* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Glucose
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
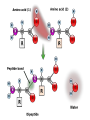
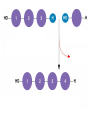
Unit 3 Major Topics 3.1 Chemical elements of water 3.2 Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins 3.3 DNA structure 3.4 DNA replication 3.5 Transcription & Translation 3.6 Enzymes 3.7 Cell Respiration 3.8 Photosynthesis 3 4,5 16-18 16-18 16-18 8 9 10 3.1 Chemical Elements & Water Essential Elements of Life • About 25 of the 92 elements are essential to life • What make up 96% of living matter? – Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen • Most of the remaining 4% consists of calcium, phosphorus, potassium, and sulfur The other 4% of elements • Sulfur – All plants need S to grow because S is in all proteins. – Also, active part of amino acids • Calcium – Calcium makes up 1.5% of the average human body – A balance of CALCIUM is maintained in a healthy animal – Used for bone production – Calcium in plants middle lamella • Phosphorus – Major components in nucleotides & ADP & ATP • Iron – Hemoglobin carries oxygen via red blood cells throughout the body. – Plays a key role in the production of chlorophyll in plants • Sodium – Sodium potassium pump (nervous system) – Most plants do not need it. Nitrogen deficiency • WATER? Iodine deficiency Resulting from Goiter Name (molecular formula) Water (H2O) Electronshell diagram Structural formula Spacefilling model • Electronegativity is an atom’s attraction for the electrons in a covalent bond • The more electronegative an atom, the more strongly it pulls shared electrons toward itself • In a nonpolar covalent bond, the atoms share the electron equally • In a polar covalent bond, one atom is more electronegative, and the atoms do not share the electron equally • The water molecule is a polar covalent molecule • Polarity allows water molecules to form hydrogen bonds with each other • THIS IS CALLED COHESION! – O H + H H2O + Hydrogen bonds Cohesion Properties • Hydrogen bonds hold water molecules together cohesion • Cohesion transports water against gravity in plants FURTHERMORE: • Surface tension is a measure of how hard it is to break the surface of a liquid • Surface tension is related to cohesion Water-conducting cells (Phloem & Xylem) 100 µm Animation: Water Transport Solvent Properties • Solution? – liquid that is a homogeneous mixture of substances • Solvent? – the dissolving agent of a solution • Solute? – the substance that is dissolved THERFORE • Water is a versatile solvent due to its polarity • Aqueous solution? – one in which water is the solvent Water is an effective solvent because it readily forms hydrogen bonds – Na+ + + – – + – – Na+ – + + Cl– Cl– + – + + – – – – 3.2 Carbohydrates, Lipids, & Proteins • Cells 70–95% water, • the rest consists mostly of carbon-based compounds like… – Proteins, DNA, carbohydrates • Carbon chains = the skeletons of most organic molecules • Carbon chains vary in length and shape • If Carbon is present, and in a living system, this is considered to be ORGANIC, if NOT THEN INORGANIC – Most also contain HYDROGEN • YOU WILL ALSO BE REQUIRED TO IDENTIFY THE FOLLOWING: GLUCOSE, RIBOSE, AMINO ACIDS, AND FATTY ACIDS • Glucose – most important monosaccharide – Glucose: C6H12O6 this is a hexose sugar (six carbons) most commonly found in this ring structure in an aqueous solution – Glucose will be known mostly as a product of photosynthesis or the substrate molecule for respiration. – Glucose is also found in a polymer as starch, glycogen or cellulose. – All bonds are covalent. Ribose: – Pentose (5 carbon sugar). – Ribose is used in photosynthesis as: – ribulose bisphosphate. (RUBP) – Where else is RIBOSE used? – deoxyribose Deoxyribonucleic acid or DNA Amino Acids: – How many? – 20 common amino acids – Amino acids are monomers which combine to form the larger polypeptides. – In turn polypeptides combine to make proteins. – Proteins uses? – enzymes and many cellular and extra cellular components. – Each of the common amino acids has the same structure as the one shown except that the R group is different. Fatty Acids: – These molecules are the basis of triglycerides and many other types of lipid. – These molecules are also the basis of the phospholipid molecules that form the bilayer of the cell membrane. – This image shows a basic saturated (no double bonds) fatty acid. H H H H H H H C C C C C C H H H H H H O C OH – There is a methyl group (-CH3) at one end of the chain. – Chain is the formed from a series of covalently bonded carbons saturated with hydrogens. – The chain is non-polar and hydrophobic – The carbonyl group is polar making this ends of the molecule hydrophilic. Fatty acids H H H H H H H C C C C C C H H H H H O C OH H Can be drawn as: O C OH Triglycerol Most macromolecules are polymers, built from monomers • A polymer is a long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks called monomers • Some Carbohydrates serve as fuel and building material, and are either monomers or polymers • Monosaccharides • Disaccharide • Polysaccharides single sugars, only 1 2 sugars many sugars • Dehydration reaction joins 2 monosaccharides to form Di or Poly Some Functions of Common Carb’s Example Type of Carb Function Glucose (MOST COMMON) Monosaccharide Energy source in animal cells Glucose Monosaccharide Component of flower nectar Lactose Disaccharide Sugar found in milk Sucrose Disaccharide Transport form of carb’s in phloem Glycogen Polysaccharide Carbs storage in liver of animals Cellulose Polysaccharide Component of plant cell walls Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of maltose 1–4 glycosidic linkage Glucose Dehydration reaction in the synthesis of sucrose Glucose Maltose 1–2 glycosidic linkage Glucose Fructose Sucrose STARCH Poly made of many GLUCOSE molecules stored in Chloroplasts! Chloroplast Starch 1 µm Amylose Amylopectin Starch: a plant polysaccharide Cellulose microfibrils in a plant cell wall Cell walls Microfibril 0.5 µm Plant cells Cellulose molecules b Glucose monomer • Cellulose in human food passes through the digestive tract as insoluble fiber • Some microbes use enzymes to digest cellulose – COWS – This is a SYMBIOTIC RELATIONSHIP Between COW & MICROBE So starch in plants, what about animal polysaccharides? • GLYCOGEN • Glycogen is a storage polysaccharide in animals • Humans and other vertebrates store glycogen mainly in liver and muscle cells • Chitin, another structural polysaccharide, is found in the exoskeleton of arthropods • Chitin can be used as surgical thread Mitochondria Glycogen granules 0.5 µm Glycogen Glycogen: an animal polysaccharide Synthesis & Breakdown of Polymers • Monomers form larger molecules by condensation reactions called dehydration reactions • Polymers are disassembled to monomers by hydrolysis, a reaction that is essentially the reverse of the dehydration reaction Lipids • Lipids are non polar, so they do not dissolve in water • The most biologically important lipids are fats, phospholipids, and steroids • The major functions of fats are: - energy storage - thermal insulation - buoyancy • Energy storage: – – – – – Fats are a more compact fuel than starch. Fat contains twice the energy-rich (C-H) bonds as glucose Fat stores twice as much energy as glucose Fat produces twice as many calories when burned Unfortunately, you need to put twice as much energy to burn off a pound of excess fat than you do of glycogen......... So which is likely to burn faster when an animal is starving, lipids or glycogen stores? GLYCOGEN Therefore: LIPIDS ARE USED FOR LONG TERM STORAGE, NOT FAST ENERGY. Uses of Lipids in Living Things Long-term energy stores Human Adipose Tissue Plant Oils Buoyancy for marine animals: lipids are less dense than water so help animals float Insulation: a layer of fat beneath the skin cuts down heat loss Production of water: fatty acids produce a lot of metabolic water when they are used during cellular respiration, for example... C17H35COOH + 26 O2 18 CO2 + 18 H2O (a typical fatty acid) Camels’ humps are an example of this metabolic water production! Furthermore, their erythrocytes can swell to 240% of normal size without bursting. (Other species can only go to 150%.)