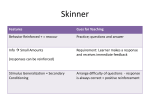
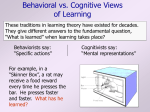
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 1
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cross-cultural psychology wikipedia , lookup
Applied behavior analysis wikipedia , lookup
Observational methods in psychology wikipedia , lookup
Classical conditioning wikipedia , lookup
History of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Learning theory (education) wikipedia , lookup
Subfields of psychology wikipedia , lookup
Social psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Educational psychology wikipedia , lookup
Experimental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Abnormal psychology wikipedia , lookup
Music psychology wikipedia , lookup
Theory of planned behavior wikipedia , lookup
Attribution (psychology) wikipedia , lookup
Developmental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Sociobiology wikipedia , lookup
Descriptive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Organizational behavior wikipedia , lookup
Theory of reasoned action wikipedia , lookup
Verbal Behavior wikipedia , lookup
Insufficient justification wikipedia , lookup
Behavior analysis of child development wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Social cognitive theory wikipedia , lookup
Psychological behaviorism wikipedia , lookup
Multiple Choice History of Modern Psych, 3e: Study Guide, Chapter 11 11-1 1. Starting the in 1930s, behaviorism became a dominant force in American psychology. Of the following factors, which contributed the least? a. Watson’s behaviorist manifesto b. the translation of Pavlov’s work into English c. the development of operationism d. Watson’s popularizing of behaviorism in the 1920s 2. Why was logical positivism attractive to American experimental psychologists? a. it provided a means to study unobservable entities and still remain “scientific” b. it enabled researchers to avoid having to take unobservable entities into account in their theorizing c. researchers like facts, not theory, and this movement enabled them to avoid theory d. it provided a way to reintroduce introspection into psychology, but to do it scientifically 3. Which of the following is inappropriately paired? a. Hull—hypothetico-deductive system b. Skinner—intervening variable c. Tolman—cognitive map d. Bridgman—operational definition 4. According to Tolman’s system, a. intervening variables are to be avoided b. logical positivism and operationism have harmed psychology c. before being able to understand molar behavior, psychology must understand molecular behavior d. behavior is goal-oriented or purposive 5. What did Hull and Tolman have in common? a. they both rejected the idea of focusing on molecular behavior b. they both investigated hypnosis and its effects c. they both included intervening variables in their systems d. they both believed that reinforcement was essential in order for learning to occur 6. Hull’s famous postulate #4 proposed that habit strength increases a. only if drive state is very low b. only if primary reinforcers are used; secondary reinforcers don’t work c. simply as a result of practice; reinforcement isn’t important d. as a function of the number of reinforced trials 7. Which of the following best summarizes Skinner’s ideas about operant conditioning? a. a stimulus paired with a response will, on recurrence, tend to elicit that response again b. learning results from the gradual construction of cognitive maps c. behaviors producing positive consequences tend to recur d. learning occurs through the repeated pairing of conditioned and unconditioned stimuli 8. Which of the following is true about Walden Two? a. written in the late 1940s, it was a product of its times (e.g., no important role for women in the community) b. only a limited amount of punishment was used in child rearing c. it was an immediate best seller, but starting in the 1960s, sales declined sharply d. child rearing was not entrusted to individual pairs of parents -1- Multiple Choice History of Modern Psych, 3e: Study Guide, Chapter 11 Answers 1. a. CORRECT ANSWER – the manifesto did not have much immediate impact b. this event, which happened in the 1920s, had a big impact c. this event, which also happened in the 1920s, had a big impact d. Watson kept at it, and had an eventual effect 2. a. CORRECT ANSWER – as long as they unobservables were operationally defined b. these unobservable entities (e.g., hunger drive) were impossible to ignore c. both Tolman and Hull were heavily involved in theory building d. in the 1920s, introspection was fading fast 3. a. Hull exemplifies the hypothetico-deductive method for theory building b. CORRECT ANSWER – Skinner did not feel these were necessary c. Tolman coined the term cognitive map d. operational definition began with Bridgman’s work 4. a. Tolman embraced intervening variables (e.g., expectancy) b. Tolman’s system benefited from logical positivism and operationism c. Tolman rejected molecular behavior in favor of molar behavior d. CORRECT ANSWER – a central idea for Tolman (“purposive” is in the title of his book) 5. a. Tolman did; Hull didn’t b. this was Hull, not Tolman c. CORRECT ANSWER – Tolman first, then Hull d. this was only true of Hull 6. a. drive affects performance, not habit strength b. both work c. reinforcement was very important for Hull d. CORRECT ANSWER – note: not just practice, but reinforced practice 7. a. sounds more like Hull b. this would be Tolman’s idea c. CORRECT ANSWER – behavior probability is a function of consequences d. this is Pavlovian conditioning, what Skinner called Type S conditioning 8. a. women played a very important role in Walden Two b. no punishment was used c. the reverse, sales in creased in the sixties d. CORRECT ANSWER – the whole community was involved in child rearing -2- 11-2