* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Compare and Order Integers and Positive Rational Numbers
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Collatz conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
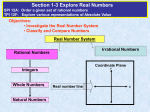
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
P-adic number wikipedia , lookup
7.1A Compare and Order Integers and Positive Rational Numbers Numbers that can be written in the form of a fraction are called rational numbers. Whole numbers, integers, fractions, mixed numbers, and some decimals are rational numbers. The whole number 9 can be written as the fraction 5 1 number -5 can be written as the fraction - . The mixed fraction 2 decimal 2.25 are both equivalent to the fraction to 9 . The 1 1 and the mixed 4 9 . The decimal 0.7 is equivalent 4 7 1 . Therefore, the number 9, the mixed fraction 2 , the mixed decimal 2.25, 10 4 and the decimal 0.7 can be written in the form of a fraction and are all rational numbers. To compare and place a group of rational numbers in order, first convert them to the same form, such as convert all to fractions or all to decimals, and then place them in order. The form you use will depend on the numbers with which you are working. Below are some methods for comparing rational numbers and placing them in order. ● To compare whole numbers, compare the digits in each place value position, starting at the farthest left position. ● To compare fractions with the same denominator, compare the numerators. ● To compare fractions with different denominators, rewrite the fractions as equivalent fractions with the same denominator, then compare the numerators. TEKSING TOWARD STAAR ©2011 7.1A Compare and Order Integers and Positive Rational Numbers To find equivalent fractions: 1. Find LCD (Least common denominator) by listing the multiples of each denominator & find the least number that is in both sets. 2. Set each fraction = LCD & multiply by # to make the equation true # 3. Compare the numerators. Example: Which is greater 5 7 or ? 6 12 Answer: 5 7 is greater than . Since the multiples of 6 are 6, 12, 24, … and the 6 12 1. multiples of 12 are 12, 24, 36, ... ; the Least Common Multiple (LCM) is 12. So, the LCD is12. 7 ? 12 12 2. 5 ? & 6 12 3. 5 2 10 & 6 2 12 7 1 7 12 1 12 4. Now that the denominators are the same, you compare the numerators and see that 5 7 is greater than . 6 12 TEKSING TOWARD STAAR ©2011 7.1A Compare and Order Integers and Positive Rational Numbers ● To compare mixed numbers, first compare the whole-number parts. If the wholenumber parts are equal, then compare the fractional parts (as shown above). ● To compare decimal numbers: 1. Compare the digits in each place value position, starting at the farthest left position. 2. When decimal numbers are compared, the numbers should all have the same number of places to the right of the decimal point. 3. Place zeros to the right of the last digit if necessary to make the decimal number have the same number of decimal places as the other numbers. 4. Look at the value of the digits to help compare decimals. 5. To determine which number is greater, compare the digits in each place value. Start at the left of each number to compare in each place value. (Note - Looking at the numbers using a place-value chart or when drawn on a number line can also help to compare decimals.) ● To compare integers (whole numbers and their opposites), use the number line to compare. On the number line, anything on the left is smaller than the number on its right. Ex. … 5 4 3 2 1 0 1 2 3.... TEKSING TOWARD STAAR ©2011