* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Fusion Roman Republic Version A
Alpine regiments of the Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the mid-Republic wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Structural history of the Roman military wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Conflict of the Orders wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Romanization of Hispania wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
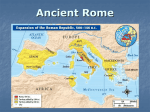
The Roman Republic World History/Napp “Italy is a long, narrow, boot-shaped peninsula extending into the Mediterranean Sea. Rome was a city-state located on a fertile plain in the middle of Italy near the west coast. To the north, the Alps Mountains protected Rome and the rest of Italy from most invaders. The sea provided further protection against invaders, while serving as a route for Roman trade and expansion. The early Roman city-state contained two main social classes: patricians or wealthy landowning families and plebeians or small farmers, craftsmen, and merchants. In early times, the Romans made Rome into a republic. In a republic, citizens vote to elect representatives, or people who will speak and govern for them. The Roman Republic lasted from 509 B.C. to 27 B.C. – almost 500 years. The Romans had two consuls. The consuls managed the government for a one-year term. Each consul could veto, or say to no, a decision by the other consul. Serving only one year and being vetoed kept the consuls from becoming too powerful. The Roman senate, made up of 300 patricians, helped the consuls’ rule. It had the power to pass laws. In times of war, it could choose a dictator for six months. The Roman Republic was not a democracy because it allowed only patricians to vote. Most Romans were plebeians or ‘common people.’ As citizens, the plebeians paid taxes and served in the army. But they had little power. They could not marry out of their class. Also, the patricians could sell plebeians into slavery if they did not pay their debts. However, the plebeians had one important power. They were citizen-soldiers. The patricians needed them to defend Rome against its enemies. In 494 B.C., the Roman Republic gave the plebeians the right to elect two tribunes or representatives of the plebeian class. The tribunes could veto any law that they did not like. ~ World History 1- Identify three geographic features of Italy. 2- How did the Mediterranean Sea benefit the Romans? 3- Identify the two main social classes of the early Roman state. 4- How did these two classes differ? 5- Define republic. 6- How did the Romans prevent political leaders from becoming too powerful? 7- Why were the plebeians able to gain rights? 8- Define tribune. 9- How did the veto benefit plebeians? Patricians/Plebeians - Patricians inherited their power and claimed that their ancestry gave them the authority to make laws for Rome - The plebeians were citizens of Rome with the right to vote but could not hold the most important government positions - In time, Rome’s leaders allowed the plebeians to form their own assembly and elect representatives called tribunes Government - Rome two consuls commanded the army and directed the government - But a consul’s term was only one year long and one consul could veto the other’s decisions - The senate had both legislative and administrative functions - Its 300 senators were chosen from the upper class of Roman society - In times of crisis, the republic could appoint a dictator - A dictator’s power lasted for only six months Army - The Romans placed great value on the military Expansion - By 265 B.C., the Romans were masters of Italy - All citizens who owned land were required to serve in the army - Rome’s location gave it easy access to the riches of the lands around the Mediterranean Sea - Roman soldiers were organized into large military units called legions - However, Carthage, once a colony of Phoenicia – located in North - The Roman legion Africa, competed was made up of some with Rome 5,000 heavily armed foot soldiers - Rome and (infantry) Carthage fought three wars known as - A group of soldiers the Punic Wars on horseback (cavalry) supported - When Rome finally each legion set Carthage afire and sold its 50,000 - Legions were inhabitants into divided into smaller slavery groups of 80 men, each of which was called a century 1- Which social class had the power to make the laws of Rome and which social class gradually gained the right to veto those laws? 2- What could consuls do and not do and why did dictators sometimes rise? 3- How was the Roman army organized? 4- What was the difference between infantry soldiers and cavalry soldiers? 5- Which kingdom competed with Rome for control of the Mediterranean Sea? 6- Why were the Punic Wars fought? 7- What happened to Carthage as a result of the Punic Wars? 1- Why was the Mediterranean Sea important to Rome and Carthage? 2- What three continents are connected by the Mediterranean Sea? 1- How did the Roman Senate differ from the American Senate? 2- What was Rome’s legal code? What is the U.S.’s legal code? 3- Who was a citizen in Rome? 4- Who is a citizen in the United States? 5- How did the executive branch of government in Rome differ from the executive branch of the government in the United States? The Roman republic was dominated by 1. patricians. 2. plebeians. 3. priest. 4. merchants. Which geographic feature was central in helping the Romans unify their empire? 1.Alps 2.Tiber River 3.Mediterranean Sea 4.Great Rift Valley At the height of its power, which ancient civilization controlled the entire coastal region surrounding the Mediterranean Sea? 1. Phoenician 2. Persian 3. Roman 4. Carthaginian How did the geography of the Italian peninsula influence the development of the Roman Empire? 1.The unnavigable rivers in the northern part of the peninsula protected the Romans from their neighbors. 2.The harsh climate prevented agricultural production on the Italian peninsula. 3.The lengthy, rugged seacoast encouraged frequent invasions of the Italian peninsula. 4.The location of the peninsula contributed to Roman control of the Mediterranean region. One contribution of ancient Roman culture was the development of 1. the concept of zero 2. the process of making silk 3. a republican form of government 4. the printing press In a republic, citizens vote for 1. Kings 3. Representatives 2. Clergy 4. Judges Roman women could own property. Roman women could make wills leaving their property to whomever they chose. A valid conclusion drawn from these facts is that Roman women 1. had the right to vote 2. enjoyed some legal rights 3. were equal to men 4. could hold political offices The ideals developed in the Athens of Pericles and in Republican Rome influenced the development of 1. a parliament in Britain 2. military juntas in Latin America 3. a communist government in China 4. a theocracy in Iran A major contribution of the Roman Republic to Western European culture was the 1. concept of government by laws 2. belief that political power should be controlled by the military 3. establishment of agricultural communes 4. rejection of the concept of slavery The ancient Romans’ most significant contribution to Europe has been in the area of 1. economics 2. poetry 3. drama 4. government The Punic Wars were fought between Rome and Carthage for control of 1. The Alps 2. The fertile plain 3. The Pyrenees 4. The Mediterranean Sea