* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Science Notes on Physical and Chemical Properties
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Acid dissociation constant wikipedia , lookup
Thermal spraying wikipedia , lookup
Thermoelectric materials wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
History of electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Ceramic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Strengthening mechanisms of materials wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Crystallization wikipedia , lookup
Thermomechanical analysis wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Implicit solvation wikipedia , lookup
Al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory wikipedia , lookup
Liquid–liquid extraction wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon proliferation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Chemical weapon wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical industry wikipedia , lookup
Solvent models wikipedia , lookup
Chemical plant wikipedia , lookup
Chemical Corps wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical potential wikipedia , lookup
State of matter wikipedia , lookup
Safety data sheet wikipedia , lookup
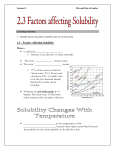
Science Notes on Physical and Chemical Properties PHYSICAL PROPERTY Definition: A feature or characteristic of matter which can be observed without changing the identity of the matter Examples: Color Density Conductivity –thermal and electrical Smell Malleability Melting Point Taste Ductility Boiling Point Texture Solubility Magnetism Malleability - how well something can be flattened or stretched without breaking Metals tend to be malleable – example is gold and copper Wood and glass are NOT malleable Ductility - the ability to be stretched into a wire Solubility - how well one material dissolves in another material. (Insoluble means cannot dissolve) measured by the amount of solute that can dissolve in 1000mL of water Things that affect solubility: 1. Temperature – as temperature increases so does the rate of dissolving 2. Stirring – speeds up dissolving 3. Surface Area - smaller pieces/particles – dissolve faster that large pieces of material 4. Amount of solute – greater amounts of solute require longer times to dissolve Solute - the chemical being dissolved: the material you add to a solvent Solvent - a chemical that dissolves things: the material in which you add a solute Examples: Chocolate mile – the syrup is the solute and the mile is the solvent Tea – the tea leaves are the solute and the hot water is the solvent Magnetism - how well something sticks to a magnet Conductivity There are 2 kinds 1. Thermal Conductivity – how well heat travels through a substance 2. Electrical Conductivity – how well electricity travels through a substance Melting Point the point at which a solid becomes a liquid Boiling Point the point at which a liquid becomes a gas Characteristic A feature of matter that is specific to the substance and does NOT change with the amount Property of substance…example…density, melting point and boiling point are characteristic properties CHEMICAL PROPERTIES Definition: How one thing reacts with another Examples: 1. Flammability – how well something reacts with oxygen to produce heat/flame 2. Reactions with acid – how well something reacts with an acid. Main reaction with and acid results in bubbling. When an acid reacts with another substance, usually hydrogen gas (which is highly explosive) is released 3. Other Reactions – include heat being released, bubbling, strong odor, smoke, flame, change of color, etc. 4. Non-Reactivity – when something fails to react…example…platinum dropped in acid has no reaction…nothing happens. Even when held into a flame, platinum has no reaction ** Main Point to Remember about Chemical Reactions… They always produce a new substance – totally different that the substance you started with Most chemical reactions cannot be reversed Characteristic Property – Can be Physical or Chemical Something unique to a substance – doesn’t matter how much or how little the sample of matter is Chemical characteristic property (of sodium) = sodium ignites when in contact with water PHYSICAL CHANGE The appearance may change, but you still have the same substance as before – can be reversed and no energy is produced Example – Tear a piece of paper into 10-15 pieces. The shape and size have changed, but its still paper Example – Change of state = physical change…add energy to ice and you get a liquid…add more energy and you get a gas…all physical changes as it is still water Example – Dissolving things is a physical change…salt in water will temporarily mix then separate out if left standing…can be separated back into water and salt CHEMICAL CHANGE A change that occurs when materials react or are broken into different materials In a chemical change the physical appearance changes and you have a different substance than what you started out with BOTH physical and chemical properties may change Energy may be produced or absorbed Usually chemical changes cannot be reversed unless you make another chemical change