* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy and Metabolism
Survey
Document related concepts
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (H+-translocating) wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Electron transport chain wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
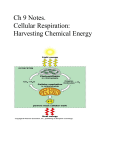
6 Energy and Metabolism 1. Where does glycolysis take place? 2. What does glycolysis do? 3. What does glycolysis use up, which needs to be restored before glycolysis can continue? 4. What is another name for the Kreb’s Cycle? 5. Where does the Kreb’s Cycle occur? 6. What is necessary for the Kreb’s Cycle to occur? 7. What does the Kreb’s Cycle do? 8. What is the waste product of the Kreb’s Cycle? 9. In the Kreb’s Cycle what is NAD reduced to? 10. Where is the NADH sent? Why? 11. What is the Electron Transport System also known as? Cytoplasm Converts glucose, fructose, or galactose (sugars) into 2 pyruvate molecules plus 2 ATP. The pyruvate is then sent to the mitochondria to undergo the Kreb’s cycle to make more energy molecules. It uses NAD because it becomes reduced to NADH. The tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA) or Citric Acid Cycle In the mitochondria Oxygen, pyruvate, and acetate (in the form of Acetyl CoA) It uses pyruvate (end product of glycolysis) and it also uses Acetyl CoA (end product of carbohydrate, fat, or protein metabolism) and creates energy molecules which are like ATP. Carbon dioxide. NADH To the Electron Transport System so it can be converted back to NAD so glycolysis can continue. The electron transport system is also known as Cellular respiration & Oxidative phosphorylation 12. How many NADH and FADH molecules are taken from glycolysis and the TCA cycle in the electron transport system? 13. In the electron transport system, what are the NADH and FADH molecules reduced to so that glycolysis can continue? 8 NADH molecules and 2 FADH molecules are taken from glycolysis and TCA cyles and taken into the electron transport system. 14. What is generated as a result of the electron transport system? 15. Which two compounds can be used as the final electron acceptor when the electron transport system is performing under anaerobic conditions? Can humans use these? ATP is generated as a result of the electron transport system. Sulfate or Nitrite are two compounds that can be used when the electron transport system is performing under anaerobic conditions. Humans do not have these to use; only microbes can do this. The NADH molecules are reduced to NAD and the FADH are reduced to FAD so that glycolysis can continue. 1 6 Energy and Metabolism 16. What are two possible waste products of the electron transport system when it is performing under anaerobic conditions? 17. If sulfate is used when the electron transport system is performing under anaerobic conditions, what is the waste product? 18. If nitrite is used when the electron transport system is performing under anaerobic conditions, what is the waste product? 19. What is consumed when the electron transport system is performing in the presence of oxygen? 20. What is the waste product of the electron transport system when performing in the presence of oxygen? 21. What three fermentation pathways are used when oxygen is not present and therefore NADH molecules can’t use the electron transport chain to be converted back to NAD? 22. Which fermentation pathway is used by humans when no oxygen is present (such as in muscles during sprint running)? 23. In a homolactic pathway the H+ from NADH is donated to what substance, converting it what kind of waste product? Hydrogen sulfide or Ammonia are two possible waste products of the electron transport system when performing under anaerobic conditions. Hydrogen sulfide is the waste product if sulfate is used when the electron transport system is performing under anaerobic conditions. Ammonia is the waste product if nitrite is used when the electron transport system is performing under anaerobic conditions. Oxygen is consumed when the electron transport system is performing in the presence of oxygen. Water is the waste product of the electron transport system when performing in the presence of oxygen. 3 Fermentation pathways: Homolactic Ethanolic 2, 3, Butanediolic Homolactic H+ is donated to pyruvate, converting it inot the waste product: Lactic Acid 24. By breathing heavily, oxygen is added to lactic acid, converting it what? Glucose 25. The lactic acid could also be carried by the bloodstream to the liver, where it is converted back to what? Pyruvate 26. In what ways can lactic acid be Increasing circulation and oxygen eliminated? Ultrasound or massage therapy for sore muscles 27. What pathway do yeasts use in order to Fermentation perform glycolysis? 2 6 Energy and Metabolism 28. In the ethanol fermentation pathway, Ethanol and carbon dioxide what is pyruvate turned into? 29. How do we benefit from yeast’s ability We use yeast to make beer and bread. to ferment? 30. What is the 2, 3, Butanediole Pathway? 31. What is the waste product of this pathway? 32. What type of organisms use this pathway? 33. How do you test a culture for this type of fermentation? 34. What does ATP stand for? 35. What is called the “molecular unit of currency” of intracellular energy transfer? 36. What is ATP’s role in energy production? 37. What happens to ATP when it is used? 38. What happens to ADP? 39. How is Guanosine triphosphate (GTP) different from ATP? A fermentation process that some organisms use when oxygen is not available to convert pyruvate to ATP. 2, 3, Butanediole Enterobacter (a type of coliform bacteria) Positive VP test. Adenosine triphosphate ATP ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism It is also used in muscle contraction, motility and cell division ATP loses one phosphate when used to become ADP (diphosphate). The phosphate that is released is the high energy particle. Metabolic processes convert ADP back to ATP, thus ATP is continuously recycled GTP can only be used as a source of energy for protein synthesis and gluconeogenesis 3