* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Charles Darwin
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary psychology wikipedia , lookup
Hindu views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Evolving digital ecological networks wikipedia , lookup
Darwinian literary studies wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Theistic evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
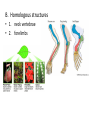
Charles Darwin 1800-1865 I. Early influences • A. Family – 1. Father a minister – 2. Early possible careers – 3. Settled as a naturalist on the voyage of Beagle B. Voyage of Beagle 1831-1836 • 1. 22years old • 2. extent of voyage • 3. influenced a lot by Galapagos Islands C. Galapagos islands • 1. Finches • Adaptive radiation 2. Galapagos tortoises • a. Unique species for each island • b. Identified by shape of carapace • c. Inefficient 3. Galapagos Iguana C. Thomas Malthus • 1. economist • 2. Malthusian Principle • 3. Provided Darwin with the idea of struggle D. Artificial selection • 1. definition • 2. change is possible over time II. Darwinian Evolutionary Theory • A. Darwin was a wimp • B. Alfred Wallace C. Actual theory • 1. Decent with modification • 2. Like a branching tree • 3. Change occurs slowly in the appearance of the species as its environment changes • 4. Organisms living today are different in appearance when compared to ancestors • 5. Living organisms share common ancestors D. Mechanism Natural Selection • 1. variety exists in all populations 2. Populations have huge reproductive potentials 3. More young produced than environment can support 4. Some phenotypes are more fit than others • Dodo bird is an example of species that go extinct 5. More fit in the population will leave more offspring 6. Slow and gradual change over time 7. Things to think about • a. Individuals don’t evolve-populations are the simplest level of biological organization that can evolve • b. There is a difference between adaptations acquired during the lifetime of an individual and those adaptations inherited from a parent • c. Evolution does not have an end point • d. Man is not necessarily the high point or end point of evolutionary change • e. Better is only for a particular environment-if the environment changes the “good” adaptation may no longer be advantageous • f. Evolution often leads to simplicity rather than complexity E. Example of evolutionary change-Beagle tongue • 1. obvious function • 2. thermoregulatory function • 3. bell-shaped distribution 4. Environmental change-global warming a. Which type of beagle has the advantage? b. Short or long eared? c. Why? III. Social ramifications • A. Social Darwinism and Spencer B. Ideologies of Imperialism • • • • 1. Competition demonstrated that some individuals were able to manifest their inherent hardiness by triumphing economically over weaker individuals. 2. Just as it was abundantly clear that there were fitter and stronger individuals, the next step was to see that nations were unequal. 3. Because it was obvious that some nations were stronger and fitter than others, so the European argument ran, then Europeans were better than other peoples. 4. Europeans saw it as their destiny to rule the world C. Racism and Darwinism 1. 2. 3. The greatest influence in the sudden development of racism in the 19th century Europe was the replacement of the Christian belief that "God created all people equal" by "Darwinism". By suggesting that man had evolved from more primitive creatures, and that some races had evolved further than others, it provided racism with a scientific mask. 'Take away the Nordic Germans and nothing remains but the dance of apes' A quote of Adolf Hitler IV. Data supporting evolutionary theory • A. Embryological similarities • 1. evolution is a conservative process • 2. builds upon what is already present • 3. example of a house B. Homologous structures • 1. neck vertebrae • 2. forelimbs C. Convergent evolution • 1. • 2. definition homoplastic features D. Coevolution E. Vestigial structures • 1. definition • 2. examples F. Fossil Record • 1. missing links-Archeopteryx 2. Phylogenies G. Comparative biochemistry