Some Reflections on the Institutions of Muslim Spain: Unity in
... Damascus caliphs occurred a few years later, after the `Abbasids took over, dethroned, and then killed most members of the Umayyad family. However, `Abd al-Rahman ibn Mu`awiya al-Dakhil, a surviving member of the Umayyad royal family, made his way to al-Andalus. After obtaining the region’s bay`ah, ...
... Damascus caliphs occurred a few years later, after the `Abbasids took over, dethroned, and then killed most members of the Umayyad family. However, `Abd al-Rahman ibn Mu`awiya al-Dakhil, a surviving member of the Umayyad royal family, made his way to al-Andalus. After obtaining the region’s bay`ah, ...
The Arabs (cont.) - Valhalla High School
... The Abbasid Dynasty (cont.) • The Abbasid Empire had problems. • It experienced much fighting over succession to the caliphate. • Harun al-Rashid’s two sons almost destroyed Baghdad when they fought to succeed him. • Vast wealth led to financial corruption, and a shortage of qualified Arabs t ...
... The Abbasid Dynasty (cont.) • The Abbasid Empire had problems. • It experienced much fighting over succession to the caliphate. • Harun al-Rashid’s two sons almost destroyed Baghdad when they fought to succeed him. • Vast wealth led to financial corruption, and a shortage of qualified Arabs t ...
As Word (text only) - Discover Islamic Art
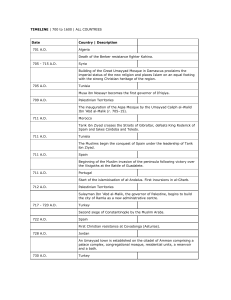
... the second Islamic capital of Egypt, is founded. Marwan ibn Muhammad, the last Umayyad Caliph in the East, is murdered in Abu Seir, Fayyum, west of the Delta. 750 A.D. ...
... the second Islamic capital of Egypt, is founded. Marwan ibn Muhammad, the last Umayyad Caliph in the East, is murdered in Abu Seir, Fayyum, west of the Delta. 750 A.D. ...
AP World History Review
... the ancient traditions of philosophy and science. E) Islamic culture excluded any recognition of the achievements of earlier civilizations. ...
... the ancient traditions of philosophy and science. E) Islamic culture excluded any recognition of the achievements of earlier civilizations. ...
AP WORLD HISTORY REVIEW 650 CE – 1450 CE
... the ancient traditions of philosophy and science. E) Islamic culture excluded any recognition of the achievements of earlier civilizations. ...
... the ancient traditions of philosophy and science. E) Islamic culture excluded any recognition of the achievements of earlier civilizations. ...
Chapter 7: Abbasid Decline and the Spread of Islamic Civilization to
... Southeast Asia from India and was spread by Sufi holy men, it developed a mystical nature that incorporated much of indigenous religion. The Sufi mystics and traders were most responsible for converting many Indians to Islam ...
... Southeast Asia from India and was spread by Sufi holy men, it developed a mystical nature that incorporated much of indigenous religion. The Sufi mystics and traders were most responsible for converting many Indians to Islam ...
Japan - cloudfront.net
... they allowed non-Arabs into government, more tolerant of Shi’ites. Umayyads came before Abbasids and were bigger. **What is one similarity? They are both Sunni Muslim empires, they both rule over roughly the same area for a time, they both instituted a jizya on non-Muslims 50 pts. Which man overthre ...
... they allowed non-Arabs into government, more tolerant of Shi’ites. Umayyads came before Abbasids and were bigger. **What is one similarity? They are both Sunni Muslim empires, they both rule over roughly the same area for a time, they both instituted a jizya on non-Muslims 50 pts. Which man overthre ...
Islamic astronomy by Owen Gingerich.
... century most of the Greek scientific texts were translated into Arabic, including Ptolemy’s Syntaxis, the apex of ancient astronomy. It was through these translations that the Greek works later became known in medieval Europe. (Indeed, the Syntaxis is still known primarily by its Arabic name, Almage ...
... century most of the Greek scientific texts were translated into Arabic, including Ptolemy’s Syntaxis, the apex of ancient astronomy. It was through these translations that the Greek works later became known in medieval Europe. (Indeed, the Syntaxis is still known primarily by its Arabic name, Almage ...
Medieval World - Calicut University
... 92. …………..became a constituent kingdom of the Holy Roman Empire in 962. a) Italy b) France c) Netherlands d) Austria 93. While Urban II remained as the Pope in Rome, Clement VII was made the Pope at Avignon in…………... This is known as the ‘western schism’. a) France b) Austria c) Spain d)Belgium 94.I ...
... 92. …………..became a constituent kingdom of the Holy Roman Empire in 962. a) Italy b) France c) Netherlands d) Austria 93. While Urban II remained as the Pope in Rome, Clement VII was made the Pope at Avignon in…………... This is known as the ‘western schism’. a) France b) Austria c) Spain d)Belgium 94.I ...
Chapter 7
... After the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the fifth century, the eastern portion of the Empire continued to thrive. Centered on the magnificent city of Constantinople, a unique Christian culture developed known as Byzantium. The Byzantines eventually converted the peoples of Eastern Europe to Ch ...
... After the fall of the Western Roman Empire in the fifth century, the eastern portion of the Empire continued to thrive. Centered on the magnificent city of Constantinople, a unique Christian culture developed known as Byzantium. The Byzantines eventually converted the peoples of Eastern Europe to Ch ...
Unit 3 - yauger.net
... would have lost tax revenues. C. They lacked the political organization to govern them and feared insurrection by non-Arabs. D. Conversion would have slowed down the process of conquest. E. They wanted to keep high religious offices among themselves. ...
... would have lost tax revenues. C. They lacked the political organization to govern them and feared insurrection by non-Arabs. D. Conversion would have slowed down the process of conquest. E. They wanted to keep high religious offices among themselves. ...
Study Guide
... and closest friends His two-year reign was marked by tribal rebellions and the expansion of the Muslim state into southern Syria and Iraq powerful Muslim clan that established first dynastic Arab caliphate. Of the same tribe as Mohammed. Expanded Muslim empire to its limits. Capital of Umayyad Calip ...
... and closest friends His two-year reign was marked by tribal rebellions and the expansion of the Muslim state into southern Syria and Iraq powerful Muslim clan that established first dynastic Arab caliphate. Of the same tribe as Mohammed. Expanded Muslim empire to its limits. Capital of Umayyad Calip ...
As Word (text only) - Discover Islamic Art
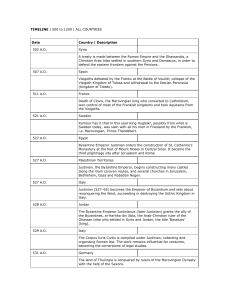
... The first Islamic gold coin devoid of iconographic representation is struck in Damascus by Umayyad Caliph ‘Abd al-Malik, with Arabic declaration of faith. Arabisation of the administration. ...
... The first Islamic gold coin devoid of iconographic representation is struck in Damascus by Umayyad Caliph ‘Abd al-Malik, with Arabic declaration of faith. Arabisation of the administration. ...
Period 3: Regional and Transregional Interactions, c. 600 C.E. to c
... Damascus: Ancient Islamic cultural center; capital of present-day Syria. ...
... Damascus: Ancient Islamic cultural center; capital of present-day Syria. ...
The Arab Muslim Empire
... The last member of the Umayyad caliphate fled to Spain and established a Muslim state. • Muslim rule lasted in parts of Spain until 1492. • They oversaw a grand age of art and architecture, exemplified by the Grand Mosque in Córdoba (left). • Leaders of Muslim Spain were more tolerant of other relig ...
... The last member of the Umayyad caliphate fled to Spain and established a Muslim state. • Muslim rule lasted in parts of Spain until 1492. • They oversaw a grand age of art and architecture, exemplified by the Grand Mosque in Córdoba (left). • Leaders of Muslim Spain were more tolerant of other relig ...
File
... The last member of the Umayyad caliphate fled to Spain and established a Muslim state. • Muslim rule lasted in parts of Spain until 1492. • They oversaw a grand age of art and architecture, exemplified by the Grand Mosque in Córdoba (left). • Leaders of Muslim Spain were more tolerant of other relig ...
... The last member of the Umayyad caliphate fled to Spain and established a Muslim state. • Muslim rule lasted in parts of Spain until 1492. • They oversaw a grand age of art and architecture, exemplified by the Grand Mosque in Córdoba (left). • Leaders of Muslim Spain were more tolerant of other relig ...
Period`3:`Regional`
... closest friends His two-year reign was marked by tribal rebellions and the expansion of the Muslim state into southern Syria and Iraq powerful Muslim clan that established first dynastic Arab caliphate. Of the same tribe as Mohammed. Expanded Muslim empire to its limits. Capital of Umayyad Caliphate ...
... closest friends His two-year reign was marked by tribal rebellions and the expansion of the Muslim state into southern Syria and Iraq powerful Muslim clan that established first dynastic Arab caliphate. Of the same tribe as Mohammed. Expanded Muslim empire to its limits. Capital of Umayyad Caliphate ...
HISTORY OF THE MEDIEVAL WORLD MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS BA HISTORY. IV SEMESTER
... mathematical thinking among Muslims. C. The caliphs adopted Persian ideas of kingship. D. Greek rational reasoning had a long-lasting influence on the theological development of Islam. 96.The nature of the society into which the prophet Muhammad was born was A. An urban-based culture with small manu ...
... mathematical thinking among Muslims. C. The caliphs adopted Persian ideas of kingship. D. Greek rational reasoning had a long-lasting influence on the theological development of Islam. 96.The nature of the society into which the prophet Muhammad was born was A. An urban-based culture with small manu ...
IV semester
... mathematical thinking among Muslims. C. The caliphs adopted Persian ideas of kingship. D. Greek rational reasoning had a long-lasting influence on the theological development of Islam. 96. The nature of the society into which the prophet Muhammad was born was A. An urban-based culture with small man ...
... mathematical thinking among Muslims. C. The caliphs adopted Persian ideas of kingship. D. Greek rational reasoning had a long-lasting influence on the theological development of Islam. 96. The nature of the society into which the prophet Muhammad was born was A. An urban-based culture with small man ...
The Early `Abbasid Baghdad
... Tigris • Ibrahim al-Fazari (d. 179/796 or 190/806) • Translated the Indian book of Astronomy, Sindhind, into Arabic for al-Mansur • Helped plan the foundation of Baghdad • The first in the Arab world to make astrolabes ...
... Tigris • Ibrahim al-Fazari (d. 179/796 or 190/806) • Translated the Indian book of Astronomy, Sindhind, into Arabic for al-Mansur • Helped plan the foundation of Baghdad • The first in the Arab world to make astrolabes ...
MWNF - Discover Baroqueart
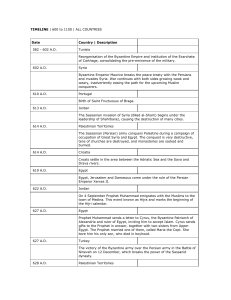
... The first Islamic gold coin devoid of iconographic representation is struck in Damascus by Umayyad Caliph ‘Abd al-Malik, with Arabic declaration of faith. Arabisation of the administration. ...
... The first Islamic gold coin devoid of iconographic representation is struck in Damascus by Umayyad Caliph ‘Abd al-Malik, with Arabic declaration of faith. Arabisation of the administration. ...
Umayyad Caliphs Build an Empire
... The last member of the Umayyad caliphate fled to Spain and established a Muslim state. • Muslim rule lasted in parts of Spain until 1492. • They oversaw a grand age of art and architecture, exemplified by the Grand Mosque in Córdoba (left). • Leaders of Muslim Spain were more tolerant of other relig ...
... The last member of the Umayyad caliphate fled to Spain and established a Muslim state. • Muslim rule lasted in parts of Spain until 1492. • They oversaw a grand age of art and architecture, exemplified by the Grand Mosque in Córdoba (left). • Leaders of Muslim Spain were more tolerant of other relig ...
A Time to Review Post-Classical Civilizations WHAP/Napp Islam
... Wave after wave of traders and travelers carried the message of Muhammad across the sands of the Sahara along caravan routes Egypt was added to Muslim territories in the tenth century The authoritarian rulers of African states in the savannas south of the Sahara Desert adapted well to the Mus ...
... Wave after wave of traders and travelers carried the message of Muhammad across the sands of the Sahara along caravan routes Egypt was added to Muslim territories in the tenth century The authoritarian rulers of African states in the savannas south of the Sahara Desert adapted well to the Mus ...
As Word (text only) - Discover Islamic Art
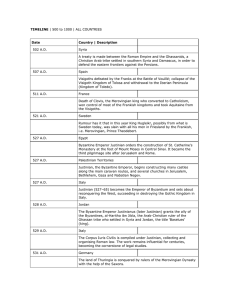
... The first Islamic gold coin devoid of iconographic representation is struck in Damascus by Umayyad Caliph ‘Abd al-Malik, with Arabic declaration of faith. Arabisation of the administration. ...
... The first Islamic gold coin devoid of iconographic representation is struck in Damascus by Umayyad Caliph ‘Abd al-Malik, with Arabic declaration of faith. Arabisation of the administration. ...
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate (/əˈbæsəd/ or /ˈæbəsəd/ Arabic: الخلافة العباسية al-Khilāfah al-‘Abbāsīyah) was the third of the Islamic caliphates to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. The Abbasid dynasty descended from Muhammad's youngest uncle, Abbas ibn Abd al-Muttalib (566–653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs, for most of their period from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after assuming authority over the Muslim empire from the Umayyads in 750 CE (132 AH).The Abbasid caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, north of the Sasanian capital city of Ctesiphon. The choice of a capital so close to Persia proper reflected a growing reliance on Persian bureaucrats, most notably of the Barmakid family, to govern the territories conquered by Arab Muslims, as well as an increasing inclusion of non-Arab Muslims in the ummah. Despite this cooperation, the Abbasids of the 8th century were forced to cede authority over Al-Andalus and Maghreb to the Umayyads, Morocco to the Idrisid dynasty, Ifriqiya to the Aghlabids, and Egypt to the Shi'ite Caliphate of the Fatimids. The political power of the caliphs largely ended with the rise of the Buyids and the Seljuq Turks. Although Abbasid leadership over the vast Islamic empire was gradually reduced to a ceremonial religious function, the dynasty retained control over its Mesopotamian demesne. The capital city of Baghdad became a center of science, culture, philosophy and invention during the Golden Age of Islam.This period of cultural fruition ended in 1258 with the sack of Baghdad by the Mongols under Hulagu Khan. The Abbasid line of rulers, and Muslim culture in general, recentered themselves in the Mamluk capital of Cairo in 1261. Though lacking in political power, the dynasty continued to claim authority in religious matters until after the Ottoman conquest of Egypt (1517).