* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells and tissues of the immune system
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
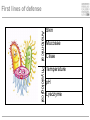
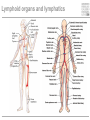
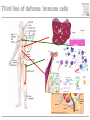
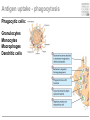
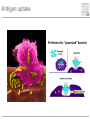
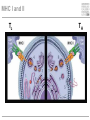
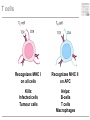
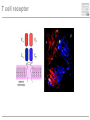
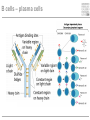
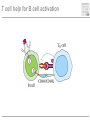
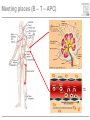
Cells and tissues of the immune system Lisbeth N. Fink Nutritional Immunology Group – CBS - DTU Protecting borders to the outside world Challenges 1) Discrimination between self and non-self – – – – – bacteria fungi vira parasites (transplants) 2) Evolution 3) Dealing with non-pathogenic factors First lines of defense Anatomical Physiological Skin Mucosae Ciliae Temperature pH Lysozyme Lymphoid organs and lymphatics Second line of defense: Humoral factors Humor = liquid (From greek, 4 humors controlling health and mood: blood, phlegm, yellow and black bile) Antibodies – specific pathogen recognition Complement system – non-specific recognition Reactive oxygen species (ROS) – bactericidal activity Inflammation – recruitment of cells Third line of defense: Immune cells Haematopoieisis Red blood cells Leukocytes/ White blood cells Lymphocytes Adaptive/Specific Innate/Non-specific Characteristics of the two parts Adaptive/Specific Innate/Non-specific T cells B cells Antibodies Memory MHC - HLA Diversity Somatic hypermutation Polymorphism Granulocytes Monocytes Macrophages Dendritic cells NK cells NK T cells Complement Pattern recognition Characteristics of the two parts Adaptive/Specific Innate/Non-specific T cells B cells APC Antibodies Memory MHC - HLA Diversity Somatic hypermutation Polymorphism Granulocytes APC Monocytes APC Macrophages APC Dendritic cells APC NK cells NK T cells Complement Pattern recognition Antigen uptake - phagocytosis Phagocytic cells: Granulocytes Monocytes Macrophages Dendritic cells Antigen uptake Preference for ”opsonized” bacteria MHC I and II Tc TH T cells Recognizes MHC I on all cells Recognizes MHC II on APC Kills: Infected cells Tumour cells Helps: B-cells T cells Macrophages T cell receptor Antigen presentation 3. Signal Cytokines ↔ Cytokine receptors Activation + Proliferation + Help or Killing B cells – plasma cells T cell help for B cell activation B cells – memory cells Meeting places (B – T – APC) What about ’endogenous’ challenges? Cancer cells – tumor antigens Immune reactions within self-tissues: autoimmunity Discontinuation of immune responses …and reactions to harmless environmental factors: allergy (to food, pollen, fur etc.) Immunity vs. Tolerance