* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rome: The Punic Wars - Kenston Local Schools
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Berber kings of Roman-era Tunisia wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
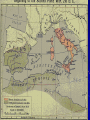
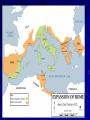
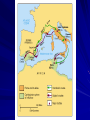
Rome: Expansion Roman Government - Other • Senate • Magistrates • Consuls • Praetors • Censors • Assemblies Groups of citizens who voted on various things within the government. • Tribunes – 10 elected officials from the assemblies who would vote to approve/disapprove of actions of the Senate or other officials. The Army All male citizens had to serve in the army for a certain amount of time. (most commanders were patrician, though plebeians could rise) Legion- Basic unit of the military 4000-6000 soldiers divided into groups of 100 Centurians Auxilia- Army units of non-citizens. Conquered territories were required to provide troops Very strict discipline, and strong incentives. “Strength and Honor” Expanding beyond Italy Romans were proud of their government and culture- thought it was their destiny to be superior to other cultures Allowed conquered people to keep their own Language, customs, religion etc… as long as they obeyed Roman law. (pay taxes, provide troops for Auxilia) Most societies adapt and blend into Rome (cosmopolitan society) The Punic Wars (Rome Vs. Carthage) Who are we fighting and why is it important? Carthage is a city in North Africa. Largest power on South side of Mediterraneanexpanding (like Rome) Wanted territory in Sicily, Sardinia, Spain- and so did Rome Carthage=Sea Power Rome= Land Power First large scale war for Rome- cemented who they were and what they were about First Punic War 264-241 bc Main argument was over Sicily War took time to start b/c Rome needed to build a navy to compete with Carthage (stole one of their boats and copied it). Developed “boarding bridges” to allow them to engage in hand-to-hand combat. Rome wins (sort of)- gets Sicily and forces Carthage to pay Reparations (damages- costs of war) Second Punic War Carthage Strikes back 218-202 BCE Carthage has a great commander- Hannibal. He attacks Rome from the North (unexpected) and uses Scorched Earth- destroys everything he passes to create panic. Cannae- 216 BCE biggest defeat Rome will ever have- can anything stop Hannibal? Rome decided the best plan is attack Carthagedraw Hannibal home- send Scipio 202 BCE Hannibal killed at battle of ZamaRome wins again- gets Spain Third Punic War 149-146 bc Carthage is defeated- but Rome decides that as long as it exists- it is still a threatno one can challenge Rome and live Attack and wipe the city off the earth For good measure- conquer Macedon/Greece because they had been Carthage’s ally. Results of Punic Wars Rome is master of the Mediterranean Have Spain, North Africa, Greece Divide conquered territories into provinces- each with a governor appointed by the senate Conquered citizens become Roman subjects (not citizens) Changes in The Roman Republic • Government • Senate/nobles more powerful • Formation of corrupt, provincial governments. • Agriculture • Small farmers lose land • Rome begins to get grain from outer provinces. • Society • Farmers cannot afford to rebuild – sell land and move to cities. • Urban poor depend on government for food (welfare) • New class of wealthy businessmen (equites)