NSC 602 - Department of Nutritional Sciences
... Analysis of current knowledge regarding the interactions between the intake, absorption, transport, processing, storage, catabolism and excretion of nutrients and the regulation of metabolic homeostasis in the intact organism. Emphasis areas include interrelationships between protein, carbohydrate a ...
... Analysis of current knowledge regarding the interactions between the intake, absorption, transport, processing, storage, catabolism and excretion of nutrients and the regulation of metabolic homeostasis in the intact organism. Emphasis areas include interrelationships between protein, carbohydrate a ...
A1985AFW3400002
... was very fortunate to be a member of Randie’s research group at a particularly exciting time. Hal Coore and Randle also devised the simple system that opened up the study of insulin secretion. I should point out, as there seems to be a danger of its being overlooked in these pages, that they showed ...
... was very fortunate to be a member of Randie’s research group at a particularly exciting time. Hal Coore and Randle also devised the simple system that opened up the study of insulin secretion. I should point out, as there seems to be a danger of its being overlooked in these pages, that they showed ...
WHY DO CARDIOMYOCYTES (HEART MUSCLE CELLS) STORE
... anaerobic energy production is extremely limited? A cardiomyocyte, deprived of its blood supply, cannot continue beating for more than a few minutes at the very most. The glycogen would therefore only be ...
... anaerobic energy production is extremely limited? A cardiomyocyte, deprived of its blood supply, cannot continue beating for more than a few minutes at the very most. The glycogen would therefore only be ...
Molecules of Life Note Taking Guide
... 12. Name three common disaccharides and describe where they are commonly found. A. sucrose—glucose + fructose—sugar that is transported by plants—sugar cane B. maltose—glucose + glucose—sugar found in corn syrup, malt & germinating seeds C. lactose—glucose + galactose—sugar found in milk 13. Draw th ...
... 12. Name three common disaccharides and describe where they are commonly found. A. sucrose—glucose + fructose—sugar that is transported by plants—sugar cane B. maltose—glucose + glucose—sugar found in corn syrup, malt & germinating seeds C. lactose—glucose + galactose—sugar found in milk 13. Draw th ...
Name - Humble ISD
... 8. ________ Substance that increases OH – concentration when added to water ...
... 8. ________ Substance that increases OH – concentration when added to water ...
Organic Chemistry IB
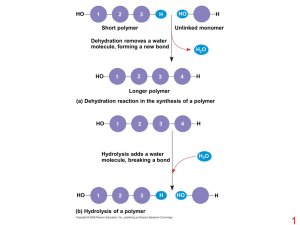
... Fatty acid chains can be of many lengths, extended by adding CH2 units. They are an efficient store of energy and bond with glycerol (a simple sugar alcohol) to make triglycerides – lipids. ...
... Fatty acid chains can be of many lengths, extended by adding CH2 units. They are an efficient store of energy and bond with glycerol (a simple sugar alcohol) to make triglycerides – lipids. ...
The liver is the largest gland in the body, weighing about 1.4 Kg. It is
... by glucose-6-phosphatase which is necessary for breakdown of glycogen and only liver has it. B- Conversion of galactose and fructose to glucose. C- Gluconeogenesis when glucose concentration begins to fall below normal. Large amount of amino acid are converted into glucos ...
... by glucose-6-phosphatase which is necessary for breakdown of glycogen and only liver has it. B- Conversion of galactose and fructose to glucose. C- Gluconeogenesis when glucose concentration begins to fall below normal. Large amount of amino acid are converted into glucos ...
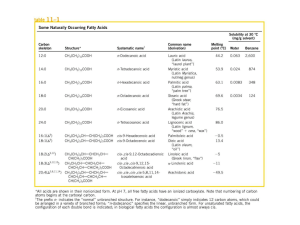
Fatty acid
... one another and crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
... one another and crystallize into a fiber; capacity to carry oxygen is greatly reduced. ...
Document
... produced? ____8________. Each cycle of -oxidation produces a single acetyl-CoA, _____1_____ (a number) FADH2 molecule(s), and _____1______ (a number) NADH molecule(s). 6. Amino nitrogen is transported out of muscle primarily in the form of what two amino acids? __alanine_____ and __glutamine______. ...
... produced? ____8________. Each cycle of -oxidation produces a single acetyl-CoA, _____1_____ (a number) FADH2 molecule(s), and _____1______ (a number) NADH molecule(s). 6. Amino nitrogen is transported out of muscle primarily in the form of what two amino acids? __alanine_____ and __glutamine______. ...
1. Diagram the biosynthetic pathway fiom UMP),
... 11. In the first bypass step of gluconeogenesis, the conversion of pyruvate to phosphoenolpyruvate, pyruvate is carboxylated by pyruvate carboxylase to oxaloacetate, which is subsequently decarboxylated by PEP carboxykinase to yield phosphoenolpyruvate. The observation that the addition of C& is di ...
... 11. In the first bypass step of gluconeogenesis, the conversion of pyruvate to phosphoenolpyruvate, pyruvate is carboxylated by pyruvate carboxylase to oxaloacetate, which is subsequently decarboxylated by PEP carboxykinase to yield phosphoenolpyruvate. The observation that the addition of C& is di ...
Biosynthesis of non-amino acids from amino acid precursors
... Fuel for gut, kidney, cells of immune Source of N for rapidly dividng cells Formation of glutamine from gluatamate and NH4+ provides a means of removing ammonia and transporting glutamate btwn cells in brain Prioritized: in metabolic acidosis kidney site of glutamine uptake; during sepsis im ...
... Fuel for gut, kidney, cells of immune Source of N for rapidly dividng cells Formation of glutamine from gluatamate and NH4+ provides a means of removing ammonia and transporting glutamate btwn cells in brain Prioritized: in metabolic acidosis kidney site of glutamine uptake; during sepsis im ...
Gluconeogenesis
... are converted to glucose. Fasting requires all the glucose to be synthesized from these non-carbohydrate precursors. Most precursors must enter the Krebs cycle at some point to be converted to oxaloacetate. ...
... are converted to glucose. Fasting requires all the glucose to be synthesized from these non-carbohydrate precursors. Most precursors must enter the Krebs cycle at some point to be converted to oxaloacetate. ...
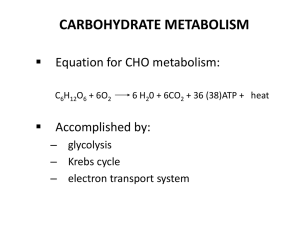
Metabolism Metabolism refers to all the chemical reactions within an
... The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions in mitochondria that oxidize acetyl residues (as acetyl-CoA) and reduce coenzymes that upon reoxidation are linked to the formation of ATP. The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the aerobic oxidation of carbohydrate, lipid, and protein b ...
... The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions in mitochondria that oxidize acetyl residues (as acetyl-CoA) and reduce coenzymes that upon reoxidation are linked to the formation of ATP. The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the aerobic oxidation of carbohydrate, lipid, and protein b ...
CELL METABOLISM - My Anatomy Mentor
... Oxidative & substrate phosphorylation Oxygen is used in the associated electron transport system. Most ATP formed here by oxidative phosphorylation ...
... Oxidative & substrate phosphorylation Oxygen is used in the associated electron transport system. Most ATP formed here by oxidative phosphorylation ...
Glucose Metabolism: Generating Energy in Life and Disease
... Generating Energy in Life and Disease ...
... Generating Energy in Life and Disease ...
Ch 19 - Chemistry Courses: About
... • Looks allosteric, but this is monomeric enzyme • May be due to conformational change upon product release— stays in active state at high concentration of glucose ...
... • Looks allosteric, but this is monomeric enzyme • May be due to conformational change upon product release— stays in active state at high concentration of glucose ...
Metabolism
... Fat burns in a flame of carbohydrate Carbohydrate is needed Without sufficient oxaloacetate from carb to drive the citric acid cycle, the acetyl coA from fatty acid beta-oxidation is converted to ketones ketosis Ketogenesis-Occurs in Liver Two molecules of acetyl coA combine to form acetoacetate Ace ...
... Fat burns in a flame of carbohydrate Carbohydrate is needed Without sufficient oxaloacetate from carb to drive the citric acid cycle, the acetyl coA from fatty acid beta-oxidation is converted to ketones ketosis Ketogenesis-Occurs in Liver Two molecules of acetyl coA combine to form acetoacetate Ace ...
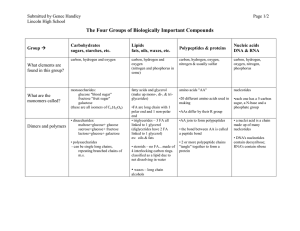
The Four Groups of Biologically Important Compounds
... sucrose=glucose+ fructose lactose=glucose+ galactose • polysaccharides - can be single long chains, repeating branched chains of m.s. ...
... sucrose=glucose+ fructose lactose=glucose+ galactose • polysaccharides - can be single long chains, repeating branched chains of m.s. ...
Lecture 24 (4/29/13) "The Food You Eat
... be surmounted before the specific reaction can occur. The total free energy released is exacly the same in (A) and (B). But if the sugar was instead oxidized to CO2 and H2) in a single step, as in (B), it would release an amount of energy much larger than could be captured for useful purposes. From: ...
... be surmounted before the specific reaction can occur. The total free energy released is exacly the same in (A) and (B). But if the sugar was instead oxidized to CO2 and H2) in a single step, as in (B), it would release an amount of energy much larger than could be captured for useful purposes. From: ...
Guide 1406 Ch, 1-5
... Define Matter, inertia, isotope, radioactivity, colloid, suspention Draw the electron shell diagram Differentiate between electrolyte and non-electrolyte The difference between Synthesis or combination reaction and decomposition What factors influence the rate of chemical reactions Difference betwee ...
... Define Matter, inertia, isotope, radioactivity, colloid, suspention Draw the electron shell diagram Differentiate between electrolyte and non-electrolyte The difference between Synthesis or combination reaction and decomposition What factors influence the rate of chemical reactions Difference betwee ...
Lipotropic injections consist of a combination of vitamins, minerals
... important for brain function and growth, as well as a properly-operating liver. It helps our livers to rid themselves of accumulating fat. Scientists believe that choline works best in our bodies when it is combined with other important vitamins, minerals and nutrients our bodies need in order to fu ...
... important for brain function and growth, as well as a properly-operating liver. It helps our livers to rid themselves of accumulating fat. Scientists believe that choline works best in our bodies when it is combined with other important vitamins, minerals and nutrients our bodies need in order to fu ...
Organic chemistry ppt
... – Fats are used for energy storage • Long-term food reserves stored in adipose (fat)cells ...
... – Fats are used for energy storage • Long-term food reserves stored in adipose (fat)cells ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.