* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download immune response
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
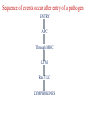
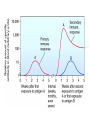
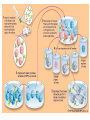
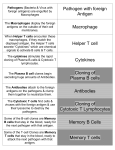
IMMUNE RESPONSE It includes reactions against any antigen. The consequences are usually beneficial or some times may be injurious to the host. The adaptive response can be antibody-mediated (humoral), cell-mediated (cellular), or both. Sequence of events occur after entry of a pathogen ENTRY APC Through MHC LYM Rec T LC LYMPHOKINES Humoral Immune Response Helper T lymphocytes (CD4) recognize the pathogen's antigens complexed with class II MHC proteins on the surface of an APC and produce cytokines that activate B cells expressing antibodies that specifically match the antigen. Major host defense functions of antibodies include neutralization of toxins and viruses and opsonization (coating) of the pathogen, which aids its uptake by phagocytic cells. It applies mainly to extracellular pathogens and their toxins. Primary and secondary immune responses It is slow, short lived with long lag phase and low titre persists for short period. Secondary response is prompt, powerful and prolonged with short negligible lag phase much higher levels of antibodies last for long period. MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES Normally antibodies produced by infection or antigens will have antibodies against multiple epitopes. A single antibody producing cell of clone produces against a single epitope. Antibodies produced by a single clone and directed against a single epitope are called as monoclonal antibodies Uses: 1. Diagnostic use 2. Therapeutic use Factors influencing antibody production 1. Genetic factors 2. Age 3. Nutritional status 4. Route of administration 5. Dose of Antigen 6. Multiple antigens 7. Adjuvants 8. Immunosuppressive agents 9. Effect of antibody Cellular immune response Each class of T cells produces cytokines, becomes activated, and expands by clonal proliferation. Helper T cell activity, promotes the development of delayed hypersensitivity and thereby also serves in the defense against intracellular agents, including intracellular bacteria (eg, mycobacteria), fungi, protozoa, and viruses. Cytotoxic T cell activity is aimed mainly at the destruction of cells in tissue grafts, tumor cells, or cells infected by some viruses. Cytokines These are biologically active substances secreted by lymphocytes, monocytes and others cells. Selected Important Cytokines. Name Major Cellular Source Selected Biologic Effects IL-1 (interleukin-1) Macrophages Cell activation, fever IL-2 (interleukin-2) T cells T cell growth and activation IL-3 (interleukin-3) T cells Hematopoiesis IL-4 (interleukin-4) T cells, mast cells B cell proliferation and switching to IgE, TH2 differentiation IL-5 (interleukin-5) T cells Differentiation of eosinophils, activates B cells IL-7 (interleukin-7) Bone marrow stroma cells T cell progenitor differentiation IL-8 (interleukin-8) Macrophages, T cells Chemotactic for neutrophils IL-10 (interleukin-10) Macrophages, T cells Inhibits activated macrophages and dendritic cells IL-12 (interleukin-12) Macrophages Differentiation of T cells, activation of NK cells IFN-alpha, beta Macrophages fibroblasts Antiviral, Activates macrophages, Immunosuppressive agents These inhibit the immune response. X- radiation, Radiomimetic drugs, Carticosteroids, Antimetabolites, Antilymphocytic serum. Used in situations like transplatation to prevent graft rejection Detection of CMI 1. Skin test. 2. Lymphocyte transformation test. 3. Migration inhibition factor. Transfer factor It is possible to transfer of CMI in man by injecting the extract from leucocytes. It is low MW substance of 2000-4000. Used in 1. T cell deficiency syndrome. 2. Treatment of disseminated infections. 3. Treatment of some cancers. THANK YOU