Carbohydrate
... adults however, adolescents and young adults are developing type 2 diabetes at an alarming rate. It develops when the body doesn't make enough insulin and doesn’t efficiently use the insulin it makes (insulin resistance). Type 1 diabetes usually occurs in children and young adults. In type 1 diabete ...
... adults however, adolescents and young adults are developing type 2 diabetes at an alarming rate. It develops when the body doesn't make enough insulin and doesn’t efficiently use the insulin it makes (insulin resistance). Type 1 diabetes usually occurs in children and young adults. In type 1 diabete ...
Integration of Metabolism
... work all the phosphocreatine is converted into creatine. During recovery phase creatine is rephosphorylated to phosphocreatine. Muscle fatigue is not the result of the depletion of phosphocreatine and glycogen reserves. Nor is muscle fatigue caused by the accumulation of lactate. Muscle fatigue is c ...
... work all the phosphocreatine is converted into creatine. During recovery phase creatine is rephosphorylated to phosphocreatine. Muscle fatigue is not the result of the depletion of phosphocreatine and glycogen reserves. Nor is muscle fatigue caused by the accumulation of lactate. Muscle fatigue is c ...
Molecules of Life Worksheet
... 13. The main difference among amino acids is their ____ group. What is the R-group on glycine? on alanine? 14. Differences in R-groups give different proteins different ______________. 15. How does a dipeptide form? 16. What do you call the covalent bonds that hold amino acids together? 17. Long cha ...
... 13. The main difference among amino acids is their ____ group. What is the R-group on glycine? on alanine? 14. Differences in R-groups give different proteins different ______________. 15. How does a dipeptide form? 16. What do you call the covalent bonds that hold amino acids together? 17. Long cha ...
CARBOHYDRATES B.SC Ist SEMESTER INTRODUCTION TO
... body. Every grounds of carbohydrates, sugar or starch when oxidized yields on an average 4 Kilo calories. Since Indians consume large quantity of cereals, most of the requirement of energy is met by carbohydrates. •PROTEIN SPARING ACTION : The body uses carbohydrates as a source of energy, when they ...
... body. Every grounds of carbohydrates, sugar or starch when oxidized yields on an average 4 Kilo calories. Since Indians consume large quantity of cereals, most of the requirement of energy is met by carbohydrates. •PROTEIN SPARING ACTION : The body uses carbohydrates as a source of energy, when they ...
Chapter 6, Section 3
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
... Organic: contains carbon ◦ All living things contain carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) Monomer: created when C,H,O, N, P bond together to form small molecules Polymer: large compounds that are formed by joining monomers together ...
PPTX - Bonham Chemistry
... Central Importance of Glucose • Glucose is an excellent fuel – Yields good amount of energy upon oxidation(-2840 kJ/mole) – Can be efficiently stored in the polymeric form – Many organisms and tissues can meet their energy needs on glucose only ...
... Central Importance of Glucose • Glucose is an excellent fuel – Yields good amount of energy upon oxidation(-2840 kJ/mole) – Can be efficiently stored in the polymeric form – Many organisms and tissues can meet their energy needs on glucose only ...
Recovery
... All are able to demonstrate understanding of the relationship between OBLA and VO2max Most are able to apply the recovery process to sport Some can analyse the causes of fatigue ...
... All are able to demonstrate understanding of the relationship between OBLA and VO2max Most are able to apply the recovery process to sport Some can analyse the causes of fatigue ...
fatty acid metabolism
... CAT required for transport of FA into mito for beta-oxidation Overnight fast in infants normally requires gluconeogenesis to maintain [glu] – Requires energy from FA oxidation ...
... CAT required for transport of FA into mito for beta-oxidation Overnight fast in infants normally requires gluconeogenesis to maintain [glu] – Requires energy from FA oxidation ...
Nutrition and Athletic Performance
... and essential fatty acids, is important in the diets of athletes. ...
... and essential fatty acids, is important in the diets of athletes. ...
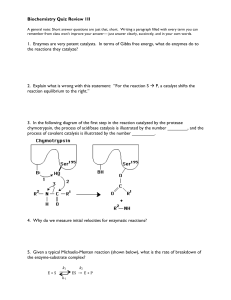
C483 Final Exam Study Guide The final will be held in Morrison 007
... A. A titration curve for lysine, with a side chain pKa of 10.5. B. A DNA melting curve for a poly(AT) sequence and a poly(GC) sequence (indicate which is poly(AT) and which is poly(GC)) C. A plot of initial velocity versus substrate concentration for a Michaelis-Menton enzyme. D. The same plot as (B ...
... A. A titration curve for lysine, with a side chain pKa of 10.5. B. A DNA melting curve for a poly(AT) sequence and a poly(GC) sequence (indicate which is poly(AT) and which is poly(GC)) C. A plot of initial velocity versus substrate concentration for a Michaelis-Menton enzyme. D. The same plot as (B ...
Structure,Classification Of Carbohydrate
... All the monomers are the same in the homo- polymer, synthesized from beta glucose units. E.g. Cellulose. ...
... All the monomers are the same in the homo- polymer, synthesized from beta glucose units. E.g. Cellulose. ...
Lecture: Biochemistry I. Inorganic Compounds A. Water (H2O)
... a. starch - long chains of glucose in plants b. glycogen - long chains of glucose in animals i. stored in liver and muscle cells ...
... a. starch - long chains of glucose in plants b. glycogen - long chains of glucose in animals i. stored in liver and muscle cells ...
Document
... a. partially/ entirely hydrophobic organic molecules composed of hydrocarbons (-CH2-)n b. include fats, phospholipids, and sterols c. Fats = a 3-carbon glycerol molecule with 3 long fatty acid chains attached i. Fatty acids with no double bonds are “saturated” & are solids at room temp. ii. Fats wit ...
... a. partially/ entirely hydrophobic organic molecules composed of hydrocarbons (-CH2-)n b. include fats, phospholipids, and sterols c. Fats = a 3-carbon glycerol molecule with 3 long fatty acid chains attached i. Fatty acids with no double bonds are “saturated” & are solids at room temp. ii. Fats wit ...
Fatty Acid Metabolism
... Clinical significances of impairment of β-oxidation: 1. acquired and genetic deficiency of carnitine substance. 2.genetic deficiency of one or more of enzymes of pathway. Hypoglycemia, muscle weakness , cardiomyopathway, coma and death ...
... Clinical significances of impairment of β-oxidation: 1. acquired and genetic deficiency of carnitine substance. 2.genetic deficiency of one or more of enzymes of pathway. Hypoglycemia, muscle weakness , cardiomyopathway, coma and death ...
Organic Molecules: The Molecules of Life
... Includes starch, glycogen and cellulose They are long chains of glucose. Starch Storage form of carbs in plants. A potato is a special root that the plant will draw energy from when needed. Doesn’t have many side branches. Is broken down during digestion into glucose which we burn to make ATP. Glyco ...
... Includes starch, glycogen and cellulose They are long chains of glucose. Starch Storage form of carbs in plants. A potato is a special root that the plant will draw energy from when needed. Doesn’t have many side branches. Is broken down during digestion into glucose which we burn to make ATP. Glyco ...
Biochemistry Review
... 2. What type of compound does not contain carbon atoms? Inorganic 3. What are the reasons carbon is unique among elements? Covalent Bonding; Form Wide Variety of Simple and Complex Organic Compounds 4. What type of structures can carbon atoms form? Ring, Straight and Branched Chains, Single, Double, ...
... 2. What type of compound does not contain carbon atoms? Inorganic 3. What are the reasons carbon is unique among elements? Covalent Bonding; Form Wide Variety of Simple and Complex Organic Compounds 4. What type of structures can carbon atoms form? Ring, Straight and Branched Chains, Single, Double, ...
Lecture 14: Alternative Pathways in Cell respiration
... cycle can be converted to stored carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Pathway for synthesis of RNA, DNA ...
... cycle can be converted to stored carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Pathway for synthesis of RNA, DNA ...
Endocrinology – glucose homeostasis
... by indirectly inhibiting gluconeogenesis via inhibition of fatty acid mobilization from adipose tissue. Second, it increases the rate of uptake of glucose into all insulin-sensitive tissues, notably muscle, adipose tissue and the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (the “satiety centre”). It do ...
... by indirectly inhibiting gluconeogenesis via inhibition of fatty acid mobilization from adipose tissue. Second, it increases the rate of uptake of glucose into all insulin-sensitive tissues, notably muscle, adipose tissue and the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus (the “satiety centre”). It do ...
Exam 2 - student.ahc.umn.edu
... d) it is driven by the hydrolysis of ATP 16) Which of the following statements is not true for the conversion of glyceraldehyde 3phosphate to 1, 3-biophosphoglycerate? a) it requires ATP b) it is an oxidative process c) it generates a high-energy compound d) it is catalyzed by a dehydrogenase * 17) ...
... d) it is driven by the hydrolysis of ATP 16) Which of the following statements is not true for the conversion of glyceraldehyde 3phosphate to 1, 3-biophosphoglycerate? a) it requires ATP b) it is an oxidative process c) it generates a high-energy compound d) it is catalyzed by a dehydrogenase * 17) ...
PL05_Glucdisp
... – Branching enzyme needed to introduce a16 branch points – Transfers a segment from one chain to another – Limit to the size of glycogen molecule • Branches become too crowded, even if they become progressively shorter • Glycogen synthase may need to interact with glycogenin to be fully active ...
... – Branching enzyme needed to introduce a16 branch points – Transfers a segment from one chain to another – Limit to the size of glycogen molecule • Branches become too crowded, even if they become progressively shorter • Glycogen synthase may need to interact with glycogenin to be fully active ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.