* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name: Assignment: Cell #4: Structure of Cell Membranes Let`s take
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
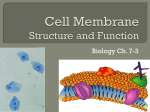
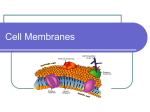
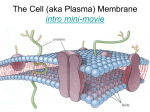
Name: _______________________________________________ Assignment: Cell #4: Structure of Cell Membranes Let's take a look at the structure of the cell membrane. Surprisingly, this barrier that separates the inside of the cell from the outside is not thick, nor is it particularly sturdy. It is composed mostly of layers of special lipids called phospholipids. Phospholipids are a lot like triglycerides. They have a glycerol. However, they have only two fatty acids. Instead of a third fatty acid, the phospholipids have a group of atoms called the phosphate group. The phosphate group contains a phosphorous atom surrounded by four oxygen atoms. If you look at the shape of the phospholipid, you could say that the phosphate group forms the head and the fatty acids form two tails. The phosphate group gives this lipid a special property. Lipids do not dissolve in water. In other words, they are nonpolar. Nonpolar substances are said to be insoluble. That is, they do not form hydrogen bonds with water. (Remember that water is a polar molecule, and only polar molecules dissolve in it.) This is only partially true for phospholipids. Whereas the fatty acid tails are nonpolar, the phosphate head has a negative charge and is, therefore, polar. Polar substances can hydrogen bond with water and are, therefore, described as soluble. So, if you drop a phospholipid into a glass of water, the phosphate head will go into the water; the fatty acid tails will float up toward the air. (1) What are the three parts of a phospholipid? 1. ____________________________________________ 2. ____________________________________________ 3. ____________________________________________ (2) What part of the phospholipid forms its: a. head? _________________________________________________________ b. tail? ___________________________________________________________ (3) Why are nonpolar molecules insoluble in water? _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 1 (4) Describe what happens it you drop a phospholipid molecule in water. ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ (5) What special property of a phospholipid causes it to do this? ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Cell membranes contain two layers of phospholipids. There is water on the inside and the outside of the cell. The water attracts the phospholipid heads but repels the fatty acid tails. As a result, the fatty acids in each layer line up inside. The phosphate heads in the outer layer face out into the water. The phosphate heads of the inner layer face the inside of the cell. The fatty acid tails in both layers face each other as they try to get as far away from the water as possible. (6) Cell membranes are made up of how many layers of phospholipids molecules? _________________________________________________________________________ (7) Why do the fatty acid tails line up on the inside? _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________________________ 2 Cell membranes contain large molecules other than phospholipids. They contain cholesterol, which increases the membrane's fluidity (the ability for molecules making up the membrane to move among one another). They also contain various types of proteins. Some proteins are attached to the surface of the membrane. Others extend completely through the membrane. Some of these proteins are called glycoproteins. They have branched sugar chains sticking out of their tops. (Some of the phospholipids also have sugar chains sticking out of the phosphate groups.) These sugar chains are like name tags. They enable cells to recognize and communicate with each other. This ability is especially important when it comes to fighting diseases. Your immune system uses these markers to differentiate between enemy cells, such as invading bacteria, and your own cells. As a result, your immune system does not attack the wrong cells. (8) What is the role of cholesterol in cell membranes? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ (9) How do glycoproteins differ from other proteins? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ (10) What is the function of glycoproteins? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 3 (11) Why is it important that cells be able to recognize one another? ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ Other proteins in the membrane act as gatekeepers. They transport, or carry, molecules back and forth across the membrane. Cell membranes are permeable to water and gases such as oxygen and carbon dioxide. These molecules are free to diffuse back and forth depending on the level of concentration. Other molecules need help from proteins in the membrane. These proteins bind to the molecules on one side of the membrane and release them on the other side. Like enzymes, transport proteins are specialized; each type can transport only one type of molecule. There are two kinds of transport. PASSIVE TRANSPORT: In passive transport, the protein moves molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration. Passive transport does not require the cell to expend, or use, energy. ACTIVE TRANSPORT: Active transport moves molecules against the level of concentration. In other words, it moves molecules from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. Active transport is equivalent to pushing a rock uphill. The cell must expend energy. That is, ATP must be broken down to release the energy required by active transport. (12) What molecules are able to pass through the lipid bilayer without the help of transport proteins? _________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________ (13) Tell whether the following are true of (A) passive transport (B) active transport (C) both active and passive (D) neither ________ - needs energy ________ - particles move from an area of high to low concentration ________ - particles move from an area of low to high concentration ________ - need to pass through transport protein molecules ________ - molecules pass directly through the phospholipid bilayer 4