* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3 – DNA Replication
Survey
Document related concepts
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
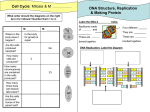
☰ Search Explore Log in Create new account Upload × DNA Replication Describe what must happen to DNA in order for cells to divide ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________ New Strands of DNA are made by: In this way, the genetic code is completely preserved and copied exactly __________________________________________ Helicase works in both directions to unwind DNA. Replication Bubbles Accessing the DNA Topoisomerase works ahead of helicase to cleave and unwind the stands of DNA. This process relieves tension ahead of each replication fork. Single-stranded DNA binding protein (SSB) prevents the unwound DNA from coiling back up. DNA Polymerase III is only able to grow from an already existing 3’ end of a nucleic acid. This means that it can only work in ONE DIRECTION. Indicate the direction of growth of the DNA daughter strand by labeling the 3’ and 5’ ends of the parent strand, the RNA primer and the growing daughter DNA molecule. RNA primer growing daughter strand DNA Polymerase III parent strand Take notes on the diagram below of a replication fork to summarize the action of each of the ENZYMES involved in DNA replication. Be sure to explain the differences between the leading and lagging strands. Study the diagram below. From memory, sketch a replication fork with all of the enzymes and labels that are relevant to DNA replication. Include the directionality of each strand. It would be wise to cover the completed diagram as you draw. Summary of the DNA Replication Process Download 1. No category 3 – DNA Replication.DOC DNA Replication DNA replication worksheet DNA Replication DNA replication worksheet – Watch the animations and answer Dna rEPLICATION - Manning's Science Replication 1 Chapter 6 Test SBI4U Alternative models of DNA replication (Fig 3.1) Biology Genetics Test Summary studylib © 2017 DMCA Report