* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Dynasties, Conquest, and Faith: The Rise of Islam WHAP/Napp Do
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Succession to Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Spread of Islam wikipedia , lookup
History of early Islamic Tunisia wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Iran wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Censorship in Islamic societies wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Abbasid Caliphate wikipedia , lookup
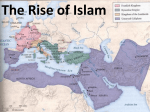
Dynasties, Conquest, and Faith: The Rise of Islam WHAP/Napp Do Now: “When the Prophet died leaving no male heir, the Muslim community feared that the umma and its political organization would break up. To preserve them, the Muslim leadership elected Abu Bakr (r. 632-634), one of Muhammad’s closest associates and the father of his wife Aisha, as caliph – that is, successor to the Prophet and head of the Muslim community. The next three caliphs [the first four caliphs are known as the Righteously Guided Caliphs] were similarly elected from among Muhammad’s relatives and companions, but amidst much more dissension. Abu Bakr mobilized to prevent Muslims from deserting their new religion and the authority of its government, attacking those who tried. Arabia was convulsed in tribal warfare…Their battles spilled over the borders of the Arabian Peninsula…The Byzantine and Sasanid Empires saw the Arab troops encroaching on their territories and fought back, but at the Battle of Ajnadayn (634), in southern Palestine, the Arab clans combined to form a unified army and defeated the Byzantine army. With their victory at Ajnadayn, the Arab warriors were no longer simple raiders in search of plunder. They were now at war for the control of settled empires. Conquest followed conquest… After Ali’s [the fourth caliph’s] assassination, the Umayyad [members of Uthman’s – the third caliph’s – family or clan] leader, Mu’awiya (r. 661-680), declared himself caliph. Moving the capital out of Arabia to Damascus in Syria, Mu’awiya distanced himself from the original Muslim elite of the Arabian Peninsula. He opened Islam to more cosmopolitan influences and a more professional style of imperial administration. Tension remained high among the various religious and tribal factions… The Abbasid clan in northern Iran – descended from an uncle of Muhammad named Abbas and also claiming support from descendants from the line of Ali – revolted against the Umayyads. Supported by Arab settlers in Iran who were protesting against high taxes, by Shi’as who were seeking their own rule, and also by a faction from Yemen, the Abbasid clan overthrew the Umayyad caliphate. In 750, Abu al-Abbas al-Saffah initiated the new Abbasid caliphate, which ruled in reality for a century and a half but held power in name until 1258. Signaling new policy directions, the Abbasid caliph built a new capital at Baghdad, 500 miles east of Damascus, along the banks of the Tigris River, in the heart of the historic fertile crescent.” ~ The World’s History 1- Why did the death of the Prophet lead to conflict in the Islamic world? ________________________________________________________________________ 2- Who was Abu Bakr and why was he significant? ________________________________________________________________________ 3- Why was the Battle of Ajnadayn a turning point in the Islamic world? ________________________________________________________________________ 4- Define caliph. ________________________________________________________________________ 5- How did the Umayyad rise to power and change the Islamic world? ________________________________________________________________________ 6- Who was Abu al-Abbas al-Saffah and how did he rise to power? ________________ I. The Caliphate A. When Muhammad died unexpectedly in 632, Abu Bakr became caliph B. A Caliph is head of state, military commander, chief judge, religious leader 1. A Theocracy: government (caliphate) regarded as divinely guided 2. But no clear line of succession caused trouble C. The First Four Caliphs 1. Abu Bakr, Umar, Uthman, and Ali a) Ali was assassinated and was succeeded by his son, Hasan b) Under pressure from prominent family in Mecca, Hasan relinquished title, leading to establishment of Umayyad Dynasty II. The Umayyad Dynasty A. Capital moved to Damascus, Syria, although Mecca was always the spiritual center B. Arabic became the official language of government C. The empire extended as far as northern African and into Spain (ruled the southern Iberian peninsula from the city of Córdoba) 1. Charles Martel, Frank, stopped Muslim advance towards Paris D. Despite successes (the Dome of the Rock was built in Jerusalem and Córdoba was one of the richest cities in Europe), problems with succession 1. Muslims split into two camps, Shi’ite and Sunni a) Shi’ite (Shia) Islam holds that Mohammad’s son-in-law, Ali, was rightful heir b) Sunnis believe that leaders should be drawn from the umma c) As Shia began to assert themselves, Umayyad Dynasty went into decline III. The Abbasid Dynasty A. Abu al-Abbas defeated Umayyad and established Abbasid Dynasty B. Established around 750 in all areas except Spain C. Dates: 750 to 1258 (Until defeated by Mongols) D. Experienced a golden age: arts and sciences flourished 1. Mohammad al-Razi published a massive medical encyclopedia 2. Expanded knowledge learned from India; contributions in algebra E. Built a magnificent capital at Baghdad F. Importance of trade: Merchants introduced the unique idea of credit G. Papermaking – Learned from Chinese Prisoners of War 1. Defeated Tang Chinese army during the Battle of Talus River in 751 CE 2. Chinese prisoners of war were carrying paper money H. Location of empire at crossroads of Europe/Asia allowed to monopolize trade I. Preservation of Greek and Roman learning 1. A significant role in preserving Western culture (like the Byzantines) J. Crusades and Rediscovery 1. Muslims and Christians battled for control of Levant (present-day Israel, Jordan, Syria, Lebanon) during Crusades 2. Europe found its own history preserved in Arabic libraries K. Often tolerant 1. Particularly of Jews and Christians (“People of the Book”) L. Sufis 1. Islamic mysticswere its most effective missionaries 2. Stressed personal relationship with Allahmade Islam highly adaptable 1- Why was the Islamic Empire a theocracy? ________________________________________________________________________ 2- Define caliph and caliphate. ________________________________________________________________________ 3- What relation did the first four caliphs have to the Prophet? ________________________________________________________________________ 4- Who was the last caliph and what happened to the last caliph? ________________________________________________________________________ 5- Why was there a problem regarding succession in the Islamic world? ________________________________________________________________________ 6- What is the primary belief of Shi’a regarding the succession of the Prophet? ________________________________________________________________________ 7- What is the primary belief of Sunni regarding the succession of the Prophet? ________________________________________________________________________ 8- To which group [Sunni or Shi’a] do the majority of Muslims belong? ________________________________________________________________________ 9- How was the Umayyad Dynasty established? ________________________________________________________________________ 10- Where was the capital of the Umayyad Dynasty? ________________________________________________________________________ 11- What land in Western Europe did the Umayyad conquer? ________________________________________________________________________ 12- Why is the Battle of Tours considered a turning point in world history? ________________________________________________________________________ 13- What led to the collapse of the Umayyad Dynasty? ________________________________________________________________________ 14- What did the Islamic world experience during the Abbasid Dynasty? ________________________________________________________________________ 15- Identify two accomplishments of the Islamic golden age. ________________________________________________________________________ 16- Where was the capital of the Abbasid Dynasty? ________________________________________________________________________ 17- Why is the Battle of Talus River significant in world history? ________________________________________________________________________ 18- What advantages did Islamic Empires have regarding trade? ________________________________________________________________________ 19- What did the Islamic Empires preserve that the Byzantines also preserved? ________________________________________________________________________ 20- What were the Crusades? ________________________________________________________________________ 21- What did the Europeans discover during the Crusades? ________________________________________________________________________ 22- Why was the Islamic Empire considered religiously tolerant? ________________________________________________________________________ 23- Who were the Sufis and what did Sufis stress? ________________________________________________________________________ 1. Which Muslim groups overthrew the Umayyad dynasty and set up a new caliphate? (A) Sassanids (B) Seljuks (C) Abbasids (D) Swahilis (E) Sunnis 2. Which of the following is true of the Sufis? (A) They were very effective missionaries (B) They sought and emotional and mystical union with Allah. (C) They used emotional sermons and song and dance to encourage devotion. (D) They tolerated observances of some non-Islamic customs. (E) All of the above. 3. Which of the following was an immediate effect of the initial Muslim conquests of the seventh century C.E.? (A) The elimination of Christianity and Judaism from the Middle East (B) The beginning of large-scale migration of Turkic-speaking nomads from Central Asia to the Middle East (C) The weakening of the Byzantine Empire and the collapse of other empires (D) A decline in the social status of women 4. During Abbasid times, the Arabs learned from China the technique of making (A) Fine silk. (B) Wood block prints. (C) Gunpowder and cannons. (D) Paper. (E) All of the above. 5. Which of the following is true of the early caliphs? (A) The early caliphs quickly rejected many of Muhammad’s teachings. (B) The caliph was strictly a political leader, not a religious leader. (C) The early caliphs were unanimously agreed upon by the umma. (D) The early caliphs concentrated on religious doctrine, not expansion. (E) None of the above. 6. The type of wall decoration illustrated above would most commonly be found in a (A) Stupa (B) Mosque (C) Cathedral (D) Temple (E) Marketplace 7. The split between Sunni and Shi’a Muslims occurred as a result of (A) Divergent interpretations of religious texts (B) Conflict over the translation of liturgy into native languages (C) Disagreement over leadership succession issues (D) A rift between more fundamentalist and more liberal branches of Islam Thesis Practice: Analyze changes and continuities in political and religious leadership from the death of the Prophet in 632 to 1258 in the Islamic world. ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________