* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download APOplast
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
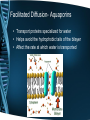
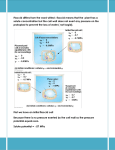
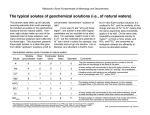
Different Mechanisms Transport Substances over Long and Short Distances Concept 36.2 Mira Patel Transport Continuums APOplast SYMplast • External to the plasma membrane • Includes cell walls, extracellular spaces, and the interior of dead cells such as vessel elements and tracheids • Cytosol • Includes the plasmodesmata, and the cytoplasmic channels that interconnect them Key Symplast Apoplast Transmembrane route Apoplast The symplast is the continuum of cytosol connected by plasmodesmata. Symplast The apoplast is the continuum of cell walls and extracellular spaces. Symplastic route Apoplastic route Transport routes between cells. At the tissue level, there are three passages: the transmembrane, symplastic, and apoplastic routes. Transport Routes • Apoplastic Route – Water and solutes move along the continuum of cell walls and extracellular spaces • Symplastic Route – Water and solutes move along continuum of the cytosol • Transmembrane Route – water and solutes move out of one cell, across the cell wall, and into the neighboring cell Transport Across the Plasma Membrane SHORT DISTANCE TRANSPORT Osmosis • Movement of water across the cell • The diffusion of free water • Water Potential (Ψ) – Quantifies the ability of water to flow • Indicates direction • Takes into account the solute concentration and physical pressure – Water moves from an area of high water potential to an area of low potential – Water Potential POTENTIAL Energy Water Potential- Solute Potential • Also called osmotic pressure • Directly proportional to the molarity (M) • An increase in solutes has a negative effect on water potential • Ψs is always a negative number • As the solute concentration increases, the solute potential becomes more negative – Unless it is pure water, in which case the solute potential is zero Water Potential- Pressure Potential • Physical pressure on a solution • Can be either positive or negative – Relative to the atmospheric pressure • Pressure potential in a living cell is usually positive – Due to the osmotic uptake of water Turgor Pressure • The cell contents press the plasma membrane against the cell wall • The cell wall presses against the protoplast – The living part of the cell Turgor Pressure • This internal pressure is critical for function • Helps maintain the stiffness of the plant • Serves as a driving force for plant elongation Plasmolysis • Flaccid cell placed inside a solution of higher concentration (hypertonic) • Results in plasmolysis – The cell’s protoplast shrinks and pulls away from the cell wall – Causes wilting Initial flaccid cell: 0.4 M sucrose solution: Plasmolyzed cell at osmotic equilibrium with its surroundings Facilitated Diffusion- Aquaporins • Transport proteins specialized for water • Helps avoid the hydrophobic tails of the bilayer • Affect the rate at which water is transported Transport Across the Plasma Membrane LONG DISTANCE TRANSPORT Bulk Flow • Movement of liquid in response to a pressure gradient • From high concentration to low concentration • Independent of solute concentration • Occur within the tracheids and vessel elements of the xylem and within the sieve-tube elements of the phloem The Beauty of it All • Diffusion, active transport, and bulk flow work harmoniously to transport through the whole plant