Cultural Institutions Under The Fatimids
... born thirty years after the death of al-Farabi and died in 429/1036 Ibn Sina was a native of Bukhara and familiar with both Parisian and Arabic He mentions in his autobiography that his father and his brother had Isma’ili sympathies, and this may have aroused his interest in philosophy, which had be ...
... born thirty years after the death of al-Farabi and died in 429/1036 Ibn Sina was a native of Bukhara and familiar with both Parisian and Arabic He mentions in his autobiography that his father and his brother had Isma’ili sympathies, and this may have aroused his interest in philosophy, which had be ...
The Effective Reasons for the Rise and fall of Abbasids State
... Both Arab researchers and contemporary scholars have conducted several studies on the Abbasids state. Tabari History, Yaghoubi history, The Meadows of Gold, The History of Caliphs, Fakhri history etc. are ancient sources used in this article. Contemporary sources are The Abbasid State by Muhammad So ...
... Both Arab researchers and contemporary scholars have conducted several studies on the Abbasids state. Tabari History, Yaghoubi history, The Meadows of Gold, The History of Caliphs, Fakhri history etc. are ancient sources used in this article. Contemporary sources are The Abbasid State by Muhammad So ...
- 1 - The Institute of Ismaili Studies Intellectual life in Fatimid Times A
... initiation process used by the Ismaili da‘is to win over people of different persuasions. Special attention is given to two important da‘is of the period, Abu ‘Abd Allah al-Shi‘i (d. 911 CE) and al-Qadi al-Nu‘man (d. 974 CE). The third chapter, The Fatimids in Egypt, offers a historical perspective ...
... initiation process used by the Ismaili da‘is to win over people of different persuasions. Special attention is given to two important da‘is of the period, Abu ‘Abd Allah al-Shi‘i (d. 911 CE) and al-Qadi al-Nu‘man (d. 974 CE). The third chapter, The Fatimids in Egypt, offers a historical perspective ...
LALLA ESSAYDI
... Revolt in the eighth century was a significant threat to the authority and stability of the Ummayad Caliphate. Ibn Battuta (1304–1368/9), a Berber from the ancient city of Tangier, personifies a number of the many significant opportunities for new forms of mobility and boundary-crossing of geographi ...
... Revolt in the eighth century was a significant threat to the authority and stability of the Ummayad Caliphate. Ibn Battuta (1304–1368/9), a Berber from the ancient city of Tangier, personifies a number of the many significant opportunities for new forms of mobility and boundary-crossing of geographi ...
Paul E. Walker, ed. and tr. Orations of the Fatimid Caliphs: Festival
... required contemplation of the world and God’s creation and a search beyond the obvious or apparent to human faculties. In this conviction they were no different from some of the great Muslim philosophers of the day, like Ibn Sina, who not coincidentally came from a family many of whose members were ...
... required contemplation of the world and God’s creation and a search beyond the obvious or apparent to human faculties. In this conviction they were no different from some of the great Muslim philosophers of the day, like Ibn Sina, who not coincidentally came from a family many of whose members were ...
The Umayyad Dynasty - Harrison Humanities
... • Set off a problem that exists today – the succession of the Islamic state • Caliph – Islamic political and religious successor to Muhammad • Eventually the Umayya clan seized leadership of Islam and set out to conquer all of the Middle East and north Africa. ...
... • Set off a problem that exists today – the succession of the Islamic state • Caliph – Islamic political and religious successor to Muhammad • Eventually the Umayya clan seized leadership of Islam and set out to conquer all of the Middle East and north Africa. ...
Abbasid Caliphate
... • The caliph Umar prohibited Arabs from assuming ownership of conquered lands • In order to serve in the army, and receive pay, soldiers needed to live in military camps • Kept the armies together, ready for action • Preserved life in the countryside • A small number of Arabs ruled of a vastly large ...
... • The caliph Umar prohibited Arabs from assuming ownership of conquered lands • In order to serve in the army, and receive pay, soldiers needed to live in military camps • Kept the armies together, ready for action • Preserved life in the countryside • A small number of Arabs ruled of a vastly large ...
essay2 - The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
... in order to be gain the full support of his people. Another way the Umayyad dynasty lost contact with the umma was through the excessive luxury and opulence of these Caliphs. Egger claims that over time “it became clear that the new rulers were not as pious as their forebears had been,” because of a ...
... in order to be gain the full support of his people. Another way the Umayyad dynasty lost contact with the umma was through the excessive luxury and opulence of these Caliphs. Egger claims that over time “it became clear that the new rulers were not as pious as their forebears had been,” because of a ...
The Arabs
... A large revolutionary movement broke out in 747 in Iran, gathering together, under the leadership of Abū Muslim, many peasants and townsmen. This revolt expanded in the following years in Syria and Iraq. Abu-al-Abbas, a ...
... A large revolutionary movement broke out in 747 in Iran, gathering together, under the leadership of Abū Muslim, many peasants and townsmen. This revolt expanded in the following years in Syria and Iraq. Abu-al-Abbas, a ...
Al Chalaffa El Rashdun
... A permanent instead of a tribal army. The Arabisation of all the system, Arab coinage, Arabic as the official language, administration in Arabic Establishment of the Dome of the Rock The Second civil war took place after Mawaya died. The enemy was the Umayyad. The caliphs after him (his son and gran ...
... A permanent instead of a tribal army. The Arabisation of all the system, Arab coinage, Arabic as the official language, administration in Arabic Establishment of the Dome of the Rock The Second civil war took place after Mawaya died. The enemy was the Umayyad. The caliphs after him (his son and gran ...
05.Wikipedia - List.of.articles.on
... o 5.2 Selection of the leader 6 Famous caliphs 7 See also 8 Notes 9 References 10 Further reading 11 External links History[edit] The caliph was often known as Amir al-Mu'minin (Arabic: نرمم ؤملا ريمأ "Commander of the Believers"). Muhammad established his capital in Medina; after he d ...
... o 5.2 Selection of the leader 6 Famous caliphs 7 See also 8 Notes 9 References 10 Further reading 11 External links History[edit] The caliph was often known as Amir al-Mu'minin (Arabic: نرمم ؤملا ريمأ "Commander of the Believers"). Muhammad established his capital in Medina; after he d ...
caliphs_and_golden_age_of_islam
... Explain how the struggle over sovereignty and the distribution of wealth within the Empire led to the demise of the Umayyad Dynasty. In your answer explain the nature of the dispute after the death of Mohamed, the social classes and political parties that existed within the Umayyad Dynasty, and the ...
... Explain how the struggle over sovereignty and the distribution of wealth within the Empire led to the demise of the Umayyad Dynasty. In your answer explain the nature of the dispute after the death of Mohamed, the social classes and political parties that existed within the Umayyad Dynasty, and the ...
The Abbasid Caliphate was the third of the Islamic
... The Fatimid Caliphate (909–1171 CE) Several factions challenged the Abbasids to their claims to the Caliphate. Most of Shi'a had supported the Abbasid war against the Umayyads because they both claimed legitimacy with their familial connection to Muhammad. However, once in power, the Abbasids embrac ...
... The Fatimid Caliphate (909–1171 CE) Several factions challenged the Abbasids to their claims to the Caliphate. Most of Shi'a had supported the Abbasid war against the Umayyads because they both claimed legitimacy with their familial connection to Muhammad. However, once in power, the Abbasids embrac ...
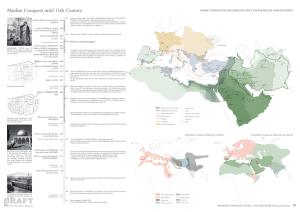
Muslim Conquest until 11th Century
... FATIMIDS (branch of Shi`its) most stable of the successor Dynasties founded in the ninth and tenth centuries gain power in Egypt and attack Palestine, Syria, and Arabia. For a time the Fatimids aspired to be rulers of the whole Islamic world, and their achievements were impressive, but the Fatimid`s ...
... FATIMIDS (branch of Shi`its) most stable of the successor Dynasties founded in the ninth and tenth centuries gain power in Egypt and attack Palestine, Syria, and Arabia. For a time the Fatimids aspired to be rulers of the whole Islamic world, and their achievements were impressive, but the Fatimid`s ...
an Islamic Empire
... Signs of things to come: • Brutal treatment of Umayyad → absolutist • Capital in Baghdad → strong Persian influence • Growing power of wazir → bureaucratization ...
... Signs of things to come: • Brutal treatment of Umayyad → absolutist • Capital in Baghdad → strong Persian influence • Growing power of wazir → bureaucratization ...
Role and History of the Caliphate
... by a council of electors (Majlis), but was soon perceived by some to be ruling as a "king" rather than an elected leader. Uthman was killed by members of a disaffected group. Ali then took control but was not universally accepted as caliph by the governors of Egypt, and later by some of his own guar ...
... by a council of electors (Majlis), but was soon perceived by some to be ruling as a "king" rather than an elected leader. Uthman was killed by members of a disaffected group. Ali then took control but was not universally accepted as caliph by the governors of Egypt, and later by some of his own guar ...
POD 7 The Golden Age of Islam
... • Theology and religious law became the focus of the court - Scholars devoted themselves to studying the Koran • Oversaw a period of conversion of conquered populations - Discrimination against non-Arab converts began to decline • Built a new shining city at Baghdad • The empire eventually became to ...
... • Theology and religious law became the focus of the court - Scholars devoted themselves to studying the Koran • Oversaw a period of conversion of conquered populations - Discrimination against non-Arab converts began to decline • Built a new shining city at Baghdad • The empire eventually became to ...
Slides Lecture 6
... entwined? • To what extent are ‘original’ Muslims more faithful to Islam than later converts? ...
... entwined? • To what extent are ‘original’ Muslims more faithful to Islam than later converts? ...
From Mrs. Walton*s World Studies I Class
... • Under the idea of jihad, or “struggle in the way of God” the early Muslims expanded their territory. The believed that defensive warfare was permitted by the Quran. ...
... • Under the idea of jihad, or “struggle in the way of God” the early Muslims expanded their territory. The believed that defensive warfare was permitted by the Quran. ...
After Muhammad`s death in 632, his father-in
... Caliphate which lasted until 661. Following Abu’s death in 634, no clear line of succession had been established. The first two caliphs succeeding Abu were assassinated. Muhammad’s son-in-law (Ali Hussein) became caliph in 656 and was assassinated five years later. These first four successors to Muh ...
... Caliphate which lasted until 661. Following Abu’s death in 634, no clear line of succession had been established. The first two caliphs succeeding Abu were assassinated. Muhammad’s son-in-law (Ali Hussein) became caliph in 656 and was assassinated five years later. These first four successors to Muh ...
Cultural Characteristics of the Middle East
... The Kurds live in several countries throughout the region. These include Turkey, Syria, Iraq, and Iran. Almost one-fifth of the population of Turkey is Kurdish. Kurdish religion used to be made up of a mixture of several different religions, but most are Sunni Muslim. ...
... The Kurds live in several countries throughout the region. These include Turkey, Syria, Iraq, and Iran. Almost one-fifth of the population of Turkey is Kurdish. Kurdish religion used to be made up of a mixture of several different religions, but most are Sunni Muslim. ...
Dynasties, Conquest, and Faith: The Rise of Islam WHAP/Napp Do
... leadership elected Abu Bakr (r. 632-634), one of Muhammad’s closest associates and the father of his wife Aisha, as caliph – that is, successor to the Prophet and head of the Muslim community. The next three caliphs [the first four caliphs are known as the Righteously Guided Caliphs] were similarly ...
... leadership elected Abu Bakr (r. 632-634), one of Muhammad’s closest associates and the father of his wife Aisha, as caliph – that is, successor to the Prophet and head of the Muslim community. The next three caliphs [the first four caliphs are known as the Righteously Guided Caliphs] were similarly ...
Islam
... consolidated the Caliph. Islam was briefly united under one caliph. Promoted religious tolerance to Sunnis, Jews, and Coptic Christians Established a massive trade network in the Mediterranean, Indian Ocean, and East Asia during the Song Dynasty of China. ...
... consolidated the Caliph. Islam was briefly united under one caliph. Promoted religious tolerance to Sunnis, Jews, and Coptic Christians Established a massive trade network in the Mediterranean, Indian Ocean, and East Asia during the Song Dynasty of China. ...
History of early Islamic Tunisia
The History of early Islamic Tunisia opens with the arrival of the Arabs who brought their language and the religion of Islam, and its calendar. The Arab conquest followed strategy designed by the Umayyad Caliphate regarding its long-term conflict with the Byzantine Empire. The native Berbers eventually converted to Islam. They might have seen some similarities between themselves and the Arabs, in similar cognate culture, such as familiarity with a pastoral way of life. The first local Islamic ruling house, the Aghlabids, consisted primarily of rule by leading members of this Arab tribe. Fundamental elements of Islamic civilization were established. Although accepting Islam, many Berbers nonetheless resisted rule by the Arabs, establishing the Rustamid kingdom following the Kharijite revolt. Next in Ifriqiya (Tunisia) arose the Shia Fatimids, inspired by a few immigrants from the east yet consisting for the most part of Ifriqiya Berbers. The Fatimids later expanded their rule east, through conquest by Berber armies of Egypt, and established their caliphate there which came to include Syria and the Hejaz.