* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER 1 Networking Concepts
Cryptanalysis wikipedia , lookup
Cross-site scripting wikipedia , lookup
Web of trust wikipedia , lookup
Next-Generation Secure Computing Base wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Airport security wikipedia , lookup
Information security wikipedia , lookup
Transport Layer Security wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
History of cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Secure multi-party computation wikipedia , lookup
Cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
International cybercrime wikipedia , lookup
Post-quantum cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
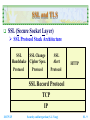
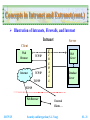
Security and Integration Technologies on the Internet (TANET 2002 Tutorial I-1) Shin-Jer Yang, Associate Professor Dept. of Computer and Information Science Soochow University, Taipei E-mail: [email protected] October 30, 2002 Security and Integration Technologies on the Internet Web Security Review SSL and TLS SET Concepts in Intranet and Extranet Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets Conclusions Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) Web Security Requirements Web Traffic Security Approaches SSL TLS Intranet Development Tools Standards Security (1) Internet Transmission (2) Firewalls (3) Filtering (4) Encryption 2017/5/25 SI - 2 Web Security Review Web Security Requirements A Comprehensive Network Security Services Confidentiality Authentication Integrity Non-repudiation Access Availability Responsibility and Control Accountability: Refers to how an audit trail is kept Authorization: Refers to responsibility for each item of information and how such responsibility is delegated to others 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 3 Web Security Review (cont.) Web Security Considerations The Internet is two ways The Web is increasingly serving as a highly visible outlet for corporate and product information and as the platform for business transaction Although Web Browser are very easy to use, Web Servers are relatively easy to configure and manage, and Web Content is increasingly easy to develop, the underlying software is extraordinarily complex A Web Server can be exploited as a launching pad into the corporation’s or agency’s entire computer complex Causal and untrained users are common Clients for Web-based services 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 4 Web Security Review (cont.) Vulnerabilities of the Web Unauthorized alteration of data at the Web site Unauthorized access to the underlying operating system at the Web server Eavesdropping on messages passed between a Web Server and a Web Browser Impersonation Web Security Responsibility A corporate responsibility Compounding the problem is that the culture of the Internet: Openness, Ease of access, and Lack of controls Sociology and Ethics 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 5 Web Security Review (cont.) Web Security Threats Security threats can be classified as passive attacks and active attacks Passive attacks: Passive attacks have to do with eavesdropping on, or monitoring, transmissions Active attacks: Active attacks include the modification of transmitted data and attempts to gain unauthorized access to computer systems Location of threats Web Server Web Browser Network traffic between Browser and Server 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 6 Web Security Review (cont.) Web Traffic Security Approaches (1) Network Level HTTP FTP SMTP TCP or UDP IP / IPSec (2) Transport Level HTTP 2017/5/25 FTP SMTP SSL or TLS TCP or UDP IP Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 7 Web Security Review (cont.) Web Traffic Security Approaches (3) Application Level S/MIME Kerberos 2017/5/25 PGP SMTP TCP or UDP IP Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SET HTTP SI - 8 SSL and TLS SSL (Secure Socket Layer) SSL Protocol Stack Architecture SSL Handshake Protocol SSL Change Cipher Spec. Protocol SSL Alert Protocol HTTP SSL Record Protocol TCP IP 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 9 SSL and TLS (cont.) Two Important SSL Concepts SSL Session An SSL session is an association between a Client and a Server Sessions are created by the Handshake Protocol Sessions define a set of cryptographic security parameters A session state is defined by the following parameters Session identifier Peer certificate Compression method Cipher spec. function Master secret Is resumable 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 10 SSL and TLS (cont.) SSL Connection A connection is a transport that provides a suitable type of service For SSL, such connections are peer-to-peer relationships The connections are transient Every connection is associated with one session A connection state is defined by the following parameters 2017/5/25 Server and Client random Server write MAC (Message Authentication Code) secret Client write MAC secret Server write key Client write key Initialization vectors Sequence numbers Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 11 SSL and TLS (cont.) SSL Record Protocol The SSL record protocol provides two services for SSL connection Confidentiality Defines a shared secret key that is used for conventional encryption of SSL payloads Message integrity Used to form a MAC SSL Record Operation (See Next) 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 12 SSL and TLS (cont.) SSL Record Protocol Operation Sender (or Client) An application message to be transmitted, Fragments the data into manageable blocks Optionally Compresses the data Applies a MAC (i.e. Add a MAC) Encrypts Appends SSL record header Transmits the resulting unit in a TCP segment Receiver (or Server) Received the data and drop the header Received data are Decrypted Verified Decompressed Reassembled and then delivered to high-level users 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 13 SSL and TLS (cont.) SSL Handshake Protocol The most complex part of SSL This protocol allows the Server and Client to authenticate each other and to negotiate an encryption and MAC algorithm and cryptographic keys to be used to protect data sent in an SSL record Each message has three fields Type (1 byte) Length (3 bytes) Content (>= 1 byte) 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 14 SSL and TLS (cont.) Handshake protocol action phases Phase 1: Establish security capabilities Phase 2: Server authentication and key exchange Phase 3: Client authentication and key exchange Phase 4: Finish Cryptographic computations Master secret creation RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) Diffie-Hellman Generation of Cryptographic parameters 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 15 SSL and TLS (cont.) TLS (Transport Layer Security) TLS is an IETF standardization initiative whose goal is to produce an Internet standard version of SSL The current version of TLS is very similar to SSL v3 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 16 SET SET (Secure Electronic Transaction) SET is an open encryption and security specification designed to protect credit card transactions on the Internet SET Provides Three Services Provides a secure communications channel among all parties involved in a transaction Provides trust by the use of X.509v3 digital certificates Ensures privacy because the information is only available to parties in a transaction when and where necessary 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 17 SET (cont.) Business Requirements for SET over Internet Provide confidentiality of payment and order information Ensure the integrity of all transmitted data Provide authentication that a cardholder is a legitimate user of a credit card account Provide authentication that a merchant can accept credit card transactions through its relationship with a financial institution Ensure the use of the best security practices and system design techniques to protect all legitimate parties in an electronic commerce transactions Create a protocol that neither depends on transport security mechanisms nor prevents their use Facilitate and encourage interoperability among software and network providers 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 18 SET (cont.) Key Features of SET Confidentiality of information Integrity of data Cardholder account authentication Merchant authentication Payment Processing and SET Participants Payment processing Purchase request Payment authorization Payment capture SET participants Cardholder, Merchant, Issuer, Acquirer, Payment Gateway, Certification Authority (CA) What are the sequences of events that are required for a transaction? Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) 2017/5/25 SI - 19 Concepts in Intranet and Extranet Intranet An Intranet is an internal organizational network that is modeled upon WWW technology Intranet software technology is the same as that of the WWW The difference between the Internet and an Intranet Internet is open to anyone The Intranet is private (VPN – Virtual Private Network) and is protected from public visits by firewalls VPN: Intranet and Firewalls Intranet vs. VPN 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 20 Concepts in Intranet and Extranet (cont.) Illustration of Intranets, Firewalls, and Internet Intranet Server Client Web Browser TCP/IP Internet TCP/IP TCP/IP F I R E W A L L Web Server Database Server TCP/IP Web Browser 2017/5/25 External Clients … Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 21 Concepts in Intranet and Extranet (cont.) Factors that drive the growth in the Intranet marketplace Open standards lead to interoperability Ease of use Effective middleware Intranet Web Web content: An organization can use the Intranet Web to enhance managementemployee communication and to provide jobrelated information easily and quickly 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 22 Concepts in Intranet and Extranet (cont.) Web / Database Applications Ease of administration Deployment Development speed Flexible information presentation Intranet Webs vs. Traditional Client/Server Long development cycles Difficulty of partitioning applications into Client and Server modules Effort involved in distributing upgrades to Client Difficulty in scaling the Servers to respond to increased load in a distributed environment Continuous requirement for increasingly powerful desktop machine 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 23 Concepts in Intranet and Extranet (cont.) Other Intranet Technologies E-mail Network News: USENET Intranet Development Tools Limitations of Intranets Intranet cannot replace complex information systems Appropriate security measures are required for Intranet Effective Intranets require careful management for planning 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 24 Concepts in Intranet and Extranet (cont.) Potential Advantages of Intranets Access to information Platform independence Allowance for multiple data types Access to data (i.e. Data Warehouses, Databases) Similar interface Return on investment (ROI) Increased productivity Increased information sharing Easy of software distribution Bottom-up approach 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 25 Concepts in Intranet and Extranet (cont.) Disadvantages or Challenges of Intranets Number of active users Infrastructure Continuous growth and change Security Bandwidth Scalability Manageability Loss of skilled Webmasters and designers On-going maintenance 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 26 Concepts in Intranet and Extranet (cont.) Intranets Are Currently Being Used for the Following Purposes 2017/5/25 Facilitate faster internal corporate communications Facilitate more coordinated work activities Facilitate easier management of complex operations with On Line Transaction Processing (OLTP) Facilitate better managerial decision support with On Line Analytical Processing (OLAP) Facilitate better system management by enabling maintenance and distribution of applications Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 27 Concepts in Intranet and Extranet (cont.) Other Intranet Applications Technology-driven marketing ERP II or EERP Logistics and supply chain management Finance and accounting Decision support / Workflow management Company policies and procedure manuals Product and pricing information Company forms (organizational directories, employee information, job openings) On-line polls Document needing signatures 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 28 Concepts in Intranet and Extranet (cont.) Extranet An Extranet is a network that uses Internet technology to link business with their partners, customers, suppliers and other businesses that share common goals The Extranet is a derivative of both an Intranet and the Internet The purpose of an Extranet is to give both internal and external environments access to computer-based information 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 29 Concepts in Intranet and Extranet (cont.) Potential Advantages of Extranets Streamlined business processes Flexibility and scalability Reduced traditional barriers Decreased costs Ease of use and maintenance Versatility Cost and return on investment Disadvantages or Challenges of Extranets No support from top management Maintenance of information Lack of training Information overload Waste of productivity Security 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 30 Concepts in Intranet and Extranet (cont.) Some Extranet Applications Private news groups Collaborative projects Common business materials Inter-Organization systems (IOS) Electronic Commerce (EC) e-Workflow Management SCM (Supply Chain Management) CRM (Customer Relationship Management): Improved customer service and sales 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 31 Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets Intranet Development Tools Advanced features for development tools Does it allow for connectivity to database? Does it have a visual-form designer? Does it generate reports? Does it support dynamic HTML or XML? Does it support Java Script or Java? Does it support version control? More general issues for development tools How easy is it to use, both for developers and end users? Is it easy to extend? 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 32 Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets (cont.) Is it easy to manage? Does it have built-in management tools? What type of performance does it have? What hardware platforms does it run on? What network operating systems and operating systems does it work with? Four common Intranet Development Tools Visual InterDev from Microsoft Corporation Visual Café for Java from Symantec Corporation IntraBuilder from Borland International Sapphire/Web from Bluestone Software 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 33 Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets (cont.) Standards TCP/IP This protocol is the basis for the Internet and it controls the reliable transmission of data from node to node HTML/XML and HTTP These support platform-independent content creation and publishing SMTP This messaging protocol is used in TCP/IP networks to exchange e-mail messages IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) IMAP’s features include selective downloading , Server-side folder hierarchies, shared mail, and mailbox synchronization (POP 3 extension version) 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 34 Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets (cont.) MIME This standard is an extension of SMTP; MIME gives each attachment of an E-mail message its own header NNTP (Network News Transport Protocol) UseNet servers transfer news items using this specialized transfer protocol LDAP Intelligent Directory Services This protocol will store and deliver contact information, registration data, certificates, configuration data, and Server information X.509 v3 Digital Certificates This standard provides for a secure container of validated and digitally signed information 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 35 Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets (cont.) S/MIME (Secure MIME) This standard uses certificate-based authentication and encryption to transmit messages between users and applications vCARD The vCARD is an industry format for describing and displaying information typically found on a business card Signed Objects These allow for trusted distribution and execution of software applications and applets as part of an Extranet EDI INT This protocol gives a set of guidelines that combine the existing EDI standards for transmission of transaction data with the Internet protocol suite 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 36 Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets (cont.) Security (1) Internet Transmissions Following security of Internet transmissions actually involves multiple processes Encryption: Renders data indecipherable to any unauthorized users that might be able to examine packets of data traffic Authorization: Screens users according to user IDs and passwords and determines by examining Access Control Lists (ACLs) whether a given user is authorized to access requested files or system resources Authentication: Uses digital signatures attached to transmitted documents to ensure both the authenticity of the author and the document’s message integrity 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 37 Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets (cont.) (2) Firewalls Firewall software usually runs on a dedicated Server that is connected to but outside of the corporate network All network packets entering the firewall are filtered, or examined, to determine whether those users have authority to access requested files or services Types of firewalls Packet-filtering routers (or Packet-filters) Application-level gateway (or Proxy Server) Circuit-level gateway Bastion host servers as a platform for an Applicationlevel or Circuit-level gateway 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 38 Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets (cont.) (3) Filtering A filter is a program that examines the source address and destination address of every incoming packet to the firewall Server Filter tables are lists of addresses whose data packets and embedded messages are either allowed to proceed or prohibited from proceeding through the firewall Server and into the corporate network Filter classification Port-level filters (Network-level filters) Application-level filters (Assured pipelines) 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 39 Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets (cont.) (4) Encryption A. Conventional Encryption Also referred to as symmetry encryption or single-key encryption A form of cryptosystem in which encryption and decryption are performed using the same key This encryption scheme has five ingredients Plaintext: Readable message or data Encryption Algorithm: Performs various substitutions and transformations on the plaintext Secret Key: The secret key is also input to the algorithm Ciphertext: This is the scrambled message produced as output Decryption Algorithm: This is essentially the encryption algorithm run in reverse 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 40 Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets (cont.) Two requirements for secure use of conventional encryption We need a strong encryption algorithm Sender and receiver must have obtained copies of the secret key in a secure fashion and must keep the key secure DES (Data Encryption Standards) Algorithm Triple DES Algorithms Double DES: Two encryption stages and two keys Triple DES with two keys: Three encryption stages and two keys Triple DES with three keys: Three encryption stages and three keys 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 41 Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets (cont.) B. Public-Key Encryption A method in which encryption and decryption are performed using different keys – public key and private key RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adlemen) algorithm Performs Encryption/Decryption, Digital signatures and Key exchange Three possible approaches to attacking the RSA Brute force Mathematical attacks Timing attacks Advantage:Public-key encryption provides us with tremendous flexibility to perform a number of securityrelated functions Key management Digital signatures 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 42 Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets (cont.) Public-Key Encryption scheme has six key ingredients Plaintext: Readable message or data Encryption Algorithm: Performs various transformations on the plaintext Public and Private Keys: This is a pair of keys that have been selected so that if one is used for encryption, the other is used for decryption Ciphertext: This is the scrambled message produced as output Decryption Algorithm: This algorithm generates the ciphertext and the matching key and produces the original plaintext 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 43 Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets (cont.) C. Digital Signatures Encryption An authentication mechanisms that enables the creator of a message to attach a code that guarantees the source and integrity of the message The digital signature process RSA approach DSS (Digital Signature Standard) approach: NIST FIP PUB 186 Public-key certificates 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 44 Integrating the Internet, Intranets and Extranets (cont.) D. Encryption Management Location of encryption devices Link encryption End-to-end encryption Key distribution Conventional encryption: It relies on KDC (Key Distribution Center); two kinds of key are identified: session key, permanent key Public-key encryption: To use public-key encryption to authenticate the public key The primary standards exist for encryption traffic on the WWW S-HTTP: Secure HyperText Transport Protocol SSL: Secure Socket Layer TLS: Transport Layer Security 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 45 Conclusions Securing the Web and Intranets Security Measures Access control Encryption Troubleshooting Payload security (e.g. PGY) Commercial products Intrusion detecting Firewalls Why firewalls? What firewalls can not do? Cost 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 46 Conclusions (con.) Integration Issues Selecting the appropriate Intranet development tool Using open application standards instead of proprietary standards for extending the Intranet into an Extranet Two primary standards exist for encryption traffic on the WWW S-HTTP (Secure Hypertext Transfer Protocol) SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) 2017/5/25 Security and Intrgartion (S. J. Yang) SI - 47