body temperature Mechanical- moves muscles Electrical
... Fatty acids are broken into 2-carbon units which combine with CoA to make acetyl CoA. Fatty Acids cannot be used to make glucose Amino Acids Most amino acids can be converted to glucose Amino acids must be deaminated first (remove the nitrogen amino group). Most can be converted to pyruvate (used fo ...
... Fatty acids are broken into 2-carbon units which combine with CoA to make acetyl CoA. Fatty Acids cannot be used to make glucose Amino Acids Most amino acids can be converted to glucose Amino acids must be deaminated first (remove the nitrogen amino group). Most can be converted to pyruvate (used fo ...
Chapter 3: Biochemistry
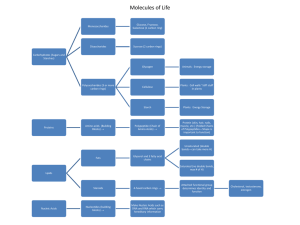
... complex molecules 6. ATP (adenosine triphosphate): compound with a large amount of energy a) covalent bond breaks and energy is released b) energy is used by the cell to drive chemical reactions II. Molecules of Life A. Carbohydrates 1. Function: 2. Monomer: Monosaccharides: a) b) ...
... complex molecules 6. ATP (adenosine triphosphate): compound with a large amount of energy a) covalent bond breaks and energy is released b) energy is used by the cell to drive chemical reactions II. Molecules of Life A. Carbohydrates 1. Function: 2. Monomer: Monosaccharides: a) b) ...
Outline06 Metabolism - Napa Valley College
... - fatty acids are synthesized from 2C units of acetyl CoA - fatty acids are combined with glycerol to form triglycerides and phospholipids 3. Tissue Utilization of Fatty Acids - triglycerides are stored mostly in adipose tissue - lipids are transported in the blood by lipoproteins: HDL, LDL - liver, ...
... - fatty acids are synthesized from 2C units of acetyl CoA - fatty acids are combined with glycerol to form triglycerides and phospholipids 3. Tissue Utilization of Fatty Acids - triglycerides are stored mostly in adipose tissue - lipids are transported in the blood by lipoproteins: HDL, LDL - liver, ...
sports-nutrition
... same as sports drinks but without the water), which are easily digested. Many gels come with added electrolytes that, as with sports drinks, help maintain fluid balance. Some gels also have added extras such as ginseng and other herbs, amino acids, vitamins, and Co-enzyme-Q10 (a nonessential substan ...
... same as sports drinks but without the water), which are easily digested. Many gels come with added electrolytes that, as with sports drinks, help maintain fluid balance. Some gels also have added extras such as ginseng and other herbs, amino acids, vitamins, and Co-enzyme-Q10 (a nonessential substan ...
Kevin Ahern's Biochemistry Course (BB 350) at Oregon State University
... 1. Oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids requires two additional enzymes beyond those of beta oxidation. The two enzymes are enoyl-CoA isomerase and 2,4 dienoyl-CoA reductase (also known as Dina). The first enzyme catalyzes conversion of cis bonds between carbons 3 and 4 to trans bonds between carbon ...
... 1. Oxidation of unsaturated fatty acids requires two additional enzymes beyond those of beta oxidation. The two enzymes are enoyl-CoA isomerase and 2,4 dienoyl-CoA reductase (also known as Dina). The first enzyme catalyzes conversion of cis bonds between carbons 3 and 4 to trans bonds between carbon ...
STARVE-FEED CYCLE 1) WELL-FED STATE (food intake
... synthesis of carnitine → blood → especially to the muscle and the heart (β-oxidation) ...
... synthesis of carnitine → blood → especially to the muscle and the heart (β-oxidation) ...
Carbohydrates and diabetes - Sheffield Teaching Hospital
... glucose. This glucose is then absorbed into our blood stream and causes blood glucose levels to rise. Foods high in protein and fat have less of an immediate effect on your blood glucose levels after a meal. This is because these foods contain very little or no carbohydrate. Healthy tip Taking care ...
... glucose. This glucose is then absorbed into our blood stream and causes blood glucose levels to rise. Foods high in protein and fat have less of an immediate effect on your blood glucose levels after a meal. This is because these foods contain very little or no carbohydrate. Healthy tip Taking care ...
Final Practice Exam
... b. Number of double bonds c. Position of first saturated bond d. Size of adjacent fatty acids on the triglyceride molecule 29. What is the main source of B12? a. Plant products b. Animal Products c. Both d. Neither 30. What is the AMDR for carbohydrates? a. 10-35% b. 45-65% c. 90-90% d. 10-45% 31. W ...
... b. Number of double bonds c. Position of first saturated bond d. Size of adjacent fatty acids on the triglyceride molecule 29. What is the main source of B12? a. Plant products b. Animal Products c. Both d. Neither 30. What is the AMDR for carbohydrates? a. 10-35% b. 45-65% c. 90-90% d. 10-45% 31. W ...
Title - Iowa State University
... b. Number of double bonds c. Position of first saturated bond d. Size of adjacent fatty acids on the triglyceride molecule 29. What is the main source of B12? a. Plant products b. Animal Products c. Both d. Neither 30. What is the AMDR for carbohydrates? a. 10-35% b. 45-65% c. 90-90% d. 10-45% 31. W ...
... b. Number of double bonds c. Position of first saturated bond d. Size of adjacent fatty acids on the triglyceride molecule 29. What is the main source of B12? a. Plant products b. Animal Products c. Both d. Neither 30. What is the AMDR for carbohydrates? a. 10-35% b. 45-65% c. 90-90% d. 10-45% 31. W ...
Insulin is a relatively small protein that in its final form consists of two
... 1. Insulin is a relatively small protein that in its final form consists of two polypeptide chains. The smaller of these two polypeptides consists of 21 amino acids and the larger consists of 30 amino acids. This is how insulin forms: In the beta cells within islets of Langerhans of the pancreas, in ...
... 1. Insulin is a relatively small protein that in its final form consists of two polypeptide chains. The smaller of these two polypeptides consists of 21 amino acids and the larger consists of 30 amino acids. This is how insulin forms: In the beta cells within islets of Langerhans of the pancreas, in ...
Fatty Acid Spiral
... Our diets must contain a reasonable ratio of the essential amino acids in order for our bodies to maintain health. – Meat, eggs, soy and milk contain the essential amino acids in a similar ratio to that needed by humans. – Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and grains tend to be high in some and low i ...
... Our diets must contain a reasonable ratio of the essential amino acids in order for our bodies to maintain health. – Meat, eggs, soy and milk contain the essential amino acids in a similar ratio to that needed by humans. – Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and grains tend to be high in some and low i ...
Document
... Ketogenic amino acids are those whose carbon skeletons can enter the Krebs cycle for energy production, or can form ketone bodies via ketogenesis for energy storage. Glucogenic amino acids are those whose carbon skeletons can enter the Krebs cycle for energy production, or can form glucose via gluco ...
... Ketogenic amino acids are those whose carbon skeletons can enter the Krebs cycle for energy production, or can form ketone bodies via ketogenesis for energy storage. Glucogenic amino acids are those whose carbon skeletons can enter the Krebs cycle for energy production, or can form glucose via gluco ...
Energy Metabolism - 35-206-202
... citric acid cycle going- fat metabolism cannot function normally. “Fat burns in the flame of carbohydrate.” ...
... citric acid cycle going- fat metabolism cannot function normally. “Fat burns in the flame of carbohydrate.” ...
LB Fat metabolism A
... liver: via the enzyme Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) Thus, unlike carbohydrates and protein, most lipids do not use the enterohepatic circulatory system. This allows lipids to be cleared by the whole body and avoids overwhelming the liver with lipid. ...
... liver: via the enzyme Lipoprotein Lipase (LPL) Thus, unlike carbohydrates and protein, most lipids do not use the enterohepatic circulatory system. This allows lipids to be cleared by the whole body and avoids overwhelming the liver with lipid. ...
Pancreatic enzymes basics
... Similar to secretin and gastrin GIP and VIP Synthesis is from a preprohormone as well. Prohormone is split releasing it to the blood Very little in blood – short ½ life ½ removed in first pass through the liver. ...
... Similar to secretin and gastrin GIP and VIP Synthesis is from a preprohormone as well. Prohormone is split releasing it to the blood Very little in blood – short ½ life ½ removed in first pass through the liver. ...
Sample exam 1
... 2. Erucic acid is 22:1, Δ13. Which one of the following choices correctly names the position(s) of the double bond(s) using the ω numbering system? a. ω-6 b. ω-9 c. ω-12 d. ω-6,9 e. ω-6,9,12 3. Which one of the following choices is not used to produce acetyl CoA in humans? a. a 15:0 fatty acid. b. P ...
... 2. Erucic acid is 22:1, Δ13. Which one of the following choices correctly names the position(s) of the double bond(s) using the ω numbering system? a. ω-6 b. ω-9 c. ω-12 d. ω-6,9 e. ω-6,9,12 3. Which one of the following choices is not used to produce acetyl CoA in humans? a. a 15:0 fatty acid. b. P ...
4f03125
... Short answer (40 points total) Provide the correct answer to each of the following questions in the space provided or in the appropriate blank. For three bonus points, please write the straight-chain structure of any monosaccharide we discussed on back of the first page of this test. Partial credit ...
... Short answer (40 points total) Provide the correct answer to each of the following questions in the space provided or in the appropriate blank. For three bonus points, please write the straight-chain structure of any monosaccharide we discussed on back of the first page of this test. Partial credit ...
All 3 fates of pyruvate from glycolysis provide for the regeneration of
... Separate pathway energy needs. Separate control of each pathway. ...
... Separate pathway energy needs. Separate control of each pathway. ...
NME2.28: fat and carbohydrate metabolism in the
... Non-hormonal control of fatty acid synthesis is through: o Citrate – activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase promoting fatty acid synthesis o Fatty acids – inhibit PDH and acetyl-CoA carboxylase restricting fatty acid synthesis o NADH – inhibits PDH restricting fatty acid synthesis ...
... Non-hormonal control of fatty acid synthesis is through: o Citrate – activates acetyl-CoA carboxylase promoting fatty acid synthesis o Fatty acids – inhibit PDH and acetyl-CoA carboxylase restricting fatty acid synthesis o NADH – inhibits PDH restricting fatty acid synthesis ...
2-A Chemical Compounds of Life Organic Compounds
... a) Provide structure, transport substances, act as chemical messengers, control chemical reactions, and control cell growth b) Built from amino acids • Each has a carboxyl group (COOH) & amino group (NH2) • variable group makes one a.a. different from another c) Polypeptide: made from many a.a. ...
... a) Provide structure, transport substances, act as chemical messengers, control chemical reactions, and control cell growth b) Built from amino acids • Each has a carboxyl group (COOH) & amino group (NH2) • variable group makes one a.a. different from another c) Polypeptide: made from many a.a. ...
Fatty Acid Oxidation and Ketone Bodies OXIDATION OF FATTY
... Peroxisomes oxidize very long chain fatty acids Very long chain acyl-CoA synthetase facilitates the oxidation of very long chain fatty acids (e.g., C20, C22). These enzymes are induced by high-fat diets and by hypolipidemic drugs such as Clofibrate. ß-oxidation takes place and ends at octanoyl-CoA. ...
... Peroxisomes oxidize very long chain fatty acids Very long chain acyl-CoA synthetase facilitates the oxidation of very long chain fatty acids (e.g., C20, C22). These enzymes are induced by high-fat diets and by hypolipidemic drugs such as Clofibrate. ß-oxidation takes place and ends at octanoyl-CoA. ...
Energy
... catabolizing ketone bodies instead of glucose. By the 40th day of starvation, metabolism has stabilized at the use of about 25 g of protein and 180 g of fat each day. So long as adequate water is available, an average person can survive in this state for several months; those with more fat can survi ...
... catabolizing ketone bodies instead of glucose. By the 40th day of starvation, metabolism has stabilized at the use of about 25 g of protein and 180 g of fat each day. So long as adequate water is available, an average person can survive in this state for several months; those with more fat can survi ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.