* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download BHS 150.1 – Course I Date: 10/18/12, 1st hour Notetaker: Laurel
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Mitochondrion wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical cascade wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
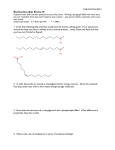
BHS 150.1 – Course I Notetaker: Laurel Hammang Date: 10/18/12, 1st hour Page1 Final will have 100 questions, new information will be 1/3 of material, tested as new (more details) Test hasn’t been written yet, so if Dr. Z writes questions on material she didn’t tell us about, she’ll send an email out Know big picture for old material, all tear stuff in detail as if tested new Homework #4 Answer sheet given out: Q1 Aerobic glycolysis Someone without contacts, or normally while awake, do aerobic glycolysis (full oxygen) Krebs’s cycle, ETC, ATP produced Enzymes need to know: those that make GTP, NADH, FADH2 Nutrition involved: niacin, pyruvate dehydrogenase, isocitrate, ketoglutarate dehydrogenase need thiamine succinate dehydrogenase, riboflavin, what complexes are doing Know what shuttle to use Know acetyl coA, glucose, how much for aerobic/anaerobic glycolysis Q2 Anaerobic glycolysis Someone with contacts or during sleep (low oxygen) *might be in a case on the final exam H and M polypeptide Q3 Healing Understand process for each type of cell healing and how they react to injury What happens with scars? Epithelial cells must heal first to form barrier if damage down to stroma Q4 Energy calculations for palmitate Palmitate (versus palmitoyl) means it’s out in cytosol and needs to be activated to be transported to mitochondria **For exam, she will give us an inactive FA in cytosol that needs to be activated for transport into mitochondria Go through calculations, practice with any even number 14, 16, 18, 10 Reactions: understand beta oxidation process Order of steps, what’s produced, know that the enzymes are dehydrogenases REVIEW OF OLD MATERIAL Structures: simpler than previous exams, (more global) Be able to id amino acid, vitamin, FA, etc she’ll let us know exactly Cells and biological buffers: related to what we’ve talked about Qs related to RER (mucin production, collagen), SER, mitochondria, based on when we covered them in lecture Acid/base: lysozyme function, protein structure Recognize acid and base (*histidine) amino acids Nutrition: 4 cal carb, 4 cal protein, 9 cal fat for energy calculations Vit’s E, C,: what they do Vit A full detail, how its used by conjunctiva cells to make mucin Niacin, thiamin, riboflavin: water soluble? What they do? Where? Function? Summarize digestion and absorption: how are things broken down? Proteolysis: zymogens, review lipids, (no lutein, zeaxanthin) TEARS & ANYTHING EYE RELATED: TESTED AS NEW MATERIAL IN FULL DETAIL Amino acids and proteins: structure and function, stabilizing bonds for each structure Proteins made by 2 organelles: RER & Golgi Know tear-related proteins and their functions Enzymes: function and how they work—how can side chains be used? Lysozymes (No graphs will be given) Proteins in normal tears vs in an infected eye Glycolysis: 1 sentence summary: what is made, location, energy calculations Enzyme names that use/make: NAD, FAD, ATP Ex: which enzyme in kreb’s cycle is dependent on niacin? Or makes NAD? Be able to separate where enzymes are, which pathway uses them for what Pentose Phosphate Pathway: 1 sentence summary: oxidative portion that makes NADPH , non oxid portion that recycles carbons Lipid Production: regulation Malonyl coA stimulates for synthesis of FA the need energy regulates break down (oxidation) calculations for break down (none for synthesis) Lipoproteins: VLDL, IDL, LDL, HDL, chylomicrons Know what each does…what gives cholesterol? What delivers TGs? Cholesterol synthesis requires Acetyl CoA (for energy, make FA, cholesterol) Dislipidemia-Diabetes-glycation, how cholesterol can be a problem Membranes: carriers, facilitated, transporters, channels, *Know how to id each type Classify all types for tear production and corneal hydration Unique example: endothelial cells in corneal hydration uses bicarb concentration levels for secondary active transport Aqueous layer of tears: production Mucin layer: role of vitamin A (retinoic acid) Receptors: metabotropic: tear regulated Ionotropic: tear regulated by Ca2+ and IP3 Classify and understand different types Be able to put together entire tear regulation process ECM: related to cornea, what we talked about again later in the cornea Collagen production and vit C role Table pg 158 Function of each type of collagen: which is structural? Which limits diameter? Corneal hydration Secondary active transporters Which is on stroma side? On cornea side? Purpose is to pull H2O out How do endothelial cells regulate hydration? Beta Oxidation: calculation questions, order of reactions, nutrition (carnitine deficiency) Antioxidants: role of vit C, E Lipid Peroxidation: process, how fixed (damage and danger) Vitamins: enzymes, SOD, catalase, GSH system Everything else is included in the HW 4 handout