* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Title goes here
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
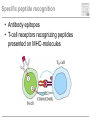
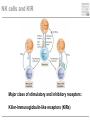
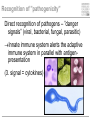
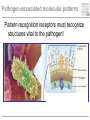
Pattern recognition in the immune system Specific peptide recognition • Antibody epitopes • T-cell receptors recognizing peptides presented on MHC-molecules Other types of recognition • MHC subclasses and levels – NK cells • Lipid antigens – NK T cells • Sugars, glycoproteins and nucleic acids – complement, B cells, T cells, dendritic cells, macrophages etc. • Unknown receptor/ligand interactions and signalling pathways NK cells and KIR Major class of stimulatory and inhibitory receptors: Killer-Immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) Different KIRs recognize different MHC I KIR-MHC combinations and disease Recognition of glycolipids MHC-like molecules (CD1d) on antigen presenting cells present glycolipids to NK T cells with an invariant T cell receptor Which ligands are recognized (self/foreign?) Recognition of ”pathogenicity” Direct recognition of pathogens – ”danger signals” (viral, bacterial, fungal, parasitic) Innate immune system alerts the adaptive immune system in parallel with antigenpresentation (3. signal = cytokines) Pathogen-associated molecular patterns Pattern recognition receptors must recognize structures vital to the pathogen! Complexity in receptor cooperation poorly understood i.e. TLRs, C-type lectins, complement Need for immunological bioinformatics!