1) Where does glycolysis occur in the cell
... 8) All of the following processes occur within mitochondria except: a) the splitting of glucose b) the formation of citric acid c) the catabolism of citric acid to produce NADH, CO2, AND H+ d) the transfer of electrons form NADH to the electron transport chain e) the reduction of oxygen to form wate ...
... 8) All of the following processes occur within mitochondria except: a) the splitting of glucose b) the formation of citric acid c) the catabolism of citric acid to produce NADH, CO2, AND H+ d) the transfer of electrons form NADH to the electron transport chain e) the reduction of oxygen to form wate ...
glucose
... •The use of blood glucose and muscle glycogen as fuels for muscular activity is greatly enhanced by the secretion of epinephrine, which stimulates the formation of blood glucose from glycogen in the liver and the breakdown of glycogen in muscle tissue. •Skeletal muscle does not contain glucose-6-pho ...
... •The use of blood glucose and muscle glycogen as fuels for muscular activity is greatly enhanced by the secretion of epinephrine, which stimulates the formation of blood glucose from glycogen in the liver and the breakdown of glycogen in muscle tissue. •Skeletal muscle does not contain glucose-6-pho ...
blood sugar - The Wellness Protocol
... Carbohydrate energy reserves are used up first 3 Days on the Pancreatic Protocol, carbohydrate reserves are depleted (glycogenolysis) ...
... Carbohydrate energy reserves are used up first 3 Days on the Pancreatic Protocol, carbohydrate reserves are depleted (glycogenolysis) ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 11. The internal reference electrode in a combination electrode is _____________. 12. The torsion angle between Cα and C is denoted as__________________. 13. Pyruvate is converted to acetyl-coA by _____________ enzyme complex. 14. The charge on a charged amino acid becomes neutral at _______________ ...
... 11. The internal reference electrode in a combination electrode is _____________. 12. The torsion angle between Cα and C is denoted as__________________. 13. Pyruvate is converted to acetyl-coA by _____________ enzyme complex. 14. The charge on a charged amino acid becomes neutral at _______________ ...
word
... Pyruvate as critical point – availability of oxygen determine next steps; lactic acidosis Shuttle for NADH into mitochondrion Glycolysis generates precursors for other paths Ch 23 oxidation of fatty acids, ketones Oxidation of long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) – from absorption or degradation from adipo ...
... Pyruvate as critical point – availability of oxygen determine next steps; lactic acidosis Shuttle for NADH into mitochondrion Glycolysis generates precursors for other paths Ch 23 oxidation of fatty acids, ketones Oxidation of long-chain fatty acids (LCFA) – from absorption or degradation from adipo ...
8. Diet revision PDF File
... Anorexia- this is an eating disorder in which somebody will reduce the amount of food they eat. This can be caused by pressure to lose weight. This will cause tiredness and will prevent them being able to participate fully in sport as they are unable to create enough energy. Obesity- this is an eati ...
... Anorexia- this is an eating disorder in which somebody will reduce the amount of food they eat. This can be caused by pressure to lose weight. This will cause tiredness and will prevent them being able to participate fully in sport as they are unable to create enough energy. Obesity- this is an eati ...
The Organic Molecules of Life
... together into longer chain The organelle in cells that acts like a power plant, producing energy for the cell; cellular respiration occurs here. common storage form of glucose in plants; composed of long chains made of hundreds of glucose molecules carboncontaining compounds synthesized by cells (2 ...
... together into longer chain The organelle in cells that acts like a power plant, producing energy for the cell; cellular respiration occurs here. common storage form of glucose in plants; composed of long chains made of hundreds of glucose molecules carboncontaining compounds synthesized by cells (2 ...
Regulation of Metabolism
... In the case of glucagon, and epinephrine, most cells with receptors respond to hormonal activation by phosphorylating (activating) target enzymes. In the case of glucagon, the enzymes are involved in fat and protein catabolism, and gluconeogenesis. Epinephrine enhances these effects but also targe ...
... In the case of glucagon, and epinephrine, most cells with receptors respond to hormonal activation by phosphorylating (activating) target enzymes. In the case of glucagon, the enzymes are involved in fat and protein catabolism, and gluconeogenesis. Epinephrine enhances these effects but also targe ...
Metabolism 2010edit
... • Regulation & coordination of production – final product is inhibitor of earlier step • allosteric inhibitor of earlier enzyme – no unnecessary accumulation of product – production is self-limiting ...
... • Regulation & coordination of production – final product is inhibitor of earlier step • allosteric inhibitor of earlier enzyme – no unnecessary accumulation of product – production is self-limiting ...
9.6 Respiration 4 (Control and other metabolites)
... • Regulation & coordination of production – final product is inhibitor of earlier step • allosteric inhibitor of earlier enzyme – no unnecessary accumulation of product – production is self-limiting ...
... • Regulation & coordination of production – final product is inhibitor of earlier step • allosteric inhibitor of earlier enzyme – no unnecessary accumulation of product – production is self-limiting ...
Biological Molecules - Parkland Secondary School
... Fats and oils OR triglycerides OR neutral fats o All formed from one glycerol molecule reacted with three fatty acid molecules through a condensation synthesis reaction. o Fatty acids come in two varieties: Saturated: the carbon chain is completely surrounded by hydrogen; only single covalent bond ...
... Fats and oils OR triglycerides OR neutral fats o All formed from one glycerol molecule reacted with three fatty acid molecules through a condensation synthesis reaction. o Fatty acids come in two varieties: Saturated: the carbon chain is completely surrounded by hydrogen; only single covalent bond ...
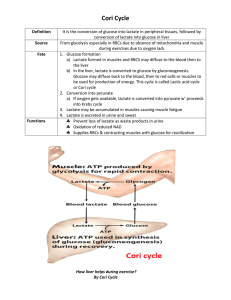
Cori Cycle - COFFEE BREAK CORNER
... It is the conversion of glucose into lactate in peripheral tissues, followed by conversion of lactate into glucose in liver From glycolysis especially in RBCs due to absence of mitochondria and muscle ...
... It is the conversion of glucose into lactate in peripheral tissues, followed by conversion of lactate into glucose in liver From glycolysis especially in RBCs due to absence of mitochondria and muscle ...
Study Guide for Chapter 5 in Fox
... Define: metabolism, catabolism, & anabolism Glucose is catabolized in 3 stages. Name these. What does “glycolysis” mean? Where in the cell does this process occur? What happens to glucose immediately as it enters a cell? Glucose could be stored in a cell as a molecule of ____________ In what 2 tissu ...
... Define: metabolism, catabolism, & anabolism Glucose is catabolized in 3 stages. Name these. What does “glycolysis” mean? Where in the cell does this process occur? What happens to glucose immediately as it enters a cell? Glucose could be stored in a cell as a molecule of ____________ In what 2 tissu ...
Sample
... 8. A food that contains an imbalanced protein means a. It is not nutritionally good to eat b.It will not yield and adequate protein-to-calorie ratio c. It does not contain enough of one or more essential amino acids d.It is non-digestible e. Its amino acid chains are branched asymmetrically ...
... 8. A food that contains an imbalanced protein means a. It is not nutritionally good to eat b.It will not yield and adequate protein-to-calorie ratio c. It does not contain enough of one or more essential amino acids d.It is non-digestible e. Its amino acid chains are branched asymmetrically ...
Glucose
... Fats are a more compact fuel than starch. Fat contains twice the energy-rich (C-H) bonds as glucose Fat stores twice as much energy as glucose Fat produces twice as many calories when burned Unfortunately, you need to put twice as much energy to burn off a pound of excess fat than you do of glycogen ...
... Fats are a more compact fuel than starch. Fat contains twice the energy-rich (C-H) bonds as glucose Fat stores twice as much energy as glucose Fat produces twice as many calories when burned Unfortunately, you need to put twice as much energy to burn off a pound of excess fat than you do of glycogen ...
Glycolysis II
... • Beta oxidation takes place inside mitochondria – so without mitochondria a tissue cannot metabolize fat for energy. ...
... • Beta oxidation takes place inside mitochondria – so without mitochondria a tissue cannot metabolize fat for energy. ...
Eating for Gestational Diabetes: Indigenous
... biscuits and sweet drinks have too much extra sugar. A tiny bit is OK, like a small teaspoon of sugar. Foods and drinks marked ‘diet’ or ‘low joule’ are low in sugar and don’t affect your blood glucose levels. ...
... biscuits and sweet drinks have too much extra sugar. A tiny bit is OK, like a small teaspoon of sugar. Foods and drinks marked ‘diet’ or ‘low joule’ are low in sugar and don’t affect your blood glucose levels. ...
March 1972 EFFECTS OF VOLATILE FA`M`Y ACIDS, KETONE
... the plasma concentration in ketotic cows, suggests an important mechanism of feedback control, in which a product derived from excessive breakdown of fatty acids participates in the regulation of fatty acid mobilization. The lack of an effect of glucose (table 1) on the release of fatty acids from b ...
... the plasma concentration in ketotic cows, suggests an important mechanism of feedback control, in which a product derived from excessive breakdown of fatty acids participates in the regulation of fatty acid mobilization. The lack of an effect of glucose (table 1) on the release of fatty acids from b ...
The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle, tricarboxylic acid cycle)
... The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions in mitochondria that oxidize acetyl residues (as acetyl-CoA) and reduce coenzymes that upon reoxidation are linked to the formation of ATP. The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the aerobic oxidation of carbohydrate, lipid, and protein b ...
... The citric acid cycle is a series of reactions in mitochondria that oxidize acetyl residues (as acetyl-CoA) and reduce coenzymes that upon reoxidation are linked to the formation of ATP. The citric acid cycle is the final common pathway for the aerobic oxidation of carbohydrate, lipid, and protein b ...
biochem study guide
... 3. Describe the structure of a typical monosaccharide such as glucose. Write out a condensation reaction between two glucose molecules, and explain hydrolysis. 4. Explain the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fatty acid. Explain how three fatty acids can react with glycerol to make a ...
... 3. Describe the structure of a typical monosaccharide such as glucose. Write out a condensation reaction between two glucose molecules, and explain hydrolysis. 4. Explain the difference between a saturated and an unsaturated fatty acid. Explain how three fatty acids can react with glycerol to make a ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.