* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Magnetic Materials
Negative-index metamaterial wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electromotive force wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical descriptions of the electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Edward Sabine wikipedia , lookup
Magnetometer wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic stripe card wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Earth's magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Superconducting magnet wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic nanoparticles wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotactic bacteria wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Magnetotellurics wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Magnetohydrodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Giant magnetoresistance wikipedia , lookup
Magnetoreception wikipedia , lookup
Force between magnets wikipedia , lookup
Multiferroics wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
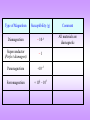
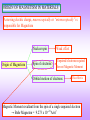
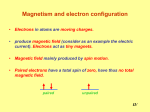
MAGNETIC MATERIALS Origin of Magnetism Types of Magnetism Hard and Soft Magnets Magnetic Materials – Fundamentals and Device Applications Nicola Spaldin Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2003) BASICS 1 p1 p2 F 40 r 2 1 p1 p2 F H p2 2 40 r 0 4 x 10 7 Wb / A / m Henry / m p1 H 2 r [ A / m] Material in a Magnetic Field The response of a material to a Magnetic Field H is called Magnetic Induction B The relationship between B and H is a property of the material In some materials and in free space B is a linear function of H but in general it is much more complicated and sometimes it is not even single valued B 0 ( H M ) M H B [Weber / m2 ] [Tesla ] Magnetic Susceptibility m M M Magnetization Magnetic Moment (m) per unit volum e V Type of Magnetism Susceptibility () Comment Diamagnetism 105 All materials are diamagnetic Superconductor (Perfect diamagnet) 1 Paramagnetism +103 Ferromagnetism + 102 – 105 ORIGIN OF MAGNETISM IN MATERIALS A moving electric charge, macroscopically or “microscopically” is responsible for Magnetism Origin of Magnetism Nuclear spin Weak effect Spin of electrons Unpaired electrons required for net Magnetic Moment Orbital motion of electrons This effect is Magnetic Moment resultant from the spin of a single unpaired electron → Bohr Magneton = 9.273 x 1024 A/m2 In the solid the outer orbitals of the atoms interact to form Energy bands → the simple picture used for an atom has to be modified Teh Superconducting Diamagnetic A pole of unit strength is one which exerts a force of one d