* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download + H 2 O(g)
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Supramolecular catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Photoredox catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Drug discovery wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Marcus theory wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Ring-closing metathesis wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Rate equation wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Detailed balance wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
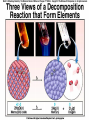
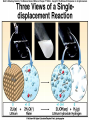
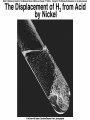
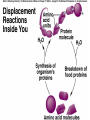
Chemical Reactions Chemical Reaction the process by which one or more substances are changed into one or more different substances REACTANTS the starting substances in a chemical reaction (the stuff on the left) PRODUCTS the final substances in a chemical reaction (the stuff on the right) General Formula for Reactions A+B C Reactants yields Products Law of Conservation of Mass/Matter Mass/Matter can not be created nor destroyed, simply changed from 1 form to another EQUATIONS CH4 + 2O2 CO2 + 2H2O REPRESENTATION OF PHYSICAL STATES IN EQUATIONS You may see these in book problems • (g) = gas • (l) = liquid • (cr) = solid (stands for crystalline) • (aq) = substance dissolved in water WRITING BALANCED EQUATIONS • STEP 1: Write all of the atoms in the reactants and the products (in the same order) • STEP 2: Put * next to the atom in step 1, if an element occurs more than once on one side of a reaction • STEP 3: Balance the equation (get the same # of atoms of each element on each side). You can only do this by changing coefficients! WARNING!!! Never Ever Ever CHANGE THE SUBSCRIPT Hints for Balancing • Balance metals first • Then balance polyatomics • Then balance non-metals • Last, balance hydrogens Hints for Balancing • If an element is by itself, balance it last • Watch for even or odds, balance accordingly • Don’t forget your diatomics in transcribed problems Hints for Balancing • balance anything that is found in 1 product/reactant st 1 , • Then, balance anything that is found in 2 or more products / reactants Reaction of Zinc with HCl Please balance the equation __Zn + __HCl __ZnCl2 + __H2 Zn = 1 Zn = 1 H=1 H=2 Cl = 1 Cl = 2 Combustion of ethane C2H6 Please balance the equation __C2H6 + __O2 __CO2 + __H2O C=2 C=1 H=6 H=2 O=2 *O = 3 Zinc + Hydrochloric Acid Please write the reaction Writing Balanced Equations When Given Words Only • STEP 1: Write out the symbols • STEP 2: Balance your charges (if needed) • STEP 3: Check for diatomics • STEP 4: Balance Equation Hints for Balancing Don’t forget your diatomics in transcribed problems • Don’t forget to Kriss Kross and use ( ) Combustion of Acetone (CH3)2CO Please write the reaction (CH3)2CO(l) + O2(g) CO2(g) + H2O(g) HOMEWORK Pg. 228 #1-12 Pg. 243 #43, 45, 46, 58 Worksheet SYNTHESIS two or more substances combine to form one new substance SYNTHESIS A + B AB Na + Cl2 NaCl Pb(IV) + O2 Pb2O4 Info on Synthesis Reactions • Also known as “combination” reactions • Always form compounds • Generally give off lots of energy • Can be reversed (decomposition) • DECOMPOSITION when a substance breaks up into simpler substances Decomposition AB A + B NaCl Na + Cl2 Pb2O4 Pb + O2 Info on Decomp Reactions • Energy is usually need to make these reactions happen • Often hard to predict products unless the substance breaks into its ionic components (or memorize some basic types of reactions) • Often are the cause of explosions Types Decomp Reactions Metallic Carbonates • When heated, metallic carbonates decompose into metallic oxides and carbon dioxide • BaCO3 --> BaO + CO2 • Cu2CO3 --> Cu2O + CO2 Types Decomp Reactions Metallic Chlorates • When heated, metallic chlorates decompose into metallic chlorides and oxygen • KClO3 --> KCl + O2 • Zn(ClO4)2 --> ZnO + O2 Types Decomp Reactions Metallic Hydroxides • When heated, metallic hydroxides decompose into metallic oxides and water • Ca(OH)2 --> CaO + H2O • Mn(OH)4 --> Mn2O4 + H2O Types Decomp Reactions Metallic Oxides • When heated, metallic oxides decompose into the metal and oxygen • K2O --> K + O2 • Pb2O4 --> Pb + O2 Decomp of Trinitrotoluene 2C7H5N3O6 (s) --> 3N2(g) + 7CO2(g) + 5H2O(g) + 7C(s) • 2 moles of TNT decompose to produce 15 moles of hot, expanding gases…that is why it is so powerful! SINGLE DISPLACEMENT one element displaces another in a compound Single Displacement Reaction Single Displacement AB + C AC + B or CB + A NaBr + Cl2 NaCl + Br2 (NH4)2S + O2 (NH4)2O + S Info on Single Replacement • Also known as single displacement reactions • Only elements with a higher activity can replace other elements (use table on pg. 217) • Nonmetals can replace other nonmetals, but is usually limited to halogens (active decreases down table) Types Single Replacement Metals • More active metal atoms will replace less active metal ions from compounds • Cu + AgNO3 --> Ag + Cu(NO3)2 • Ag + Cu(NO3) --> No Reaction Types Single Replacement Halogens • More active halogen atoms will replace less active halogen ions from compounds • F2 + NaCl --> Cl2 + NaF • Cl2 + FCl --> No Reaction Types Single Replacement Halogens • More active halogen atoms will replace less active halogen ions from compounds • F2 + NaCl --> Cl2 + NaF • Cl2 + FCl --> No Reaction DOUBLE DISPLACEMENT the positive or negative portions of two compounds are switched Double Displacement AB + CD AD + CB NaBr + Pb2S3 Na2S + PbBr3 K2SO4 + Ba(OH)2 KOH + BaSO4 Info on Double Replacement • Also known as double displacement reactions • Reactants must be two ionic compounds in aqueous solution • Cations switch positions • Usually produces a precipitate (ppt) For Double Replacement to Occur one is Usually True • Also known as double displacement reactions • Reactants must be two ionic compounds in aqueous solution • Cations switch positions • Usually produces a precipitate (ppt) COMBUSTION (aka OXIDATION) hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide and water Writing Out Equations • STEP 1: Determine type of rxn • STEP 2: Write out symbols • STEP 3: Kriss-Kross where necessary • STEP 4: Diatomics • STEP 5: Balance the equation Common Words • Decomposes = breaks apart • Combusts = a combustion rxn • Reacts with = A + B • “To form” or “to get”= • Yields = • Displaces = have a single D. rxn • And = plus (+) Common Words • Decomposes = breaks apart • Combusts = a combustion rxn • Reacts with = A + B • “To form” or “to get”= • Yields = • Displaces = have a single D. rxn • And = plus (+) HOMEWORK Pg. 231 #13-22













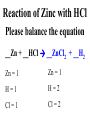
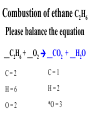






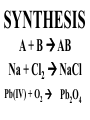



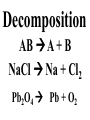








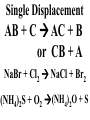







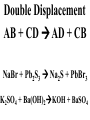

















![Lecture Notes Elements[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008391610_1-fc64e5dd8865e54a6a66a1207eb2c76b-150x150.png)