Powerpoint
... straight, solid @ room temp., “fat” 2. Unsaturated – at least one C=C bond, structurally bent, liquid at room temp., “oil” 3. Polyunsaturated – many C=C bonds so few H’s (e.g veggie oils) ...
... straight, solid @ room temp., “fat” 2. Unsaturated – at least one C=C bond, structurally bent, liquid at room temp., “oil” 3. Polyunsaturated – many C=C bonds so few H’s (e.g veggie oils) ...
Metabolic Adaptation - Washington State University
... Mammalian brown fat: Sometimes, a futile cycle is OK • Located around heart and around thorax and neck of infant humans and true hibernators. • Brown color is due to abundant mitochondria – in contrast to ordinary adipose tissue which is white fat. • Epinephrine released in cold stress or spring re ...
... Mammalian brown fat: Sometimes, a futile cycle is OK • Located around heart and around thorax and neck of infant humans and true hibernators. • Brown color is due to abundant mitochondria – in contrast to ordinary adipose tissue which is white fat. • Epinephrine released in cold stress or spring re ...
Nutrition Power Point
... Micronutrients are nutrients required by humans in small amounts to orchestrate a wide variety of physiological functions but are not made by the organism ...
... Micronutrients are nutrients required by humans in small amounts to orchestrate a wide variety of physiological functions but are not made by the organism ...
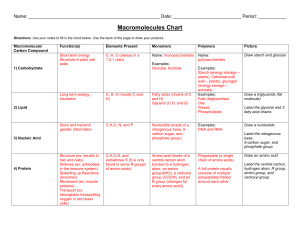
chapter 5 large biological molecules
... monomers, ex. amylose. Angles make them helical. o Glycogen – storage form for animals, more branched. Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen in liver and muscle cells. In humans glycogen bank can be depleted within one day. o Cellulose – structural part of plant cell walls. Has beta glucose co ...
... monomers, ex. amylose. Angles make them helical. o Glycogen – storage form for animals, more branched. Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen in liver and muscle cells. In humans glycogen bank can be depleted within one day. o Cellulose – structural part of plant cell walls. Has beta glucose co ...
Triacylglycerol Metabolism Gone Bad: A major cause of disease
... – For each two carbons removed, 1 FADH2 and 1 NADH + H+ are produced – For palmitoyl-CoA, the reaction is: ...
... – For each two carbons removed, 1 FADH2 and 1 NADH + H+ are produced – For palmitoyl-CoA, the reaction is: ...
Slide 1
... 1- They are soluble in aqueous solution, so do not need to be incorporated into lipoproteins or carried by albumin as do other lipids 2- They are synthesized in the liver when amount of acetyl CoA exceeds oxidative capacity of liver 3- They are important sources of energy during prolonged periods of ...
... 1- They are soluble in aqueous solution, so do not need to be incorporated into lipoproteins or carried by albumin as do other lipids 2- They are synthesized in the liver when amount of acetyl CoA exceeds oxidative capacity of liver 3- They are important sources of energy during prolonged periods of ...
Lipids Metabolism - GIT
... 1- They are soluble in aqueous solution, so do not need to be incorporated into lipoproteins or carried by albumin as do other lipids 2- They are synthesized in the liver when amount of acetyl CoA exceeds oxidative capacity of liver 3- They are important sources of energy during prolonged periods of ...
... 1- They are soluble in aqueous solution, so do not need to be incorporated into lipoproteins or carried by albumin as do other lipids 2- They are synthesized in the liver when amount of acetyl CoA exceeds oxidative capacity of liver 3- They are important sources of energy during prolonged periods of ...
Unit 3: Chemistry of Life
... composed of three molecules of fatty acids and joined to one molecule of glycerol Solid at room temp fats; Liquid at room temp oils ...
... composed of three molecules of fatty acids and joined to one molecule of glycerol Solid at room temp fats; Liquid at room temp oils ...
Chapter 34 HEIN
... • After the initial contraction, the muscle cells look for other energy sources. • Muscle glycogen is the next available source. • This polymer breaks down to glucose, which is oxidized to replenish the ATP supply. • Because glucose oxidation is a complex process, muscle contraction must proceed at ...
... • After the initial contraction, the muscle cells look for other energy sources. • Muscle glycogen is the next available source. • This polymer breaks down to glucose, which is oxidized to replenish the ATP supply. • Because glucose oxidation is a complex process, muscle contraction must proceed at ...
Perspectives in Nutrition, 8th Edition
... For cells that are not capable of aerobic respiration (lack mitochondria; e.g., RBCs) or need to produce energy in the absence of oxygen (e.g., during intense ...
... For cells that are not capable of aerobic respiration (lack mitochondria; e.g., RBCs) or need to produce energy in the absence of oxygen (e.g., during intense ...
No Slide Title - Orange Coast College
... Degradation products of most fuels Oxidized to CO2 and H2O in citric acid ...
... Degradation products of most fuels Oxidized to CO2 and H2O in citric acid ...
Topic D.1 Human Nutrition
... E.g. vitamin K – in adults, produced by metabolism of symbiotic bacteria in intestines; in babies, have not built up colonies of such bacteria yet; in ppl with digestive disorders, colonies may be disrupted ...
... E.g. vitamin K – in adults, produced by metabolism of symbiotic bacteria in intestines; in babies, have not built up colonies of such bacteria yet; in ppl with digestive disorders, colonies may be disrupted ...
Carbohydrates - Rainbow Lunches
... someone say that they “need to cut down on their carb intake” or they are on a “low carb diet”. Carbohydrates are converted into glucose, the form of sugar that is transported and used by the body more readily than proteins or fats. A diet too high in carbohydrates can upset the delicate balance of ...
... someone say that they “need to cut down on their carb intake” or they are on a “low carb diet”. Carbohydrates are converted into glucose, the form of sugar that is transported and used by the body more readily than proteins or fats. A diet too high in carbohydrates can upset the delicate balance of ...
Slide 1
... In this part of discussion we will mainly focus of the digestion, transport and catabolism of triglycerides. Although other lipids like cholesterol, sphingolipids are important too but they will not be covered in this course. Sources of Fat available for oxidation: 1. Dietary fat, 2. Excess dietary ...
... In this part of discussion we will mainly focus of the digestion, transport and catabolism of triglycerides. Although other lipids like cholesterol, sphingolipids are important too but they will not be covered in this course. Sources of Fat available for oxidation: 1. Dietary fat, 2. Excess dietary ...
Metabolism
... • Fatty acids are stored as triglycerides • High fat diets: most go to straight to fat stores • High protein diets: body converts most of excess protein to fat • High carb diets: does not convert protein to fat; however, it shifts your body’s fuel preferences to burn more carbs than fat ...
... • Fatty acids are stored as triglycerides • High fat diets: most go to straight to fat stores • High protein diets: body converts most of excess protein to fat • High carb diets: does not convert protein to fat; however, it shifts your body’s fuel preferences to burn more carbs than fat ...
Cellular Functions PP
... hydrolyzed into glucose, which passes on to glycolysis. – Lipids are converted to fatty acids, which become acetate (then acetyl CoA), and glycerol, which is converted to an intermediate in glycolysis. – Proteins are hydrolyzed into amino acids, which feed into glycolysis or the citric acid cycle. ...
... hydrolyzed into glucose, which passes on to glycolysis. – Lipids are converted to fatty acids, which become acetate (then acetyl CoA), and glycerol, which is converted to an intermediate in glycolysis. – Proteins are hydrolyzed into amino acids, which feed into glycolysis or the citric acid cycle. ...
Organic compounds
... Used by cells to store and release energy Carbohydrates: example glucose ...
... Used by cells to store and release energy Carbohydrates: example glucose ...
Catalogue Number CTK-468 Introduction Insulin decreases blood
... contains an intrachain disulfide bond. Insulin regulates the cellular uptake, utilization, and storage of glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids and inhibits the breakdown of glycogen, protein, and fat. Insulin Porcine is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques. ...
... contains an intrachain disulfide bond. Insulin regulates the cellular uptake, utilization, and storage of glucose, amino acids, and fatty acids and inhibits the breakdown of glycogen, protein, and fat. Insulin Porcine is purified by proprietary chromatographic techniques. ...
chapter 24
... fatty acids get processed once they’re broken apart Activated by the hormones glucagon or epinephrine ...
... fatty acids get processed once they’re broken apart Activated by the hormones glucagon or epinephrine ...
Citric acid Cycle:
... forward or backward? b. How does this reaction proceeds in forward direction? c. Calculate the G for this reaction in forward direction if concentration of oxaloacetate is 1x 10-8 M, malate 0.2 mM, and NAD+/NADH ratio in rat liver mitochondria is 10. ...
... forward or backward? b. How does this reaction proceeds in forward direction? c. Calculate the G for this reaction in forward direction if concentration of oxaloacetate is 1x 10-8 M, malate 0.2 mM, and NAD+/NADH ratio in rat liver mitochondria is 10. ...
Ketosis

Ketosis /kɨˈtoʊsɨs/ is a metabolic state where most of the body's energy supply comes from ketone bodies in the blood, in contrast to a state of glycolysis where blood glucose provides most of the energy. It is characterised by serum concentrations of ketone bodies over 0.5 millimolar, with low and stable levels of insulin and blood glucose. It is almost always generalized with hyperketonemia, that is, an elevated level of ketone bodies in the blood throughout the body. Ketone bodies are formed by ketogenesis when liver glycogen stores are depleted (or from metabolising medium-chain triglycerides). The main ketone bodies used for energy are acetoacetate and β-hydroxybutyrate, and the levels of ketone bodies are regulated mainly by insulin and glucagon. Most cells in the body can use both glucose and ketone bodies for fuel, and during ketosis, free fatty acids and glucose synthesis (gluconeogenesis) fuel the remainder.Longer-term ketosis may result from fasting or staying on a low-carbohydrate diet, and deliberately induced ketosis serves as a medical intervention for intractable epilepsy. In glycolysis, higher levels of insulin promote storage of body fat and block release of fat from adipose tissues, while in ketosis, fat reserves are readily released and consumed. For this reason, ketosis is sometimes referred to as the body's ""fat burning"" mode.