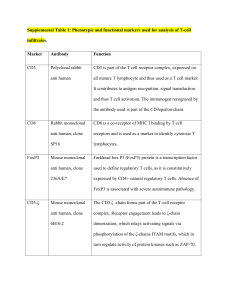
A Brief Overview of Immunology
... Antibodies react with foreign agent Activated T cells react with foreign agent Activated T cells may influence other cells Antibodies provide specificity to nonspecific cytotoxic systems Immune system “remembers: what it did. ...
... Antibodies react with foreign agent Activated T cells react with foreign agent Activated T cells may influence other cells Antibodies provide specificity to nonspecific cytotoxic systems Immune system “remembers: what it did. ...
File - Classes with Mrs. Sheetz
... • Helper T-cells: present the pathogen’s antigen to B-cells and cytotoxic T-cells • B-cells: makes antibodies directed toward a specific antigen; target the antigen for removal • Cytotoxic T-cells: make proteins called receptors specific to the one antigen; sticks to antigen and kills it • Suppress ...
... • Helper T-cells: present the pathogen’s antigen to B-cells and cytotoxic T-cells • B-cells: makes antibodies directed toward a specific antigen; target the antigen for removal • Cytotoxic T-cells: make proteins called receptors specific to the one antigen; sticks to antigen and kills it • Suppress ...
Chapter 21 The Immune System
... • New Terms: – Antigen: usually a protein found on the cell membrane of the pathogen that has attacked the body – Antibody: protein (nonliving) that reacts w/ antigen to mark the pathogen allowing it to be recognized & then eaten by a phagocyte ...
... • New Terms: – Antigen: usually a protein found on the cell membrane of the pathogen that has attacked the body – Antibody: protein (nonliving) that reacts w/ antigen to mark the pathogen allowing it to be recognized & then eaten by a phagocyte ...
Human Immune System - West Linn High School
... Memory B cells & plasma cells Memory B cells remain after infection Memory B cells allow a rapid response during re-infection ...
... Memory B cells & plasma cells Memory B cells remain after infection Memory B cells allow a rapid response during re-infection ...
Autoimmune Diseases
... •Regulatory T cells play a crucial in controlling autoimmune responses: CD25+FoxP3+ CD4+T cells block the effect of autoimmune responses mediated by autoreactive T cells. This blocking may or may not require the secretion of suppressive cytokines such as TGF and IL-10. Some autoimmune diseases appe ...
... •Regulatory T cells play a crucial in controlling autoimmune responses: CD25+FoxP3+ CD4+T cells block the effect of autoimmune responses mediated by autoreactive T cells. This blocking may or may not require the secretion of suppressive cytokines such as TGF and IL-10. Some autoimmune diseases appe ...
Autoimmune Disease
... Why would the body attack itself? What is the mistake made by the immune system? Hint: In order for the immune system to be successful in defending the body, what two things must it be able to distinguish? ...
... Why would the body attack itself? What is the mistake made by the immune system? Hint: In order for the immune system to be successful in defending the body, what two things must it be able to distinguish? ...
The Immune System
... -shut down response after pathogens are cleared 2. Humoral Immune Response -B cells change into plasma cells and produce antibodies. Antibodies – chemicals that binds to antigen to disable the pathogen (block reproduction). -Antigen specific -Stores antibodies for the future use ...
... -shut down response after pathogens are cleared 2. Humoral Immune Response -B cells change into plasma cells and produce antibodies. Antibodies – chemicals that binds to antigen to disable the pathogen (block reproduction). -Antigen specific -Stores antibodies for the future use ...
Drugs for Modifying Biologic Response
... Rituximab: a monoclonal antibiody that binds specifically to CD20 antigen on t;he surface of Malignant B lymphocytes and causes cell lysis ...
... Rituximab: a monoclonal antibiody that binds specifically to CD20 antigen on t;he surface of Malignant B lymphocytes and causes cell lysis ...
Adaptive or acquired immune system
... 5. Alternate complement pathway – cascade of serum proteins that are activated by bacterial cell wall components 2. Adaptive or acquired immune system: Found only in vertebrates (fish, amphibians, birds and mammals), Must be induced to be active against infections or tumors. Antigen-specific – a ...
... 5. Alternate complement pathway – cascade of serum proteins that are activated by bacterial cell wall components 2. Adaptive or acquired immune system: Found only in vertebrates (fish, amphibians, birds and mammals), Must be induced to be active against infections or tumors. Antigen-specific – a ...
Freeman 1e: How we got there
... antigens that compose our body tissue. Thus, T cells must achieve tolerance, or specific unresponsiveness to self antigens. • The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ that provides an environment for the maturation of antigen-reactive T cells. ...
... antigens that compose our body tissue. Thus, T cells must achieve tolerance, or specific unresponsiveness to self antigens. • The thymus is a primary lymphoid organ that provides an environment for the maturation of antigen-reactive T cells. ...
Gender differences wrt immune responses
... Gender differences w.r.t immune responses- In mice • Female mice have higher tendency to develop TH1 responses than males and, resistant to the infection resolved with Th1 responses • An excellent example is infection by viruses such as – vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) – herpes simplex virus (HSV ...
... Gender differences w.r.t immune responses- In mice • Female mice have higher tendency to develop TH1 responses than males and, resistant to the infection resolved with Th1 responses • An excellent example is infection by viruses such as – vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) – herpes simplex virus (HSV ...
Auto-immune diseases – 19/03/03
... Microbes are immunogenic, self antigens are tolerogenic/ignorance. Immunologic tolerance, therefore, can be induced either when lymphocytes are maturing in lymphoid organs called central tolerance, or when they are matured and come into contact with self antigens called peripheral tolerance. Periphe ...
... Microbes are immunogenic, self antigens are tolerogenic/ignorance. Immunologic tolerance, therefore, can be induced either when lymphocytes are maturing in lymphoid organs called central tolerance, or when they are matured and come into contact with self antigens called peripheral tolerance. Periphe ...
IMMUNE SYSTEM SPECIFIC DEFENSE
... caused by a retrovirus 1. has enzymes to transcribe its RNA to DNA 2. new DNA inserted into host cell’s DNA 3. host cell now makes proteins to assemble more HIV viruses ...
... caused by a retrovirus 1. has enzymes to transcribe its RNA to DNA 2. new DNA inserted into host cell’s DNA 3. host cell now makes proteins to assemble more HIV viruses ...