* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam Review two KEY
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
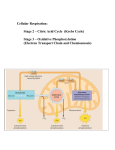
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Questions for Exam 2 review: 1. What product of the light reactions is used by the Calvin Cycle? A. Oxygen B. ATP C. NADPH D. B & C 2. Which step of glucose breakdown produces the most ATP? A. Glycolysis B. Pyruvate breakdown C. Citric Acid Cycle D. Oxidative Phosphorylation 3. Select the TRUE statement: A. Competitive inhibitors bind the active site of an enzyme while noncompetitive inhibitors bind an allosteric site. B. Noncompetitive inhibitors bind the active site of an enzyme while noncompetitive inhibitors bind an allosteric site. C. Both competitive inhibitors and noncompetitive inhibitors are irreversible and result in having to make a new enzyme D. Competitive inhibition would be considered to be an ‘ON’ activator while noncompetitive inhibition would be considered an ‘OFF’ activator. 4. What happens to the electrons as they move from Photosystem II to Photosystem I? A. Gains energy along the way. B. Energy stays the same. C. Loses energy, this is why a 2nd input of light is needed in Photosystem I. D. Electrons move from Photosystem I to Photosystem II and lose energy along the way. 5. What are the four nitrogen bases for DNA? A. Uracil, Thymine, Adenine, and Guanine B. Cytosine, Thymine, Adenine and Guanine C. Thymine, Adenine, Lytosine, and Guanine D. Thymine, Adenise, Guanine, Cytosol 6. The new DNA strand formed after DNA replication is an exact copy of its parent strand. A. True B. False 7. Which of the following is a characteristic of RNA but not DNA? A. B. C. D. E. Single stranded Double stranded Thymine Double helix All of the above 8. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? A. 3 B. 6 C. 9 D. 12 E. It can’t be done 9. During what stage of photosynthesis are ATP and NADPH converted to ADP + Pi and NADP+? A. The light dependent reactions B. The light independent reactions C. Both of the above D. None of the above 10. What energy-rich organic compound is produced as a result of the calvin cycle? A. NADPH B. CO2 C. ATP D. H2O E. Glucose 11. The oxygen that is released as O2 during photosynthesis came from _________ molecules. A. Carbon dioxide B. Water C. Glucose D. Chlorophyll E. ATP 12. Light is required for the light dependent reactions because… A. It is the source for electrons B. It splits the water molecule C. It energizes electrons in the reaction center D. It splits ATP molecules which generates the energy necessary to power the light independent reactions. 13. Which stage of aerobic respiration requires ATP? A. Alcohol Fermentation B. Lactate Fermentation C. Glycolysis D. Photosynthesis 14. As protons flow through the _________, energy is released and exploited to combine ADP and inorganic phosphate to form ATP. A. Electron transport chain B. Mitochondrial membrane C. ATP Synthase D. NADH 15. The end product of glycolysis is: A. Pyruvate B. Lactate C. Acetyl CoA D. NADH 16. What substance is produced by the oxidation of pyruvate and feeds into the citric acid cycle? A. Glucose B. Oxygen C. Carbon dioxide D. Acetyl CoA E. Pyruvate 17. The stages of glucose oxidation are listed below. Which of the following stages occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell? A. Krebs citric acid cycle B. Glycolysis C. Oxidation of pyruvate to acetyl CoA D. Electron transport 18. How does Ligase assist in the creation of mRNA? A. Synthesize Okazaki fragments B. Connect Okazaki fragments C. Take away the tension of replication D. Make the replication bubble 19. What is an example of an “ON” activator? A. Competitive inhibition B. Positive allosteric regulation C. Noncompetitive inhibition D. Protein synthesis 20. What is NOT an example of an “OFF” inhibitor? A. Competitive inhibition B. Non competitive inhibition C. Positive allosteric regulation D. Feedback inhibition 21. How are metabolic pathways inhibited? A. Gene regulation by turning on or off genes that make the pathway proteins on or off. B. Cellular regulation of receiving signals that travel to turn off or on the protein. C. Biochemical reactions such as feedback inhibition D. All of the above 22. What is the final product of glycolysis? A. Pyruvate formation B. Acetyl CoA C. ATP D. ADP + Pi 23. What is made from Anaerobic respiration? A. Alcohol B. Lactate C. ATP D. Both A & B 24. What does the oxidative part mean in oxidative phosphorylation? A. Making water from oxygen B. Making water from ATP C. The formation of ATP D. The formation of ADP + Pi 25. What does the phosphorylation mean in oxidative phosphorylation? A. The formation of ATP from ADP + Pi B. The formation of glucose C. The formation of oxygen D. The formation of phosphorous 26. What are some symptoms of DNP ingestion? A. Nausea B. Weakness C. Sweating D. All of the above 27. How can you monitor the Electron Transport Chain? A. Monitoring ATP made B. Monitoring Oxygen consumed C. Monitoring glucose breakdown D. Both A & B 28. What did the Peter Mitchell chemiosmotic theory tell us? A. Protons move out by the electron transport chain B. Protons move in through ATP synthase C. Protons move in by the electron transport chain D. Both A & B 29. What does competitive inhibition do? A. Binds to active site to stop the enzyme from working B. Binds to allosteric site to stop the enzyme from working C. Binds to the substrate to stop the enzyme from working D. Both A & B 30. What is true about the following graph? A. It is exergonic and will occur spontaneously B. It is exergonic and will not occur spontaneously C. It is endergonic and will occur spontaneously D. It is endergonic and will not occur spontaneously 31. According to the second law of thermodynamics, A. Energy cannot be created nor destroyed B. Each energy transfer decreases the entropy C. Energy is constant in the universe D. Each energy transfer increases entropy 32. Reactions that release free energy are, A. Spontaneous B. Endergonic C. Exergonic D. Both A and C 33. Which of the following processes require energy? A. Creating ion gradients across membranes B. Muscle shortening C. Protein synthesis D. All of the above 34. Heat is an example of A. Potential energy B. Electrical energy C. Kinetic energy D. All of the above 35. In DNA, hydrogen bonding occurs, A. Between sugars of each nucleotide B. Between the nitrogenous bases C. Between phosphate group of one nucleotide and the hydroxyl group of another D. All of the above 36. Which of the following may be involved in combinatorial control of gene expression? A. Activator proteins B. Repressor proteins C. DNA methylation D. All of the above 37. What would occur if the TATA box was mutated? A. Transcription would not happen B. Translation would not happen C. Transcription would still occur D. Translation would still occur 38. Which of the following statements regarding ATP is false? A. Breaking the phosphate bond requires energy B. Reforming new bonds after breaking the phosphate bond releases energy C. The total change of energy for ATP hydrolysis is +8.2 kcal/mol D. It is easy to break the high energy phosphate bond 39. What does ATP stand for? A. Adenosine triphosphate B. Adenine triphosphate C. Adenosine transphosphate D. Adenine transphosphate 40. What word refers to a reaction that releases energy? A. Exergonic B. Endergonic C. Intergonic D. Intragonic 41. What type of fermentation occurs in animal cells is the absence of oxygen? A. Lactic acid fermentation B. Alcoholic fermentation C. Galactic fermentation D. None of those 42. Which of the following statements regarding chlorophyll is true? A. Chlorophyll absorbs green light the best; this is why we see plants green B. Light is captured in the head region of the chlorophyll C. Chlorophyll absorbs light at all wavelengths of the visible spectrum D. The tail region of chlorophyll has no known function 43. Where does the Calvin cycle take place? A. Thylakoid membrane B. Cytoplasm C. Stroma D. Granum 44. The replication fork is: A. The Y-shaped region where the DNA is split into two separate strands for coding B. Growing as DNA replication proceeds because synthesis is bidirectional C. The location at which the replication process begins D. Present only in bacterial cells and not in eukaryotes 45. Reverse transcriptase is commonly found in what types of organism? A. Viruses B. Bacteria C. Plants D. Animals 46. What does it mean that the genetic code is redundant? A. Most amino acids are coded for by more than one codon B. One codon never codes for more than one amino acid C. One codon can always code for multiple amino acids D. None of the above - genetic code isn’t redundant 48. Which of the following is a level of gene expression in eukaryotes? A. Chromatin remodeling B. RNA processing C. Post-translational D. All of the above 50. What is the mRNA of the following template strand? A. 5’ - UCGACCGAU - 3’ B. 3’ - UCGACCGAU - 5’ C. 5’ - TCGACCGAU - 3 ‘ D. 3’ - TCGACCGAU - 5’ 5’ - ATCGGTCGA - 3’ 51. What kind of mutation results in the abrupt stopping of the amino acid sequences? A. Missense B. Nonsense C. Silent D. Frameshift 52. According to the graph above, if cases are defined as Alcoholics, and controls as non alcoholics, you are most likely to not be an alcoholic if … A. You have ADH 3 heterozygote B. You have ALDH 2 homozygous 1 C. You have ADH3 homozygous 1 D. You have ADH 2 homozygous 1 53. If oxygen in cellular respiration was labeled with oxygen isotopes, what molecule in the cell would we look for to have the isotope? A. Glucose B. Water C. CO2 D. ATP 54. In Hershey and Chase experiment, what would have happened if protein was the genetic information of life? A. Phosphate isotopes would be found in the host cell B. Phosphate isotopes would be found in the new viruses C. Sulfur isotopes would be found in the host cell D. Sulfur isotopes would be found in the new viruses E. Both A & D F. B & C 55.Please put the following in the right order Nucleosome (A), chromatid (B),Histones (C), 30 nm Fiber (D) A. A,B,D,C B. C,B, A, D C. C,A,D,B D. C,A,B,D 56. True or False: HATs put positive acetyl groups on histone, causing it to further condense, and reducing gene expression.