Metabolism of lipids
... Summary of the flow of electrons and protons through the four complexes of the respiratory chain. Electrons reach CoQ via Complexes I and II. CoQH2 serves as a mobile carrier of electrons and protons. It transfers electrons to Complex III, which transfers them to another mobile connecting link, cyto ...
... Summary of the flow of electrons and protons through the four complexes of the respiratory chain. Electrons reach CoQ via Complexes I and II. CoQH2 serves as a mobile carrier of electrons and protons. It transfers electrons to Complex III, which transfers them to another mobile connecting link, cyto ...
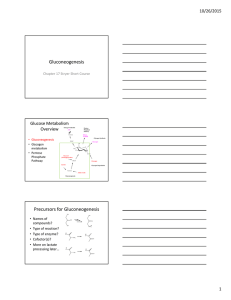
Gluconeogenesis Precursors for Gluconeogenesis
... – Costs ATP to make driving force for next reaction – First step in biosynthesis of glucose and many other molecules • Related to which amino acid? ...
... – Costs ATP to make driving force for next reaction – First step in biosynthesis of glucose and many other molecules • Related to which amino acid? ...
Metabolism - CSU, Chico
... So a typical fatty acid spins the TCA cycle 9 times No wonder fats have so much energy associated with them glucose = 36 – 38 ATPs 16 carbon FA = 129 ATPs Adipose fat HDL cells cytosol mitochondria hormone sensitive lipase carnitine ...
... So a typical fatty acid spins the TCA cycle 9 times No wonder fats have so much energy associated with them glucose = 36 – 38 ATPs 16 carbon FA = 129 ATPs Adipose fat HDL cells cytosol mitochondria hormone sensitive lipase carnitine ...
Chapter 6: Biochemistry
... A. contain many carbon atoms B. they are polymers (long chains of small molecules) C. condensation reactions make monomers into polymers ...
... A. contain many carbon atoms B. they are polymers (long chains of small molecules) C. condensation reactions make monomers into polymers ...
Chapter 26
... removed from the arteries • Desirable to maintain a low LDL concentration – signifies high rate of cholesterol deposition in arteries – smoking, saturated fats, coffee and stress LDLs ...
... removed from the arteries • Desirable to maintain a low LDL concentration – signifies high rate of cholesterol deposition in arteries – smoking, saturated fats, coffee and stress LDLs ...
Chapter 26
... cholesterol is being removed from the arteries • Desirable to maintain a low LDL concentration – signifies high rate of cholesterol deposition in arteries – smoking, saturated fats, coffee and stress LDLs ...
... cholesterol is being removed from the arteries • Desirable to maintain a low LDL concentration – signifies high rate of cholesterol deposition in arteries – smoking, saturated fats, coffee and stress LDLs ...
Q26to35
... B. Glucokinase is inhibited by a build up of glucose 6-phosphate only HK is inhibited by G6P ...
... B. Glucokinase is inhibited by a build up of glucose 6-phosphate only HK is inhibited by G6P ...
Chapter 26
... cholesterol is being removed from the arteries • Desirable to maintain a low LDL concentration – signifies high rate of cholesterol deposition in arteries – smoking, saturated fats, coffee and stress LDLs ...
... cholesterol is being removed from the arteries • Desirable to maintain a low LDL concentration – signifies high rate of cholesterol deposition in arteries – smoking, saturated fats, coffee and stress LDLs ...
In Anaerobic Respiration glucose is broken down
... Phosphofructokinase is high concentrations ATP inhibited by The rate of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle are synchronised by If citrate consumption increases ...
... Phosphofructokinase is high concentrations ATP inhibited by The rate of glycolysis and the citric acid cycle are synchronised by If citrate consumption increases ...
Nutrition and Fitness: Fueling Your Body!
... When athletic events last more than 60 minutes, athletes benefit by eating carbohydrates during exercise. The extra fuel helps them stay competitive longer. Slightly sweetened beverages that contain less than 24 grams of carbohydrate per one cup (8oz) may be used. Following training or competing, it ...
... When athletic events last more than 60 minutes, athletes benefit by eating carbohydrates during exercise. The extra fuel helps them stay competitive longer. Slightly sweetened beverages that contain less than 24 grams of carbohydrate per one cup (8oz) may be used. Following training or competing, it ...
Fatigue and the Recovery Process
... muscles glycogen to glucose Overall the glycogen gets turned into Glucose These stores only last 2 hours so once these are used up the body becomes fatigued ...
... muscles glycogen to glucose Overall the glycogen gets turned into Glucose These stores only last 2 hours so once these are used up the body becomes fatigued ...
WEEK SEVENTY-THREE :: What Are The Best Foods For Cutting? In the
... How does one determine how many calories they should consume when cutting? For those who had a controlled diet before cutting, the number of calories consumed is simply going to be around 300 to 500 calories per day fewer than what it was before. This would be for a goal of losing 1 or 2 pounds per ...
... How does one determine how many calories they should consume when cutting? For those who had a controlled diet before cutting, the number of calories consumed is simply going to be around 300 to 500 calories per day fewer than what it was before. This would be for a goal of losing 1 or 2 pounds per ...
Theory21_30
... Use the following information to answer Questions 28-29 The following enzymes (A-E) are all involved in the synthesis of fatty acids from glucose: ...
... Use the following information to answer Questions 28-29 The following enzymes (A-E) are all involved in the synthesis of fatty acids from glucose: ...
Lecture 6
... in small supply in skeletal muscle • Found in large amts in liver and kidneys • Pyruvate kinase (last step of glycolysis): – virtually irreversible in skeletal muscle – In liver, can be inhibited by cAMP and ...
... in small supply in skeletal muscle • Found in large amts in liver and kidneys • Pyruvate kinase (last step of glycolysis): – virtually irreversible in skeletal muscle – In liver, can be inhibited by cAMP and ...
Macromolecules - Uplift Education
... Monosaccharides Glucose – used to transport energy through the blood to all cells in the body ...
... Monosaccharides Glucose – used to transport energy through the blood to all cells in the body ...
Gluconeogenesis
... tests and medulla require glucose from blood as their major fuel source - Important precursors of the glucose: Lactate, pyruvate, glycerol and back bone of certain amino acids - Fasting requires all the glucose to be synthesized from these noncarbohydrate precursors. ...
... tests and medulla require glucose from blood as their major fuel source - Important precursors of the glucose: Lactate, pyruvate, glycerol and back bone of certain amino acids - Fasting requires all the glucose to be synthesized from these noncarbohydrate precursors. ...
3.2 Carbohydrates, lipids annd proteins
... 3.2.5: Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides. ...
... 3.2.5: Outline the role of condensation and hydrolysis in the relationships between monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides; between fatty acids, glycerol and triglycerides; and between amino acids and polypeptides. ...
AP bio summer answers
... B. portions of eukaryotic DNA which cannot be transcribed have been_____ C. enzyme that catalyzes the elongation of repetitive DNA at the end of a chromosome; often this enzyme is highly active in cancerous cells D. gene that can trigger cancerous growth E. hormone (protein) that regulates the cell ...
... B. portions of eukaryotic DNA which cannot be transcribed have been_____ C. enzyme that catalyzes the elongation of repetitive DNA at the end of a chromosome; often this enzyme is highly active in cancerous cells D. gene that can trigger cancerous growth E. hormone (protein) that regulates the cell ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.