against pathogens it is done by introducing nonpathogenic forms or components of these pathogens this induces an immune response and creates memory of the matching epitopes Adaptive immunity ...
... innate immunity adaptive immunity Vaccine is the process of stimulating protective adaptive immune responses against pathogens it is done by introducing nonpathogenic forms or components of these pathogens this induces an immune response and creates memory of the matching epitopes Adaptive immunity ...
IMMUNOLOGICAL TOLERANCE
... The thymus also has an unusual mechanism for expressing protein antigens that are typically present only in certain peripheral tissues, so that immature T cells specific for these antigens can be deleted from the developing T cell repertoire. Some of these peripheral tissue antigens are expressed in ...
... The thymus also has an unusual mechanism for expressing protein antigens that are typically present only in certain peripheral tissues, so that immature T cells specific for these antigens can be deleted from the developing T cell repertoire. Some of these peripheral tissue antigens are expressed in ...
Immune
... Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a transmembrane protein that has been speculated to play a major role in suppressing the immune system during particular events such as pregnancy, tissue allografts, autoimmune disease and other disease states such as hepatitis. ...
... Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) is a transmembrane protein that has been speculated to play a major role in suppressing the immune system during particular events such as pregnancy, tissue allografts, autoimmune disease and other disease states such as hepatitis. ...
Autoimmune Disease
... Alternatively, self peptides may drive the positive selection of developing thymocytes that are specific for particular autoantigens. ...
... Alternatively, self peptides may drive the positive selection of developing thymocytes that are specific for particular autoantigens. ...
Document
... Chemical property • Proteins are the most effective immunogens • Nucleic acids and most lipids are antigenic but not immunogenic ...
... Chemical property • Proteins are the most effective immunogens • Nucleic acids and most lipids are antigenic but not immunogenic ...
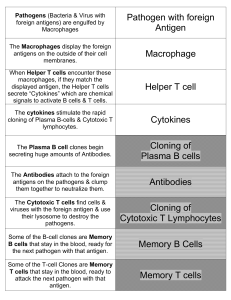
Pathogens (Bacteria with foreign antigens) are
... Pathogens (Bacteria & Virus with foreign antigens) are engulfed by Macrophages ...
... Pathogens (Bacteria & Virus with foreign antigens) are engulfed by Macrophages ...
4.-autoimmunity-and
... • Some allergies are so severe that they can trigger anaphylactic shock where the histamine causes such a huge drop in blood pressure it can be life threatening. ...
... • Some allergies are so severe that they can trigger anaphylactic shock where the histamine causes such a huge drop in blood pressure it can be life threatening. ...
Immune System Outline 3 - Madison County Schools
... 2. Hodgkin’s Lymphoma - This is a cancer of the lymphocyte white blood cells.(Lymph nodes destroyed.) 3. Stress – This weakens the immune system. 4. HIV/AIDS - This is caused by a retrovirus. a. Host cell is the T-helper lymphocyte. (It keys in on the CD 4 membrane marker protein.) II. Plant defense ...
... 2. Hodgkin’s Lymphoma - This is a cancer of the lymphocyte white blood cells.(Lymph nodes destroyed.) 3. Stress – This weakens the immune system. 4. HIV/AIDS - This is caused by a retrovirus. a. Host cell is the T-helper lymphocyte. (It keys in on the CD 4 membrane marker protein.) II. Plant defense ...
Autoimmune disease I
... b) Non-HLA genes (cont.) Recent examples: 1- Polymorphisms in a gene called PTPN-22 (most frequently implicated with AD, a\w RA & type 1 DM. Mechanism : defect in encoded phosphatase > defect in control of tyrosine kinases activity>defect of lymphocyte responses>> excessive activation 2- Polymorphis ...
... b) Non-HLA genes (cont.) Recent examples: 1- Polymorphisms in a gene called PTPN-22 (most frequently implicated with AD, a\w RA & type 1 DM. Mechanism : defect in encoded phosphatase > defect in control of tyrosine kinases activity>defect of lymphocyte responses>> excessive activation 2- Polymorphis ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... Give an account on the applications of Monoclonal antibodies. Describe the role of cytokines in immunogenic reaction. Explain the immune responses shown to viral, bacterial and parasite infections. Discuss the role of secondary lymphoid organs in immunity. Write notes on AIDS. Part C ...
... Give an account on the applications of Monoclonal antibodies. Describe the role of cytokines in immunogenic reaction. Explain the immune responses shown to viral, bacterial and parasite infections. Discuss the role of secondary lymphoid organs in immunity. Write notes on AIDS. Part C ...