* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4.-autoimmunity-and
Herd immunity wikipedia , lookup
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Inflammatory bowel disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Ankylosing spondylitis wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Neuromyelitis optica wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis research wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatoid arthritis wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Sjögren syndrome wikipedia , lookup
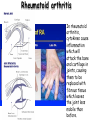
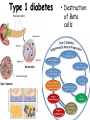
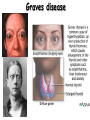
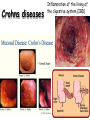
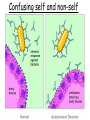
Unit 4 Immunology and Public Health Unit 4 – Immunology and Public Health 1. The Immune System a)Non-specific defences b)Specific cellular defences 2. Infectious Diseases and immunity a)Transmission and control b)Active Immunisation and Vaccination and the evasion of immune responses 1. The Immune System b) specific cellular defences By the end of this section you will be able to ….. • describe the role of T lymphocytes in recognising self and non-self • explain what is meant by an autoimmune disease in relation to lymphocyte regulation • state what is meant by the term ‘allergy’ and give examples of common allergic reactions Decide if each card is TRUE or FALSE Crohns disease, type 1 diabetes, Graves disease, psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis are examples of autoimmune diseases. Chicken pox, CJD, legionnaires’ disease and meningitis are examples of autoimmune diseases. An autoimmune disease is caused by an overactive immune response in which the body’s own cells are destroyed. Autoimmune diseases can be caught from close contact with infected people. Treatment of autoimmune disease only serves to alleviate the symptoms, it does not cure the disease. Autoimmune diseases can be easily cured with a combination of antibiotics and anti-viral drugs. There is no known prevention for autoimmune disease. Children can be vaccinated against autoimmune diseases – this prevents them from getting ill in later life. Rheumatoid arthritis In rheumatoid arthritis, cytokines cause inflammation which will attack the bone and cartilage in joints, causing them to be replaced with fibrous tissue which leaves the joint less mobile than before. Type 1 diabetes • Destruction of Beta cells Graves disease Psoriasis skin condition that causes red, flaky, crusty patches of skin covered with silvery scales Crohns diseases Inflammation of the lining of the digestive system (IBD) Multiple Sclerosis Confusing self and non-self • T-lymphocytes have specific surface proteins that should be able to read the surface antigens of a cell and tell if it is self or non-self. • However, sometimes T-lymphocyte regulation can fail • T-lymphocytes fail to distinguish between the surface proteins of the body’s own cells and surface proteins on foreign cells and therefore attacks body cells. • The immune response against our own self cells is called autoimmunity. – Rheumatoid arthritis – Type 1 diabetes – Multiple sclerosis. Confusing self and non-self Allergies • B-lymphocytes sometimes over-react to harmless substances like dust, pollen and feathers etc. or even medicines such as penicillin. • The hypersensitive B-lymphocytes release antibodies which cause mast cells to release histamine. • Some allergies are so severe that they can trigger anaphylactic shock where the histamine causes such a huge drop in blood pressure it can be life threatening. Can you now …. • describe the role of T lymphocytes in recognising self and non-self • explain what is meant by an autoimmune disease in relation to lymphocyte regulation • state what is meant by the term ‘allergy’ and give examples of common allergic reactions