biochem study guide
... 3. Describe the structure of a typical monosaccharide such as glucose. Write out a condensation reaction between two glucose molecules, and explain hydrolysis. 4. Explain the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fatty acid. Explain how three fatty acids can react with glycerol to make a ...
... 3. Describe the structure of a typical monosaccharide such as glucose. Write out a condensation reaction between two glucose molecules, and explain hydrolysis. 4. Explain the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fatty acid. Explain how three fatty acids can react with glycerol to make a ...
Work and Energy in Muscles
... Activity lasting over many minutes and hours cannot be supported by the limited bodily reserves of glucose and glycogen. Fatty acids from food and adipose tissue, therefore, supply most of the substrate used by muscle tissue working over time. Branched-chain amino acids can also serve as substrates ...
... Activity lasting over many minutes and hours cannot be supported by the limited bodily reserves of glucose and glycogen. Fatty acids from food and adipose tissue, therefore, supply most of the substrate used by muscle tissue working over time. Branched-chain amino acids can also serve as substrates ...
MTC15 - toddgreen
... Starch is an α-D-glucose polysaccharide used for energy storage and has two different forms: amylose and amylopectin (roughly 1:3 ratio) Amylose is linear and joined by 1α-4 linkages Amylopectin is branched with branches forming 1α-6 linkages Glycogen is another branched polysaccharide (with similar ...
... Starch is an α-D-glucose polysaccharide used for energy storage and has two different forms: amylose and amylopectin (roughly 1:3 ratio) Amylose is linear and joined by 1α-4 linkages Amylopectin is branched with branches forming 1α-6 linkages Glycogen is another branched polysaccharide (with similar ...
Homeostatic Control of Metabolism
... Insulin Increases Glucose Transport • Required for resting skeletal muscle and adipose tissue • Moves GLUT-4 transporters to cell membrane • Exercising skeletal muscle does not require insulin for glucose uptake • In liver cells, indirect influence on glucose ...
... Insulin Increases Glucose Transport • Required for resting skeletal muscle and adipose tissue • Moves GLUT-4 transporters to cell membrane • Exercising skeletal muscle does not require insulin for glucose uptake • In liver cells, indirect influence on glucose ...
The Mistake of Eating Low Fat Foods
... 2) 13.9% increase in LDL cholesterol. It also doubled Apoprotein B which is an index of the number of LDL particles. 3) 44.9% increase in the dreaded small LDL, compared to 13.3% with glucose. 4) While glucose (curiously) reduced the overall after-eating triglyceride response, fructose increased aft ...
... 2) 13.9% increase in LDL cholesterol. It also doubled Apoprotein B which is an index of the number of LDL particles. 3) 44.9% increase in the dreaded small LDL, compared to 13.3% with glucose. 4) While glucose (curiously) reduced the overall after-eating triglyceride response, fructose increased aft ...
Final Review
... A. Oxidation can be considered as loss of hydrogen or gain of oxygen. B. Reduction can be considered as gain of hydrogen or loss of oxygen. C. NADè is the oxidized form of NADH. D. An oxidation reaction cannot occur unless a reduction reaction also occurs. E. FAD is the reduced form of FADH2. ...
... A. Oxidation can be considered as loss of hydrogen or gain of oxygen. B. Reduction can be considered as gain of hydrogen or loss of oxygen. C. NADè is the oxidized form of NADH. D. An oxidation reaction cannot occur unless a reduction reaction also occurs. E. FAD is the reduced form of FADH2. ...
Chem 2B
... A. Oxidation can be considered as loss of hydrogen or gain of oxygen. B. Reduction can be considered as gain of hydrogen or loss of oxygen. C. NADè is the oxidized form of NADH. D. An oxidation reaction cannot occur unless a reduction reaction also occurs. E. FAD is the reduced form of FADH2. ...
... A. Oxidation can be considered as loss of hydrogen or gain of oxygen. B. Reduction can be considered as gain of hydrogen or loss of oxygen. C. NADè is the oxidized form of NADH. D. An oxidation reaction cannot occur unless a reduction reaction also occurs. E. FAD is the reduced form of FADH2. ...
Nutrition
... 2. The glycerol component is converted to glucose (which enters into glycolysis) or G3P (which eventually enters the Krebs cycle) 3. The fatty acid components are oxidized into acetic acid fragments which bind to coenzyme A and enter the Krebs cycle as acetyl CoA 4. Dietary fats not needed for energ ...
... 2. The glycerol component is converted to glucose (which enters into glycolysis) or G3P (which eventually enters the Krebs cycle) 3. The fatty acid components are oxidized into acetic acid fragments which bind to coenzyme A and enter the Krebs cycle as acetyl CoA 4. Dietary fats not needed for energ ...
Diet for a person with a 10km run in a weeks time
... Diet for a person with a 10km run in a weeks time Nutritionalist – Anna Perry ...
... Diet for a person with a 10km run in a weeks time Nutritionalist – Anna Perry ...
Biochemistry Test Review
... 8. Be able to draw a triglyceride, showing how glycerol and three fatty acids link together. Name the kind of reaction that links the fatty acids to glycerol. How many molecules of water are formed? 9. Distinguish between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. 10. How do trans fats differ from other ...
... 8. Be able to draw a triglyceride, showing how glycerol and three fatty acids link together. Name the kind of reaction that links the fatty acids to glycerol. How many molecules of water are formed? 9. Distinguish between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids. 10. How do trans fats differ from other ...
Cellular Respiration - Peoria Public Schools
... Amino acids are taken up by liver Amino acids are used to make needed proteins Amino acids can be converted into pyruvic acid and acetyl-CoA • Metabolism results in ammonia which is converted to urea (liver) ...
... Amino acids are taken up by liver Amino acids are used to make needed proteins Amino acids can be converted into pyruvic acid and acetyl-CoA • Metabolism results in ammonia which is converted to urea (liver) ...
Jennifer Atkinson October 14, 2013 HUN 3230 Section 81944
... monosaccharides and polysaccharides that can consist of hundreds to thousands of glucose molecules. Starch, glycogen, and most fibers are considered to be polysaccharides. Food sources that are composed of complex carbohydrates include breads, potatoes, rice, nuts, and flour. The RDA for carbohydrat ...
... monosaccharides and polysaccharides that can consist of hundreds to thousands of glucose molecules. Starch, glycogen, and most fibers are considered to be polysaccharides. Food sources that are composed of complex carbohydrates include breads, potatoes, rice, nuts, and flour. The RDA for carbohydrat ...
ppt
... • Monomeric protein which displays cooperativity • Potential anti-diabetic therapeutic • Current. Crystal structures solved in 2004 ...
... • Monomeric protein which displays cooperativity • Potential anti-diabetic therapeutic • Current. Crystal structures solved in 2004 ...
Macromolecules - Uplift Mighty Prep
... Monosaccharides Glucose – used to transport energy through the blood to all cells in the body ...
... Monosaccharides Glucose – used to transport energy through the blood to all cells in the body ...
Macromolecules - Uplift Education
... Monosaccharides Glucose – used to transport energy through the blood to all cells in the body ...
... Monosaccharides Glucose – used to transport energy through the blood to all cells in the body ...
Temperature Homeostasis (thermoregulation)
... and mammals) are called endotherms, while those that have a variable body temperature (all others) are called ectotherms. Endotherms normally maintain their body temperatures at around 35 - 40°C, so are sometimes called warm-blooded animals, but in fact ectothermic animals can also have very warm bl ...
... and mammals) are called endotherms, while those that have a variable body temperature (all others) are called ectotherms. Endotherms normally maintain their body temperatures at around 35 - 40°C, so are sometimes called warm-blooded animals, but in fact ectothermic animals can also have very warm bl ...
File
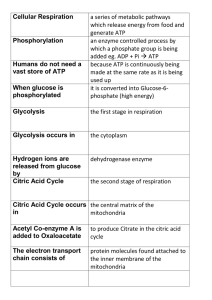
... added eg. ADP + Pi ATP because ATP is continuously being made at the same rate as it is being used up it is converted into Glucose-6phosphate (high energy) ...
... added eg. ADP + Pi ATP because ATP is continuously being made at the same rate as it is being used up it is converted into Glucose-6phosphate (high energy) ...
Chapter 5: The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
... -starch = glucose polymer in plants used for energy storage ( ...
... -starch = glucose polymer in plants used for energy storage ( ...
OVERVIEW OF LIPID METABOLISM
... 1) Glycogen breakdown provides glucose and protein breakdown provides alanine, which is converted to glucose in the liver. The blood glucose is used by the brain and red blood cells. Most other tissues, including resting muscle, are relying primarily on fatty acids as an energy source. Exercising mu ...
... 1) Glycogen breakdown provides glucose and protein breakdown provides alanine, which is converted to glucose in the liver. The blood glucose is used by the brain and red blood cells. Most other tissues, including resting muscle, are relying primarily on fatty acids as an energy source. Exercising mu ...
CARBOHYDRATES: METABOLISM (cont.)
... • Ketones can be used by the liver or transported to other tissues to enter the CA cycle – Lipid anabolism consists of the synthesis of triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids, and prostaglandins • Made from glycerol and FA or excess glucose or aa • Most FA can be made by the body, but some must b ...
... • Ketones can be used by the liver or transported to other tissues to enter the CA cycle – Lipid anabolism consists of the synthesis of triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids, and prostaglandins • Made from glycerol and FA or excess glucose or aa • Most FA can be made by the body, but some must b ...
Chapter 26 - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... • Amino acid pool - dietary amino acids plus 100 g of tissue protein broken down each day into free amino acids • May be used to synthesize new proteins • As fuel -- first must be deaminated (removal of NH2)--what remains is converted to pyruvic acid, acetyl-CoA or part of citric acid cycle – during ...
... • Amino acid pool - dietary amino acids plus 100 g of tissue protein broken down each day into free amino acids • May be used to synthesize new proteins • As fuel -- first must be deaminated (removal of NH2)--what remains is converted to pyruvic acid, acetyl-CoA or part of citric acid cycle – during ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.