* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Major histocompatibility complex wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
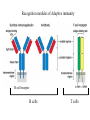
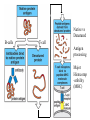
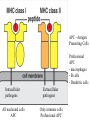
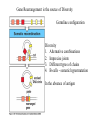
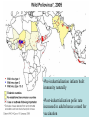
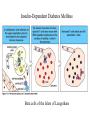
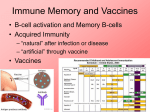
Adaptive Immunity 1. Vertebrates only 2. Specificity - recognition modules - BCR, Ab and TCR - gene rearrangement is the source of diversity - clonal selection 3. Small lymphocytes - types and sub-types - functions Recognition concept Receptor or Antibody molecule Antigen - structure recognized by an Ab, BCR or TCR Epitope - particular sub-structure of the Ag that is bound Affinity - how much a molecule likes to bind to a structure Small lymphocyte sub-types B-cells BCR is Immunoglobulin (Ig) Plasma cells - effector cells that secrete Ab T-cells Tc = cytotoxic (CD8+) TH = helper T-cells (CD4+) Th1 (inflammation) Th2 (help B-cells make AB) Recognition modules of Adaptive immunity B-cell receptor B cells T cells Native vs Denatured B-cells T-cell Antigen processing Major Histocomp -atibility (MHC) How does MHC work? APC - Antigen Presenting Cells Professional APC - macrophages - B cells - Dendritic cells Intracellular pathogens Extracellular pathogens All nucleated cells APC Only immune cells Professional APC Figure 1-26 MHC class I communicates with Tc cells MHC class II communicates with TH cells Figure 1-27 Dendritic cells interact with naïve T-cells and initiate differentiation How do Antibodies work? Parasitic infection Parasite + Mast cell Inflammation Mast cell activated Expel and/or destroy pathogen • • • Neutralization Opsonization Inflammation Principles of Adaptive Immunity Diversity Specificity Memory Self-tolerance Gene Rearrangement is the source of Diversity Germline configuration Diversity 1. Alternative combinations 2. Imprecise joints 3. Different types of chains 4. B-cells - somatic hypermutation In the absence of antigen Clonal Selection 1. Each cell = one receptor 2. Millions of lymphocytes are generated 3. Small subset will recognize a pathogen 4. Proliferation and differentiation 5. Acquired immunity - the adaptive immunity provided by immunological memory Antibodies are usually very specific Figure 1-22 Concept Behind Vaccination Figure 1-30 Some memory lymphocytes Few specific Many lymphocytes lymphocytes •Pre-industrialization infants built immunity naturally •Post-industrialization polio rate increased in adults hence a need for vaccination Polio Vaccine - Inactive vs Oral “live” version VDPV - vaccine derived polio virus - mutations can lead to polio at extremely low rate Principle of Self-tolerance B-cells with BCR that bind to self will undergo Apoptosis More complicated scheme of selection for T cells Selection of T cells 1. Thymocytes 2. Positive selection -Self MHC 3. Negative selection Mechanism of Self-tolerance Immunodeficiencies Inherited deficiencies e.g. Bubble boy disease Stress induced nutrition, emotional Pathogen caused deficiencies HIV - attacks CD4 T lymphocyte Cells and molecules involved in Hypersensitivity Diseases Figure 1-32 • IgE • IgG • CD4 TH1 • CD8 CTL Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus Figure 1-33 Beta cells of the Islets of Langerhans Inflammatory Adaptive Immune Response Figure 1-34 Hygiene Hypothesis