* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Psych Disorders
Bipolar disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antipsychotic wikipedia , lookup
Reactive attachment disorder wikipedia , lookup
Emil Kraepelin wikipedia , lookup
Substance use disorder wikipedia , lookup
Schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Bipolar II disorder wikipedia , lookup
Conduct disorder wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatric institutions wikipedia , lookup
Depersonalization disorder wikipedia , lookup
Emergency psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Conversion disorder wikipedia , lookup
Panic disorder wikipedia , lookup
Antisocial personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Kleptomania wikipedia , lookup
Personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Sluggish schizophrenia wikipedia , lookup
Obsessive–compulsive disorder wikipedia , lookup
Autism spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Asperger syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Glossary of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Schizoaffective disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental status examination wikipedia , lookup
Narcissistic personality disorder wikipedia , lookup
Generalized anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Mental disorder wikipedia , lookup
Separation anxiety disorder wikipedia , lookup
Dissociative identity disorder wikipedia , lookup
Spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
Pyotr Gannushkin wikipedia , lookup
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders wikipedia , lookup
History of psychiatry wikipedia , lookup
Classification of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Causes of mental disorders wikipedia , lookup
Child psychopathology wikipedia , lookup
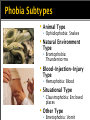
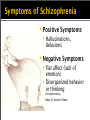
Announcements Exam 3: Wednesday, 12/14 50 MC Optional Cumulative Exam: Wednesday, 12/14 50 MC questions from Exams 1-3 Replaces lowest exam score (i.e., cannot hurt you) Psychological Disorders Psychological Disorders: Introduction to Psychological Disorders Anxiety Disorders Mood Disorders Psychotic Disorders Services Counseling Phone (Office hours): (206) 934-2917 http://seattlecentral.edu/counsel/index.php If you are interested in visiting the Counseling Center for personal concerns, please call to schedule an appointment or email Lori Ann Miller [email protected] Introduction to Psychological Disorders Intro to ψ Disorders: Outline Defining “abnormal” behavior How do we understand psychological disorders? (causes) How do we classify psychological disorders? Rates of psychological disorders What is “Abnormal”? Abnormal (dictionary) Away from the usual or typical Statistically, a deviation from some norm or standard How do we decide if a behavior is abnormal? Defining “Abnormal” Behavior “3 D’s” of diagnosis: Deviant Distressful Dysfunctional Defining Abnormal “I felt the need to clean my room … would spend four to five hours at it … At the time I loved doing it. Then I didn't want to do it any more, but I couldn’t stop … The clothes hung … two fingers apart …I touched my bedroom wall before leaving the house … I had constant anxiety … I thought I might be nuts.” Marc, diagnosed with obsessive-compulsive disorder (from Summers, 1996) Causes of ψ Disorders Prior to the 1800’s: Demons or possessed Ancient treatments of psychological disorders Beating Burning Castrating Animal blood transfusion Stoning Torturing Trephination (boring holes in the skull to remove evil forces) Causes of ψ Disorders Medical Model (1800’s) Psychological disorders as mental illnesses with physical causes that can be diagnosed, treated, and in most cases cured Key components: Etiology: Cause and development Diagnosis: Identifying symptoms Treatment: Treating disorders Prognosis: Forecast Causes of ψ Disorders Bio-psycho-social Approach Psychological disorders as influenced by biological, psychological, and social-culture influences Classifying Disorders DSM: Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (American Psychological Association) Describes the symptoms and prevalence of various disorders Criticisms of Classification: Labeling Labeling is biggest criticism of DSM Labels can be stigmatizing Labels create preconceptions that guide our perception and interpretations Ex. Rosenhan Study (1972) Ex. Rent Study Rates of ψ Disorders Prevalence: 450 million people worldwide suffer from a psychological disorder 26% of Americans in any given year 46% of Americans some time in their lives Most common U.S. disorders: Phobias, alcohol abuse, and mood disorders (e.g., depression) ψ Disorders: U.S. ψ Disorders: Worldwide Intro to ψ Disorders: Summary Defining “abnormal” behavior “3 D’s” How do we understand psychological disorders? Prior to 1800’s, Medical Model, Bio-psycho-social approach How do we classify psychological disorders? DSM-IV-TR Rates of psychological disorders Anxiety Disorders Anxiety Disorders “Panic is a sudden desertion of us, and a going over to the enemy of our imagination.” ~Christian Nevell Bovee “Fear is a darkroom where negatives develop.” ~Usman B. Asif Anxiety Disorders Anxiety Disorders (AD): Category of mental disorders characterized by: Distressing, persistent anxiety (or) Maladaptive behaviors that reduce anxiety Examples Panic disorder Phobias Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Anxiety Disorders Anxiety Disorders (AD): Category of mental disorders characterized by: Distressing, persistent anxiety (or) Maladaptive behaviors that reduce anxiety Examples Panic disorder Phobias Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Anxiety Disorders: Phobias Who thinks they have a phobia? What are you afraid of? Do you have these symptoms? Diarrhea Panic Attacks Temporary Paralysis Anxiety Disorders: Phobias Phobia: An AD marked by a persistent, irrational fear and avoidance of a specific object or situation. Prevalence Lifetime rates 7-11% of population Ratio of women to men is 2:1 Phobia Subtypes Animal Type Ophidiophobia: Snakes Natural Environment Type Brontophobia: Thunderstorms Blood-Injection-Injury Type Hemaphobia: Blood Situational Type Claustrophobia: Enclosed places Other Type Emetophobia: Vomit Examples of “Other” Phobias Anthropophobia: people Ataxiophobia: disorders Bymnophobia: nudity Gamophobia: marriage Hedonophobia: pleasure Kakorrhaphiophobia: failure Phrenophobia: going insane Hippopotomonstrosesquippedaliophobia long words Treatment of Phobias Behavioral Therapy: Mostly exposure therapy Based on principles of operant conditioning ▪ Extinguish fear behavior ▪ Develop new behavior Virtual Exposure Therapy Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD) Anxiety Disorders: OCD OCD: An AD characterized by: unwanted repetitive thoughts (Obsessions) (and/or) unwanted repetitive actions (Compulsions) Prevalence of OCD Lifetime rates of 2.5% Adults: Equally common in women and men Treatment of OCD Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy Similar to phobias – exposure therapies Treatment of OCD Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy Similar to phobias – exposure therapies Medication Serotonin Anxiety Disorders: Summary Overview of anxiety disorders Phobias Subtypes Treating phobias with behavioral therapies Obsessive Compulsive Disorder Characteristics Video: Treatment Mood Disorders Mood Disorders “I have studiously tried to avoid ever using the word 'madness' to describe my condition. Now and again, the word slips out, but I hate it. 'Madness' is too glamorous a term to convey what happens to most people who are losing their minds. That word is too exciting, too literary, too interesting in its connotations, to convey the boredom, the slowness, the dreariness, the dampness of depression.” - Elizabeth Wurtzel Prozac Nation Mood Disorders “to the person in The Bell Jar, black and stopped as a dead baby, the world itself is a bad dream” - Sylvia Plath, 1971 Sylvia Plath, Self Portrait Mood Disorders Mood Disorders: A category of disorders characterized by a disturbance in mood Examples Bipolar Disorder Dysthymic Disorder Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) The Guitarist (1903) Pablo Picasso Mood Disorders Mood Disorders: A category of disorders characterized by a disturbance in mood Examples Bipolar Disorder Dysthymic Disorder Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) The Guitarist (1903) Pablo Picasso Mood Disorders: MDD MDD: A mood disorder in which a person experiences 2+ weeks of: Depressed mood (OR) Loss of interest/pleasure in most activities Accompanied by other symptoms: Weight and sleep change Fatigue or low energy Trouble concentrating Feelings of worthlessness Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) Cultural variations in symptoms presentation Prevalence Wide range (5-25%) Women diagnosed more than men Treatment of MDD Treatment Cognitive therapy (focus on thoughts) Interpersonal therapy (focus on relationships) Medication ▪ Anti-depressants Mood Disorders: Summary Overview of mood disorders Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) Characteristics and prevalence Treatment Psychotic Disorders Psychotic Disorders “When I was 16 or 17, I suddenly got up in the middle of the day [at school] and started walking home several miles away, something I'd never done before. I was a good girl — I never skipped school. And as I was walking, the houses got very ominous and foreboding, and I started to think that they were sending me messages. 'Look! See! You must see! You are bad! You are evil!' I didn't hear it as voices; they were thoughts, but I thought they were thoughts put in my head by the houses. It was very scary.” - Elyn Saks Psychotic Disorders Psychotic Disorders: A category of disorders that include psychotic symptoms Examples Delusional Disorder Schizophrenia Psychotic Disorders Psychotic Disorders: A category of disorders that include psychotic symptoms Examples Delusional Disorder Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Schizophrenia: A group of severe disorders characterized by Disorganized and delusional thinking Disturbed perceptions Inappropriate emotions and actions Subtypes of Schizophrenia Paranoid Preoccupation with delusions or hallucinations Disorganized Disorganized speech or behavior; flat or inappropriate emotion Catatonic Immobility & extreme negativitism, parroting Undifferentiated Many and varied symptoms Residual Withdrawal, after hallucinations & delusions have disappeared Symptoms of Schizophrenia Positive Symptoms Hallucinations, delusions Negative Symptoms Flat affect (lack of emotion) Disorganized behavior or thinking Schizophrenia by Haley N. ‘Everlorn’ Baker Schizophrenia Cultural variations Prevalence U.S.: 0.5% - 1.5% Treatment Mostly medication ▪ Antipsychotics Skill-based therapy Cats Louis Wain Schizophrenia “I would not dare to say that there is a direct relation between mathematics and madness, but there is no doubt that great mathematicians suffer from maniacal characteristics, delirium and symptoms of schizophrenia.” ~ John Forbes Nash Video: Overcoming Schizophrenia: John Nash’s Beautiful Mind ψ Disorders: Summary Anxiety Disorders Phobias OCD Mood Disorders MDD Psychotic Disorders Schizophrenia