Digestion Review Outline
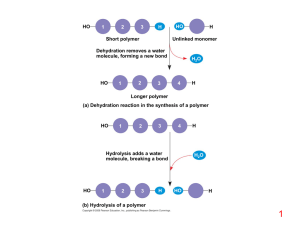
... Some compounds (food) we eat are too large to diffuse into cells so they need to be digested (broken down). A. Carbohydrates or starches (broken down into building blocks simple sugars, or glucose) B. Proteins (broken down into building blocks amino acids) C. Lipids or fats (broken down into buildin ...
... Some compounds (food) we eat are too large to diffuse into cells so they need to be digested (broken down). A. Carbohydrates or starches (broken down into building blocks simple sugars, or glucose) B. Proteins (broken down into building blocks amino acids) C. Lipids or fats (broken down into buildin ...
Ch 26 Powerpoint
... • Excess glycerol & fatty acids undergo lipogenesis to form triglycerides in the liver. • Glucose or amino acids converted into lipids Glucose glyceraldehyde glyceraldehyde3-phosphate glycerol or to acetyl CoA which can go on to form fatty acids • Amino acids Acetyl CoA fatty acids, etc. ...
... • Excess glycerol & fatty acids undergo lipogenesis to form triglycerides in the liver. • Glucose or amino acids converted into lipids Glucose glyceraldehyde glyceraldehyde3-phosphate glycerol or to acetyl CoA which can go on to form fatty acids • Amino acids Acetyl CoA fatty acids, etc. ...
macromolecule notes
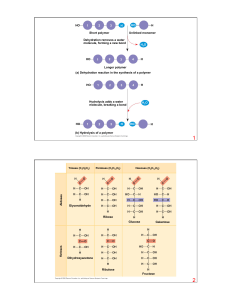
... gives strength and rigidity to plant cells. 3. ________________: a common storage form of glucose in animals (stored in the ______________ and _______________ to be used as quick energy) II. Lipids (include fats, oils, waxes, etc.) i. Class of macromolecules that ____________________________________ ...
... gives strength and rigidity to plant cells. 3. ________________: a common storage form of glucose in animals (stored in the ______________ and _______________ to be used as quick energy) II. Lipids (include fats, oils, waxes, etc.) i. Class of macromolecules that ____________________________________ ...
JMT Coffee
... simplex infections, or cold sores. They are called essential amino acids not because they are more important than other amino acids but because it is essential that they are included in the daily diet since they are not produced naturally by the body. ...
... simplex infections, or cold sores. They are called essential amino acids not because they are more important than other amino acids but because it is essential that they are included in the daily diet since they are not produced naturally by the body. ...
4 Classes of Large Biological Molecules Carbohydrates Lipids
... Fat from plants comes from seeds Phospholipids Has two fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule The 3rd –OH group is attached to a phosphate group (- charge) Show ambivalent properties toward water Steroids Have C skeletons consisting of 4 rings, only variation come in functional groups Cholester ...
... Fat from plants comes from seeds Phospholipids Has two fatty acids attached to a glycerol molecule The 3rd –OH group is attached to a phosphate group (- charge) Show ambivalent properties toward water Steroids Have C skeletons consisting of 4 rings, only variation come in functional groups Cholester ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... interact with one another and crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
... interact with one another and crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
Integration of Metabolism
... 3.Protein metabolism: Muscle proteins are degraded and the amino acids are utilized for glucose synthesis by liver. Protein breakdown is reduced if the starvation is prolonged. Brain in starvation During the first two weeks of starvation, the brain mostly dependent on glucose, supplied by liver glu ...
... 3.Protein metabolism: Muscle proteins are degraded and the amino acids are utilized for glucose synthesis by liver. Protein breakdown is reduced if the starvation is prolonged. Brain in starvation During the first two weeks of starvation, the brain mostly dependent on glucose, supplied by liver glu ...
L-VIAVA TRADE NAME L-VIAVA INTERNATIONAL
... Levocarnitine is a natural substance relative to B-group vitamins. Takes part in metabolic process as a carrier of fatty acids through the cell memdrane from cytoplasm into mitochondria where these acids are subjected to β-oxidation with the production of a large amount of energy (as ATP). Releasing ...
... Levocarnitine is a natural substance relative to B-group vitamins. Takes part in metabolic process as a carrier of fatty acids through the cell memdrane from cytoplasm into mitochondria where these acids are subjected to β-oxidation with the production of a large amount of energy (as ATP). Releasing ...
Ch.05The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules
... cylinder to change shape in such a way that it creates a ...
... cylinder to change shape in such a way that it creates a ...
Connections of Carbohydrate, Protein, and Lipid
... cholesterol starts with acetyl groups and proceeds in only one direction. The process cannot be reversed. Triglycerides are a form of long-term energy storage in animals. Triglycerides are made of glycerol and three fatty acids. ...
... cholesterol starts with acetyl groups and proceeds in only one direction. The process cannot be reversed. Triglycerides are a form of long-term energy storage in animals. Triglycerides are made of glycerol and three fatty acids. ...
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 4 Types of Macromolecules
... different. The “R” group may vary in size, shape, charge, hydrophobicity and reactivity. The sequence of amino acids will determine which protein is made. ...
... different. The “R” group may vary in size, shape, charge, hydrophobicity and reactivity. The sequence of amino acids will determine which protein is made. ...
experiment six
... measured after to stop administration of medicine a few days later 2.The protein in urine would interfere in the reaction. It can be done after boiling urine in acid condition and filtrating it 3.Uric acid salt would interfere in the reaction because of its weak reducing. Remain the urine in refrige ...
... measured after to stop administration of medicine a few days later 2.The protein in urine would interfere in the reaction. It can be done after boiling urine in acid condition and filtrating it 3.Uric acid salt would interfere in the reaction because of its weak reducing. Remain the urine in refrige ...
Review Sheet - Phillips Scientific Methods
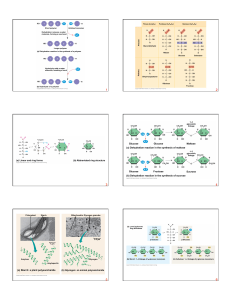
... Saturated fats are solid at room temperature o Hydrogen at every possible position 1 or more double bonds between carbon leads to unsaturated fatty acid. o Kink where double bond. We need cis, not trans Most animal fats are solid saturated Diet rich in saturated leads to cardiovascular disea ...
... Saturated fats are solid at room temperature o Hydrogen at every possible position 1 or more double bonds between carbon leads to unsaturated fatty acid. o Kink where double bond. We need cis, not trans Most animal fats are solid saturated Diet rich in saturated leads to cardiovascular disea ...
The Biochemistry of Life
... • Plants convert excess glucose into starch for storage • Rice, wheat, and corn are also major sources of starch in the human diet • Before starches can enter (or leave) cells, they must be digested. The hydrolysis of starch is done by amylases. • Examples: – amylose consists of linear, unbranched c ...
... • Plants convert excess glucose into starch for storage • Rice, wheat, and corn are also major sources of starch in the human diet • Before starches can enter (or leave) cells, they must be digested. The hydrolysis of starch is done by amylases. • Examples: – amylose consists of linear, unbranched c ...
biol 3 biomolecules table activity
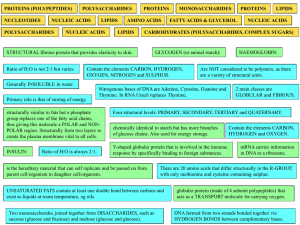
... structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma membrane vital to all cells. INSULIN: ...
... structurally similar to fats but a phosphate group replaces one of the fatty acid chains, thus giving this molecule a POLAR and NONPOLAR region. Structurally form two layers to create the plasma membrane vital to all cells. INSULIN: ...
What are macromolecules?
... Cellulose = structural glucose that forms the cell wall in plant cells ...
... Cellulose = structural glucose that forms the cell wall in plant cells ...
Aesthetic Solutions NY Aleksandr Benji FNP 98
... Inositol (I)- a nutrient belonging to the B vitamin complex, is closely associated with choline. It aids in the metabolism of fats and helps reduce blood cholesterol. Inositol participates in action of serotonin, a neurotransmitter known to control mood and appetite. Choline (C) - supports the healt ...
... Inositol (I)- a nutrient belonging to the B vitamin complex, is closely associated with choline. It aids in the metabolism of fats and helps reduce blood cholesterol. Inositol participates in action of serotonin, a neurotransmitter known to control mood and appetite. Choline (C) - supports the healt ...
Biomolecules
... molecules that are not soluble in water. (Do not mix with water) include fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes. Phospholipids make up the lipid bilayer of cell membranes. ...
... molecules that are not soluble in water. (Do not mix with water) include fats, phospholipids, steroids, and waxes. Phospholipids make up the lipid bilayer of cell membranes. ...
glycogen disappears
... • Glycogen represents the principal storage form of carbohydrate in the mammalian body, mainly in the liver and muscle. • In the liver, its major function is to provide glucose for extrahepatic tissues. In muscle, it serves mainly as a ready source of metabolic fuel for use in muscle. • Glycogen is ...
... • Glycogen represents the principal storage form of carbohydrate in the mammalian body, mainly in the liver and muscle. • In the liver, its major function is to provide glucose for extrahepatic tissues. In muscle, it serves mainly as a ready source of metabolic fuel for use in muscle. • Glycogen is ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.