* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 12: Microbial Pathogenicity
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Type three secretion system wikipedia , lookup
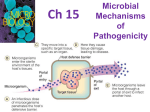
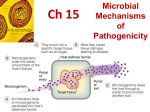
Chapter 12: Microbial Pathogenicity • Pathogenicity The ability to cause disease • Virulence The extent of pathogenicity Portals of Entry • Mucous membranes • Skin • Parenteral route Numbers of Invading Microbes • ID50: Infectious dose for 50% of the test population • LD50: Lethal dose (of a toxin) for 50% of the test population Bacillus anthracis Portal of entry Skin ID50 10-50 endospores Inhalation 10,000-20,000 endospores Ingestion 250,000-1,000,000 endospores Adherence of Microbe • Adhesins/ligands bind to receptors on host cells • Glycocalyx Streptococcus mutans • Fimbriae Escherichia coli • Streptococcus pyogenes • Neisseria gonorrhoeae Pathogenicity Promoters • Coagulates blood • Digests fibrin clots • Hyaluronidase Hydrolyzes hyaluronic acid • Collagenase Hydrolyzes collagen Pathogenicity Promoters • IgA proteases Destroy IgA antibodies • Siderophores Take iron from host ironbinding proteins • Alter surface proteins Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Penetration into the Host Cell Figure 15.2 Toxins • Toxin Substances that contribute to pathogenicity • Toxigenicity Ability to produce a toxin • Toxemia Presence of toxin in the host's blood • Toxoid Inactivated toxin used as a vaccine • i.e. diptheria and tetanus toxoid • Antitoxin Antibodies against a specific toxin Endotoxin Figure 15.4b Endotoxin Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Endotoxins Figure 15.6 Endotoxins Source Gram negative bacteria Location Outer membrane Chemistry Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) → Lipid A Fever? Yes Neutralized by antitoxin No LD50 Relatively large Exotoxins Figure 15.4a Types of Exotoxins • • Cause an intense immune response due to release of cytokines from host cells • Fever, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, shock, death • Types of Exotoxins • Membrane-disrupting toxins • Lyse host cells by: • Making protein channels in the plasma membrane (e.g., • Disrupting phospholipid bilayer • S. aureus and Streptococci ) Types of Exotoxins • A-B toxins • Disrupts internal cellular mechanisms; • Clostridium botulinum produces an A-B neurotoxin • Vibrio cholerae produces an A-B enterotoxin Figure 15.5 Exotoxins Exotoxin Lysogenic conversion • Clostridium botulinum A-B toxin - Neurotoxin + • Vibrio cholerae A-B toxin - Enterotoxin + Exotoxin Source Mostly Gram positive location Secreted by cell Chemistry Fever? Neutralized by antitoxin LD50 Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Protein Type I (Superantigens) Yes Small Pathogenic Properties of Fungi • Fungal metabolic waste products may cause allergies • Proteases • • Vaginal yeast infection • Capsule prevents phagocytosis • LINK • Can cause skin or nervous tissue disease • Found in soil and pigeon droppings Pathogenic Properties of Fungi • Aflatoxin; second link • Aspergillus flavus • • • Infrequently, contaminated peanut butter recalled Neurotoxins • • • mushrooms May be fatal if ingested Ergot toxin • Claviceps purpurea Pathogenic Properties of Protozoa • Avoid host defenses by • Growing inside host cell • i.e. • Antigenic variation • Avoiding host immune system • campers: be careful what you drink! Pathogenic Properties of Helminths • Presence of parasite may interfere with host function • i.e. vessels link parasite clogs lymphatic Pathogenic Properties of Algae • Neurotoxins produced by - Paralytic shellfish poisoning Portals of Exit • Respiratory tract • Coughing, sneezing • Gastrointestinal tract • Feces, saliva • Genitourinary tract • Urine, vaginal secretions, semen • Skin • Skin infections • Blood • Biting arthropods, needles/syringes Mechanisms of Pathogenicity