* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Genetically modified crops wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
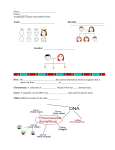
Chapter 10.1 Mendelian Genetics Gregor Mendel Austrian Monk Studied patterns of _____________ (passing on of characteristics from parent to offspring) Used the common garden pea in experiments. Why Mendel used peas Sexually reproducing: able to isolate both male and female ___________. Easy to identify ____________ (characteristics that are inherited). Short life cycle: grow quickly. Hybrid Any offspring of parents with different traits (ex: tall plant x short plant). ___________________ cross: cross-pollination (breeding) between two parents with only one variation difference (ex: tall plant x short plant). ___________________ cross: cross-pollination (breeding) between two parents with two variation differences (ex: tall, green plant x short, yellow plant). Pea Cross-Pollination Experiment Parent Generation (P1) Tall true breed x short true breed Filial Generation (F1) All tall hybrids Filial Generation (F2) 75 % tall hybrids, 25 % short hybrids What did Mendel Observe? When a true-breeding tall plant is crossed with a true-breeding short plant in the P generation, the F1 height trait is always predictable. _____ are tall plants. What happens when the F1 generation are crossed together? Mendel observed that in the F2 generation, the offspring of F1 plants, are always in a fixed ratio of _____; tall:short Pea Traits that Mendel Identified Through multiple crosses, Mendel determined that all these traits displayed a mathematical predictability for ___________. Seed Shape Seed Color Seed Coat Color Pod Shape Pod Color Flower Position round round grey smooth green axial wrinkled smooth round yellow white constricted grey smooth yellow green terminal axial Plant Height tall short tall Mendel’s Conclusions There must be two variations for every trait, where each variation is called an ___________. Each offspring inherits only _______ allele from each parent. The alleles are either ________________ or _________________ To show the recessive trait, ______ recessive alleles must be inherited. Dominant and Recessive Traits The traits that seem to mask other traits when present are called _______________ traits. The traits that seem to be hidden in the presence of dominant traits are called _________________ traits. BB – Homozygous Dominant purple Bb – Heterozygous purple Bb – Homozygous Recessive white Homozygous vs. Heterozygous ___________: inherits two similar alleles from the parents for a particular gene. Ex. tall allele and tall allele, written as _____. Ex. short allele and short allele, written as _____. ________________: inherits two different alleles from the parents for a particular gene. Ex. tall allele and short allele, written as _____. Law of Segregation Mendel concluded only ______ allele is passes from parent to offspring for each trait. F1 plants must be __________________ because the P generation only passed on one tall allele and one short allele. The F1 plant will then pass on to its offspring either a tall or a short allele, never both. Using a Punnett Square AA x aa = 100% Aa Each of the four squares represents 25% chance of inheritance for one offspring. A A a a Phenotype vs. Genotype ______________: physical appearance of the trait. Ex.: purple flowers. ______________: homozygous or heterozygous inheritance. Ex. PP, Pp, pp Law of Independent Assortment Because organisms are made up of more than one trait, Mendel concluded that the inheritance of one trait does not influence the inheritance of a second trait. Example: ____________ of the pea plant doesn’t influence the __________ of the peas. * Height is independently assorted from color. Dihybrid cross to show independent assortment. A smooth, yellow pea (______) can pass on these combinations of genes to its offspring: ___, ___, ___, or ___. Modernizing Mendelian Genetics Gene for hairline Allele: A DNA is the basis for inheritance. Genotype: Aa DNA are coiled into ___________________. Parts of the DNA that code for a trait are called Gene for hairline Allele: a _________. Some genes have only two alleles and others have more. Variations on Mendel _________________ dominance: the heterozygous genotype shows a blend of the two parents and not the dominant allele. _________________: the heterozygous genotype shows both inherited alleles. Ex. a roan horse coat: AA (dark red) x aa (white) = Aa (dark red and white) Multiple ____________: when there are more than two alleles that code for a trait. Ex. ABO blood type A type = AA or Ao B type = BB or Bo O type = oo AB type = AB _______________ trait: when more than one gene codes for a particular trait. Ex. fur color, human height, human skin color, eye color. Linked genes: Mendel concluded that traits are assorted independently, but some traits are ____________. o This means that two genes are almost always inherited together (red hair, green eyes) Now let’s practice!!