* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rome Spreads its Power
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
First secessio plebis wikipedia , lookup
Berber kings of Roman-era Tunisia wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
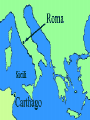
Don’t Go To Your Seat We have a new seating chart Assignment Who is your best friend? Why is this person important to you? BOOKBAGS AT FRONT OF THE ROOM Early Rome The Legend of Rome Twin brothers Remus Romulus Abandoned along the Tiber River Raised by a She-Wolf The Beginnings of Rome Founded along the Tiber River. Fertile soil Settlers arrived between 1000-500 BC 3 groups Latins Greeks Etruscans Three Periods in Roman History Age of Kings- 753-506 B.C. Age of the Republic- 506-30 B.C. Age of the Roman Empire- 30 B.C.- A.D. 476 The Early Republic 600 BC An Etruscan becomes King Tarquin the Proud Formed a Republic A form of government in which power rests with citizens who have the power to vote to select their leaders Class Struggles Patricians The aristocratic landowners who held most of the power. Plebeians The common farmers, artisans, and merchants who made up the majority of the population. Roman Government Twelve Tables Established all Roman citizens had the protection of the law Written down in stone (literally) Consuls 2 Consuls One controlled the Government One controlled the army Term only 1 year long Tribunes The Senate Elected official who represented the plebeians Aristocratic Branch Assemblies Democratic Branch Centuriate Tribal Dictator Elected during times of crisis Legion 5,000 heavily armed foot soldiers Government of Conquered Lands 1. 2. Full Citizenship Partial Citizenship 3. No voting Allies Rome’s Commercial Network Easy access to the Mediterranean Sea Traded with other areas to get what they lacked. Their trading also interfered with other civilizations at the time Carthage War with Carthage Known as the Punic Wars Rome and Carthage go to war in 264 BC War lasted till 146 BC The Punic Wars were divided into 3 separate wars: 1st Punic War Over Sicily Very fertile soil Rome wins Gained its first province overseas. 2nd Punic War Hannibal Carthaginian General Gathered 50,000 infantrymen, 9,000 cavalry, and 60 elephants and crossed the alps Intent on capturing Rome Cannae 216 BC Hannibal’s greatest victory Never captured Rome Roman general Scipio attacks Carthage Hannibal retreats back to Carthage to defend it Hannibal loses at Zama in 202 BC 3rd Punic War (149-146 BC) Carthage was not a threat any longer Romans still bitter Carthage began to flourish once again Cato the Elder urged for the destruction of Carthage Sent troops over and they burned the city Result of conquering Carthage Rome now controlled the Mediterranean Macedonia Greece Parts of Anatolia