* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download By Erik,Brianna,michael,wyatt
Magnetosphere of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic storm wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetosphere of Saturn wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Van Allen radiation belt wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
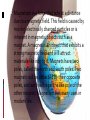
Magnetism BY ERIK, BRIANNA, MICHAEL, WYATT The properties or effects of magnetic fields. There is magnetism in credit cards, phones, and the earth. On Earth one needs a sensitive needle to find magnetic forces, and out in space they are usually a lot weaker. But beyond the dense atmosphere, such forces have a much bigger role, and a region exists around the Earth where they dominate the environment, a region known as the Earth's magnetosphere. That region contains a mix of electrically charged particles, and electric and magnetic rather than gravity determine its structure. We call it the Earth's atmosphere. Magnetism is a force that acts at a distance due to a magnetic field. This field is caused by moving electrically charged particles or is inherent in magnetic objects such as a magnet. A magnet is an object that exhibits a strong magnetic field and will attract materials like iron to it. Magnets have two poles, called the north and south poles. Two magnets will be attracted by their opposite poles, and each will repel the like pole of the other magnet. Magnetism has many uses in modern life. wwwistp.gsfc.nasa.gov/Education/Imagnet.html http://www.school-forchampions.com/science/magnetism.htm http://www.mcwdn.org/Physics/Magnetism.ht ml.com











![magnetism review - Home [www.petoskeyschools.org]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/002621376_1-b85f20a3b377b451b69ac14d495d952c-150x150.png)

